Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the national capital.

Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with Maryland to its north and east. It was named after George Washington, the first president of the United States. The district is named for Columbia, the female personification of the nation.

Georgetown is a historic neighborhood and commercial district in Northwest Washington, D.C., situated along the Potomac River. Founded in 1751 as part of the colonial-era Province of Maryland, Georgetown predated the establishment of Washington, D.C. by 40 years. Georgetown was an independent municipality until 1871 when the United States Congress created a new consolidated government for the entire District of Columbia. A separate act, passed in 1895, repealed Georgetown's remaining local ordinances and renamed Georgetown's streets to conform with those in Washington, D.C.

William Cranch was a United States circuit judge and chief judge of the United States Circuit Court of the District of Columbia. A staunch Federalist and nephew of President John Adams, Cranch moved his legal practice from Massachusetts to the new national capital, where he became one of three city land commissioners for Washington, D.C., and during his judicial service also was the 2nd Reporter of Decisions of the Supreme Court of the United States and a Professor of law at Columbian College.

The Council of the District of Columbia is the legislative branch of the government of the District of Columbia. As permitted in the United States Constitution, the district is not part of any U.S. state and is overseen directly by the federal government.

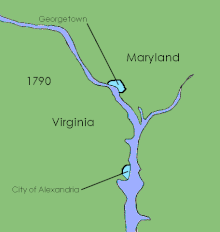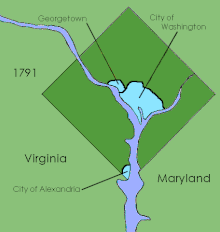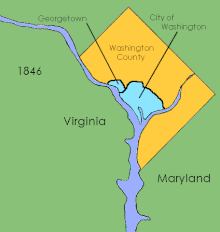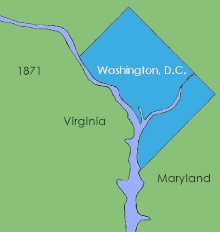
The Residence Act of 1790, officially titled An Act for establishing the temporary and permanent seat of the Government of the United States, is a United States federal statute adopted during the second session of the 1st United States Congress and signed into law by President George Washington on July 16, 1790. The Act provides for a national capital and permanent seat of government to be established at a site along the Potomac River and empowered President Washington to appoint commissioners to oversee the project. It also set a deadline of December 1800 for the capital to be ready, and designated Philadelphia as the nation's temporary capital while the new seat of government was being built. At the time, the federal government operated out of New York City.

District of Columbia home rule is the District of Columbia residents' ability to govern their local affairs. The District is the federal capital; as such, the Constitution grants the United States Congress exclusive jurisdiction over the District in "all cases whatsoever".

The County of Washington was one of five original political entities within the District of Columbia, the capital of the United States. Formed by the Organic Act of 1801 from parts of Montgomery and Prince George's County, Maryland, Washington County referred to all of the District of Columbia "on the east side of the Potomac, together with the islands therein." The bed of the Potomac River was also considered to be part of Washington County.

