
Fonio is the term for two cultivated grasses in the genus Digitaria that are notable crops in parts of West Africa. They are millets with small grains.

Cynodon is a genus of plants in the grass family. It is native to warm temperate to tropical regions of the Old World, as well as being cultivated and naturalized in the New World and on many oceanic islands.

Digitaria is a genus of plants in the grass family native to tropical and warm temperate regions but can occur in tropical, subtropical, and cooler temperate regions as well. Common names include crabgrass, finger-grass, and fonio. They are slender monocotyledonous annual and perennial lawn, pasture, and forage plants; some are often considered lawn pests. Digitus is the Latin word for "finger", and they are distinguished by the long, finger-like inflorescences they produce.

Digitaria exilis, referred to as findi or fundi in areas of Africa, such as The Gambia, with English common names white fonio, fonio millet, and hungry rice or acha rice, is a grass species. It is the most important of a diverse group of wild and domesticated Digitaria species known as fonio that are harvested in the savannas of West Africa. The grains are very small. It has potential to improve nutrition, boost food security, foster rural development and support sustainable use of the land. Despite its valuable characteristics and widespread cultivation, fonio has generally received limited attention research and development, which is also why the species is sometimes referred to as an underutilized crop.

Axonopus is a genus of plants in the grass family, known generally as carpet grass. They are native primarily to the tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas with one species in tropical Africa and another on Easter Island. They are sometimes rhizomatous and many are tolerant of periodic submersion.

Digitaria sanguinalis is a species of grass known by several common names, including hairy crabgrass, hairy finger-grass, large crabgrass, crab finger grass, purple crabgrass. It is one of the better-known species of the genus Digitaria, and one that is known nearly worldwide as a common weed. It is used as animal fodder, and the seeds are edible and have been used as a grain in Germany and especially Poland, where it is sometimes cultivated. This has earned it the name Polish millet.

Leersia is a genus of plants in the grass family which includes species known generally as cutgrasses.

Eriachne is a genus of plants in the grass family. Most of the species are found only in Australia, with the ranges of a few extending northward into New Guinea, parts of Asia, and Micronesia.

Omiodes demaratalis, the Hawaiian grass leafroller, is a species of moth in the family Crambidae. It is endemic to the Hawaiian islands of Niihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Maui and Hawaii.

Tricholaena is a genus of Asian, African, and Italian plants in the grass family.
Platycarpha is a genus of South African plants dandelion subfamily within the daisy family.

Hypocysta adiante, the orange ringlet, is a species of butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Australia, including Queensland, New South Wales, the Northern Territory and the north of Western Australia.
Elachista amamii is a moth of the family Elachistidae. It is found in the Ryukyu Islands of Japan and in Taiwan.
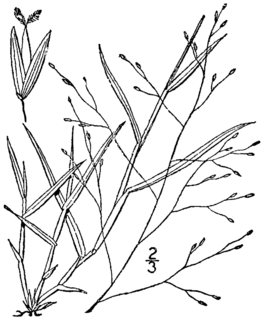
Digitaria cognata is a species of grass known by the common names fall witchgrass, Carolina crabgrass, and mountain hairgrass.

Digitaria didactyla is a species of grass known by the common names blue couch, Queensland blue couch, blue serangoon grass, green serangoon grass, blue stargrass, and petit gazon. It is native to Mauritius, Réunion, parts of mainland Africa, and Madagascar. It has been introduced widely outside its native range, mainly for use as a pasture and turf grass. It has naturalized in some regions.

Digitaria eriantha, commonly known as digitgrass or Pangola-grass, is a grass grown in tropical and subtropical climates. It grows relatively well in various soils, but grows especially well in moist soils. It is tolerant to droughts, water lodging, suppresses weeds and grows relatively quickly post grazing. This grass demonstrates great potential for farmers in Africa in subtropical and tropical climates, mostly for livestock feed.

Digitaria insularis is a species of grass commonly known as sourgrass. It is native to Central and South America and the southern parts of the United States and has been introduced into other parts of the world. It was first described by the German botanist Friedrich Karl Georg Fedde in 1904.

Digitaria ciliaris is a species of grass known by the common names southern crabgrass, tropical finger-grass, tropical crabgrass or summer grass.

Anthaenantia is a New World genus of plants in the grass family, native to North and South America including the West Indies. The genus name is sometimes spelled Anthenanthia or Anthenantia.
Digitaria stenotaphrodes is a species of flowering plant in the family Poaceae, native to Pacific islands. The species was first described in 1853, as Panicum stenotaphrodes, by Christian Nees von Esenbeck. It was transferred to Digitaria in 1906 by Otto Stapf.















