DNA topoisomerases are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues in DNA arise due to the intertwined nature of its double-helical structure, which, for example, can lead to overwinding of the DNA duplex during DNA replication and transcription. If left unchanged, this torsion would eventually stop the DNA or RNA polymerases involved in these processes from continuing along the DNA helix. A second topological challenge results from the linking or tangling of DNA during replication. Left unresolved, links between replicated DNA will impede cell division. The DNA topoisomerases prevent and correct these types of topological problems. They do this by binding to DNA and cutting the sugar-phosphate backbone of either one or both of the DNA strands. This transient break allows the DNA to be untangled or unwound, and, at the end of these processes, the DNA backbone is resealed. Since the overall chemical composition and connectivity of the DNA do not change, the DNA substrate and product are chemical isomers, differing only in their topology.

Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids is an analytical technique to separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules are placed on a gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids to migrate toward the positively charged anode. The molecules separate as they travel through the gel based on the each molecule's size and shape. Longer molecules move more slowly because the gel resists their movement more forcefully than it resists shorter molecules. After some time, the electricity is turned off and the positions of the different molecules are analyzed.
In a chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a common three-dimensional structure that appears in a variety of different, evolutionarily unrelated molecules. A structural motif does not have to be associated with a sequence motif; it can be represented by different and completely unrelated sequences in different proteins or RNA.

The nucleoid is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a typical prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell dimensions, so it needs to be compacted in order to fit. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Instead, the nucleoid forms by condensation and functional arrangement with the help of chromosomal architectural proteins and RNA molecules as well as DNA supercoiling. The length of a genome widely varies and a cell may contain multiple copies of it.

DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that identify a base pair.
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-polymerase or by helicase in front of the progressing replication fork. It is the only known enzyme to actively contribute negative supercoiling to DNA, while it also is capable of relaxing positive supercoils. It does so by looping the template to form a crossing, then cutting one of the double helices and passing the other through it before releasing the break, changing the linking number by two in each enzymatic step. This process occurs in bacteria, whose single circular DNA is cut by DNA gyrase and the two ends are then twisted around each other to form supercoils. Gyrase is also found in eukaryotic plastids: it has been found in the apicoplast of the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum and in chloroplasts of several plants. Bacterial DNA gyrase is the target of many antibiotics, including nalidixic acid, novobiocin, albicidin, and ciprofloxacin.
DAPI, or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, is a fluorescent stain that binds strongly to adenine–thymine-rich regions in DNA. It is used extensively in fluorescence microscopy. As DAPI can pass through an intact cell membrane, it can be used to stain both live and fixed cells, though it passes through the membrane less efficiently in live cells and therefore provides a marker for membrane viability.

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The structure was discovered by Maurice Wilkins, Rosalind Franklin, her student Raymond Gosling, James Watson, and Francis Crick, while the term "double helix" entered popular culture with the 1968 publication of Watson's The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA.
Topoisomerase IV is one of two Type II topoisomerases in bacteria, the other being DNA gyrase. Like gyrase, topoisomerase IV is able to pass one double-strand of DNA through another double-strand of DNA, thereby changing the linking number of DNA by two in each enzymatic step. Both share a hetero-4-mer structure formed by a symmetric homodimer of A/B heterodimers, usually named ParC and ParE.

DNA supercoiling refers to the amount of twist in a particular DNA strand, which determines the amount of strain on it. A given strand may be "positively supercoiled" or "negatively supercoiled". The amount of a strand's supercoiling affects a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA and regulating access to the genetic code. Certain enzymes, such as topoisomerases, change the amount of DNA supercoiling to facilitate functions such as DNA replication and transcription. The amount of supercoiling in a given strand is described by a mathematical formula that compares it to a reference state known as "relaxed B-form" DNA.
In molecular biology Type I topoisomerases are enzymes that cut one of the two strands of double-stranded DNA, relax the strand, and reanneal the strand. They are further subdivided into two structurally and mechanistically distinct topoisomerases: type IA and type IB.
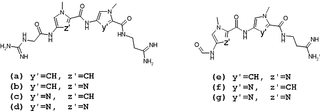
Lexitropsins are members of a family of semi-synthetic DNA-binding ligands. They are structural analogs of the natural antibiotics netropsin and distamycin. Antibiotics of this group can bind in the minor groove of DNA with different sequence-selectivity. Lexitropsins form a complexes with DNA with stoichiometry 1:1 and 2:1. Based on the 2:1 complexes were obtained ligands with high sequence-selectivity.
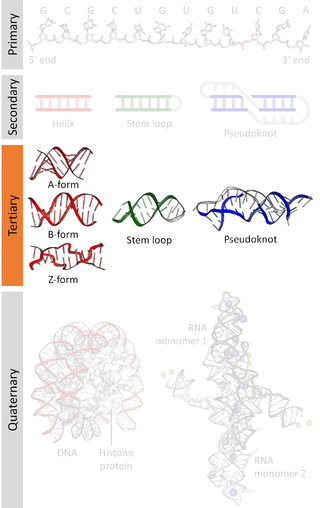
Nucleic acid tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a nucleic acid polymer. RNA and DNA molecules are capable of diverse functions ranging from molecular recognition to catalysis. Such functions require a precise three-dimensional structure. While such structures are diverse and seemingly complex, they are composed of recurring, easily recognizable tertiary structural motifs that serve as molecular building blocks. Some of the most common motifs for RNA and DNA tertiary structure are described below, but this information is based on a limited number of solved structures. Many more tertiary structural motifs will be revealed as new RNA and DNA molecules are structurally characterized.