The history of Washington, D.C., is tied to its role as the capital of the United States. The site of the District of Columbia along the Potomac River was first selected by President George Washington. The city came under attack during the War of 1812 in an episode known as the Burning of Washington. Upon the government's return to the capital, it had to manage the reconstruction of numerous public buildings, including the White House and the United States Capitol. The McMillan Plan of 1901 helped restore and beautify the downtown core area, including establishing the National Mall, along with numerous monuments and museums.
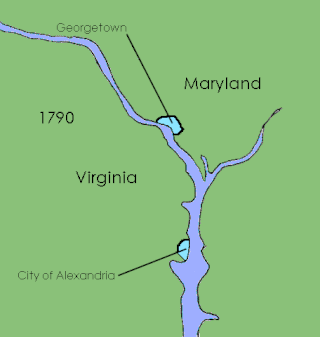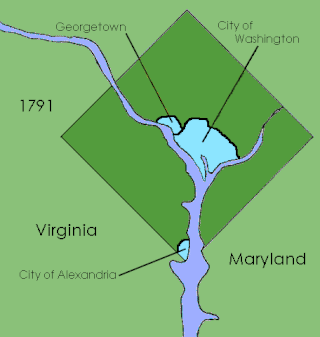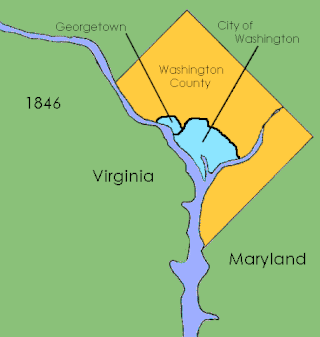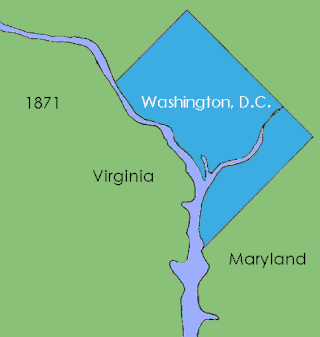
District of Columbia retrocession is the act of returning some or all of the land that had been ceded to the federal government of the United States for the purpose of creating its federal district for the new national capital, which was moved from Philadelphia to what was then called the City of Washington in 1800. The land was originally ceded to the federal government by Virginia and Maryland in 1790. After moving through various stages of federal and state approval, the Virginia portion was returned in March 1847.

Washington, D.C. is located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States at 38°53′42″N77°02′11″W, the coordinates of the Zero Milestone, on The Ellipse. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a geographical area of 68.3 square miles (176.9 km2), 61.4 square miles (159.0 km2) of which is land, and the remaining 6.9 square miles (17.9 km2) (10.16%) of which is water. The Anacostia River and the smaller Rock Creek flow into the Potomac River in Washington.

Streetcars in Washington, D.C. transported people across the city and region from 1862 until 1962.
The streets and highways of Washington, D.C., form the core of the surface transportation infrastructure in Washington, D.C., the federal capital of the United States. Given that it is a planned city, the city's streets follow a distinctive layout and addressing scheme. There are 1,500 miles (2,400 km) of public roads in the city, of which 1,392 miles (2,240 km) are owned and maintained by city government.

The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1871 is an Act of Congress that repealed the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown and established a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbia. Though Congress repealed the territorial government in 1874, the legislation was the first to create a single municipal government for the federal district. Direct rule by Congress continued until the 1973 passage of the District of Columbia Home Rule Act, a century later.
The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801, officially An Act Concerning the District of Columbia, is an organic act enacted by the United States Congress in accordance with Article 1, Section 8 of the United States Constitution. It formally placed the District of Columbia under the control of the United States Congress and organized the territory within the district into two counties: Washington County to the north and east of the Potomac River and Alexandria County to the west and south. The charters of the existing cities of Georgetown and Alexandria were left in place and no change was made to their status. The common law of both Maryland and Virginia remained in force within the district. A court was established in each of the new counties.

John Mason was an early American merchant, banker, officer, and planter. As a son of George Mason, a Founding Father of the United States, Mason was a scion of the prominent Mason political family.
The following is a timeline of the history of Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States.

A referendum on statehood for the District of Columbia was held on November 8, 2016. It was the first referendum on statehood to be held in the district. The District of Columbia was created following the passage of the Residence Act on July 9, 1790, which approved the creation of a national capital, the City of Washington on the Potomac River.

The Washington, D.C., Admission Act, often referred to simply as the D.C. Admission Act, is a bill introduced during the 116th United States Congress. The bill would grant Washington, D.C., admission into the Union as a state. The bill was originally introduced in the 116th Congress on January 3, 2019, and was reintroduced on January 4, 2021, and January 9, 2023, in the 117th and 118th Congresses. The United States House of Representatives passed it on April 22, 2021.