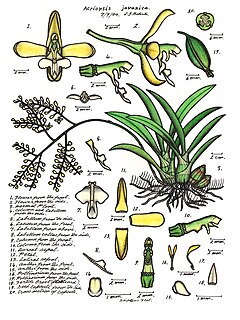
Acriopsis, commonly known as chandelier orchids or 合萼兰属 is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orchidaceaes. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic herbs with spherical or cylindrical pseudobulbs, creeping, branched rhizomes, thin white roots, two or three leaves and many small flowers. The flowers are non-resupinate with the lateral sepals joined along their edges and have spreading petals and a three-lobed labellum. The column has projections that extend hood-like beyond the anther.

Dipodium, commonly known as hyacinth orchids, is a genus of about forty species of orchids native to tropical, subtropical and temperate regions of south-east Asia, New Guinea, the Pacific Islands and Australia. It includes both terrestrial and climbing species, some with leaves and some leafless, but all with large, often colourful flowers on tall flowering stems. It is the only genus of its alliance, Dipodium.

Trichoglottis, commonly known as cherub orchids or 毛舌兰属 , is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic plants with thick roots, relatively thick, fibrous stems and many large, thick, leathery leaves arranged in two ranks. The flowers are usually small and yellowish with light brown or purple markings. The flowers have broad sepals, narrower petals and a labellum which has three lobes and is often hairy. There are about 85 species distributed from tropical and subtropical Asia to the north-western Pacific. Most species grow in rainforest.

Dipodium punctatum, commonly known as the blotched hyacinth-orchid, is a leafless orchid that is a native to eastern and south-eastern continental Australia. In summer it produces a tall flowering stem with up to sixty pale to bright pink flowers with heavy red blotches. A widespread and common species it is often confused with D. roseum and some authorities regard it as a synonym of D. squamatum.

Vrydagzynea, commonly called tonsil orchids, is a genus of orchids in the tribe Cranichideae. About forty five species of Vrydagzynea have been formally described. They are native to India, Taiwan, Southeast Asia, Malesia, Melanesia and Polynesia. A single species in Australia is possibly extinct. They have thinly textured, stalked leaves and small, dull-coloured resupinate flowers with the dorsal sepal and petals overlapping to form a hood over the column.

Schoenorchis, commonly known as flea orchids, or 匙唇兰属 , is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are small epiphytes with thin roots, thin leafy stems with leaves in two ranks and tiny fragrant, almost tube-shaped flowers with a prominently spurred labellum. There are about twenty five species found from tropical and subtropical Asia to the Western Pacific.

Dipodium hamiltonianum, commonly known as yellow hyacinth-orchid, is a leafless mycoheterotroph orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to twenty five greenish flowers with dark red spots on a tall flowering stem.

Dipodium variegatum, commonly known as the slender hyacinth-orchid, or blotched hyacinth-orchid, is a leafless mycoheterotrophic orchid that is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It forms mycorrhizal relationships with fungi of the genus Russula.
Dipodium fevrellii is an orchid species that is endemic to Sulawesi in Indonesia. The species was formally described in 1933 by Dutch botanist Johannes Jacobus Smith.
Dipodium bicallosum is an orchid species that is native to Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra in Indonesia. The species was formally described in 1927 by Dutch botanist Johannes Jacobus Smith.
Dipodium parviflorum is an orchid species that is native to Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra in Indonesia. The species was formally described in 1911 by Dutch botanist Johannes Jacobus Smith.
Dipodium purpureum is an orchid species that is native to Borneo. The species was formally described in 1910 by Dutch botanist Johannes Jacobus Smith.
Dipodium conduplicatum is an orchid species that is native to Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra. The species was formally described in 1927 by Dutch botanist Johannes Jacobus Smith.

Dipodium pictum, commonly known as brittle climbing-orchid or climbing hyacinth-orchid, is an orchid species that is native to Malesia and the Cape York Peninsula in Australia.
Dipodium elegans is an orchid species that is native to Sumatra in Indonesia. The species was formally described in 1900 by Dutch botanist Johannes Jacobus Smith.
Dipodium freycinetioides is an orchid species that is native to Palau. The species was formally described in 1937 by Japanese botanist Noriaki Fukuyama. Fukuyama described the species as climbing up trees in Aimeliik on the island of Babeldaob and distinguishes it from D. pictum by the shape of the labellum and flower color. Specimens cited by Fukuyama in his description of D. freycinetioides were collected while producing flowers and fruits in August and September 1932 and 1933. Dipodium freycinetioides is named for its resemblance to the vegetation in the genus Freycinetia.
Dipodium gracile is an orchid species that is native to Sulawesi in Indonesia. The species was formally described in 1911 by German botanist Rudolf Schlechter.

Dipodium paludosum is a terrestrial orchid species that is native to south-east Asia. It occurs in Cambodia, Thailand, Vietnam, the Philippines, Sumatra, Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo. The leaves up to 30 cm long and 2.5 cm wide. The axillary racemes comprise 6 to 12 fleshy flowers which are each up to 4 cm wide and are cream with purple-magenta spots.
Dipodium pulchellum is an almost leafless orchid that is endemic to north-east New South Wales and south-east Queensland in Australia. Up to forty pink flowers with darker blotches are borne in summer and winter on flowering spikes up to 90 cm (40 in) long.
Dipodium squamatum is a mycoheterotrophicorchid species of the tribe Cymbidieae.