Nucleic acid structure refers to the structure of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. Chemically speaking, DNA and RNA are very similar. Nucleic acid structure is often divided into four different levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
In molecular biology, bacterial DNA binding proteins are a family of small, usually basic proteins of about 90 residues that bind DNA and are known as histone-like proteins. Since bacterial binding proteins have a diversity of functions, it has been difficult to develop a common function for all of them. They are commonly referred to as histone-like and have many similar traits with the eukaryotic histone proteins. Eukaryotic histones package DNA to help it to fit in the nucleus, and they are known to be the most conserved proteins in nature. Examples include the HU protein in Escherichia coli, a dimer of closely related alpha and beta chains and in other bacteria can be a dimer of identical chains. HU-type proteins have been found in a variety of bacteria and archaea, and are also encoded in the chloroplast genome of some algae. The integration host factor (IHF), a dimer of closely related chains which is suggested to function in genetic recombination as well as in translational and transcriptional control is found in Enterobacteria and viral proteins including the African swine fever virus protein A104R.

In molecular biology, the LuxR-type DNA-binding HTH domain is a DNA-binding, helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain of about 65 amino acids. It is present in transcription regulators of the LuxR/FixJ family of response regulators. The domain is named after Vibrio fischeri luxR, a transcriptional activator for quorum-sensing control of luminescence. LuxR-type HTH domain proteins occur in a variety of organisms. The DNA-binding HTH domain is usually located in the C-terminal region of the protein; the N-terminal region often containing an autoinducer-binding domain or a response regulatory domain. Most luxR-type regulators act as transcription activators, but some can be repressors or have a dual role for different sites. LuxR-type HTH regulators control a wide variety of activities in various biological processes.
Streptomyces lavendulae is a species of bacteria from the genus Streptomyces. It is isolated from soils globally and is known for its production of medically useful biologically active metabolites. To see a photo of this organism click here.

Distamycin is a polyamide-antibiotic, which acts as a minor groove binder, binding to the small furrow of the double helix.
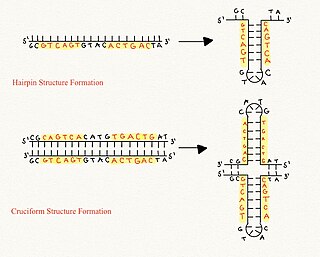
Cruciform DNA is a form of non-B DNA, or an alternative DNA structure. The formation of cruciform DNA requires the presence of palindromes called inverted repeat sequences. These inverted repeats contain a sequence of DNA in one strand that is repeated in the opposite direction on the other strand. As a result, inverted repeats are self-complementary and can give rise to structures such as hairpins and cruciforms. Cruciform DNA structures require at least a six nucleotide sequence of inverted repeats to form a structure consisting of a stem, branch point and loop in the shape of a cruciform, stabilized by negative DNA supercoiling.
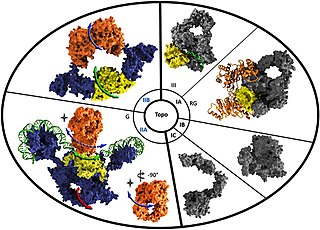
Reverse gyrase is a type I topoisomerase that introduces positive supercoils into DNA, contrary to the typical negative supercoils introduced by the type II topoisomerase DNA gyrase. These positive supercoils can be introduced to DNA that is either negatively supercoiled or fully relaxed. Where DNA gyrase forms a tetramer and is capable of cleaving a double-stranded region of DNA, reverse gyrase can only cleave single stranded DNA. More specifically, reverse gyrase is a member of the type IA topoisomerase class; along with the ability to relax negatively or positively supercoiled DNA, type IA enzymes also tend to have RNA-topoisomerase activities. These RNA topoisomerases help keep longer RNA strands from becoming tangled in what are referred to as "pseudoknots." Due to their ability to interact with RNA, it is thought that this is one of the most ancient class of enzymes found to date.
















