 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
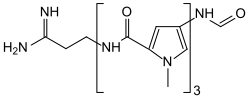
| IUPAC name N-{5-[(5-{[(3Z)-3-Amino-3-iminopropyl]carbamoyl}-1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)carbamoyl]-1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl}-4-formamido-1-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide | |
| Other names Distamycin A, Herperetin, Stallimycin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.823 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H27N9O4 | |
| Molar mass | 481.508 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Distamycin is a polyamide-antibiotic, which acts as a minor groove binder, binding to the small furrow of the double helix. [1]