
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: a progestin and estrogen. When taken correctly, it alters the menstrual cycle to eliminate ovulation and prevent pregnancy.

The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus.

Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid.

Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin.
Hormone therapy or hormonal therapy is the use of hormones in medical treatment. Treatment with hormone antagonists may also be referred to as hormonal therapy or antihormone therapy. The most general classes of hormone therapy are oncologic hormone therapy, hormone replacement therapy, androgen replacement therapy (ART), oral contraceptive pills, and transgender hormone therapy.

Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with a history of recurrent miscarriage, hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency, treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer, and other uses. By 2007, it was only used in the treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer. In 2011, Hoover and colleagues reported on adverse health outcomes linked to DES including infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, preeclampsia, preterm birth, stillbirth, infant death, menopause prior to age 45, breast cancer, cervical cancer, and vaginal cancer. While most commonly taken by mouth, DES was available for use by other routes as well, for instance, vaginal, topical, and by injection.

A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word mamma, "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates, the udder in ruminants, and the dugs of other animals. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances.
Hot flashes are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to 30 minutes for each occurrence.
In the biological context of organisms' production of gene products, downregulation is the process by which a cell decreases the quantity of a cellular component, such as RNA or protein, in response to an external stimulus. The complementary process that involves increases of such components is called upregulation.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors, which are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular receptors, and membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), which are mostly G protein-coupled receptors. This article refers to the former (ER).

Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) or sex steroid-binding globulin (SSBG) is a glycoprotein that binds to androgens and estrogens. When produced by the Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis, it is called androgen-binding protein (ABP).

A gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist is a type of medication which affects gonadotropins and sex hormones. They are used for a variety of indications including in fertility medicine and to lower sex hormone levels in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers such as prostate cancer and breast cancer, certain gynecological disorders like heavy periods and endometriosis, high testosterone levels in women, early puberty in children, as a part of transgender hormone therapy, and to delay puberty in transgender youth among other uses. GnRH agonists are given by injections into fat, as implants placed into fat, and as nasal sprays.
Feminizing hormone therapy, also known as transfeminine hormone therapy, is hormone therapy and sex reassignment therapy to change the secondary sex characteristics of transgender people from masculine or androgynous to feminine. It is a common type of transgender hormone therapy and is used to treat transgender women and non-binary transfeminine individuals. Some, in particular intersex people but also some non-transgender people, take this form of therapy according to their personal needs and preferences.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vaginal atrophy, accelerated skin aging, vaginal dryness, decreased muscle mass, sexual dysfunction, and bone loss or osteoporosis. They are in large part related to the diminished levels of sex hormones that occur during menopause.

The Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI) is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering research in oncology that was established in August 1940. It is published monthly by Oxford University Press and is edited by Patricia A. Ganz. It was merged with Cancer Treatment Reports in January 1988. JNCI used to be the official journal of the National Cancer Institute (NCI); however, in 1996, the NCI and JNCI agreed to grow apart. Over the next five years, JNCI became independent of the NCI.

Gynecomastia is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Gynecomastia can cause significant psychological distress or unease.

Endocrine-Related Cancer is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering cancers in endocrine organs — such as the breast, prostate, pituitary, testes, ovaries, and neuroendocrine system — and hormone-dependent cancers occurring elsewhere in the body. Its scope covers basic, translational, clinical and experimental studies.
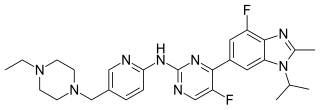
Abemaciclib, sold under the brand name Verzenio among others, is a medication for the treatment of advanced or metastatic breast cancers. It was developed by Eli Lilly and it acts as a CDK inhibitor selective for CDK4 and CDK6.

GTx-758 is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen which was under development by GTx, Inc. for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. As of 2016, it had completed two phase II clinical trials.
A hormone-sensitive cancer, or hormone-dependent cancer, is a type of cancer that is dependent on a hormone for growth and/or survival. Examples include breast cancer, which is dependent on estrogens like estradiol, and prostate cancer, which is dependent on androgens like testosterone.













