
Chlamydomonadales, also known as Volvocales, are an order of flagellated or pseudociliated green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. Chlamydomonadales can form planar or spherical colonies. These vary from Gonium up to Volvox. Each cell has two flagella, and is similar in appearance to Chlamydomonas, with the flagella throughout the colony moving in coordination.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of freshwater unicellular algae, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships among the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear, in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes.
Chromulinales is an order of Chrysophyceae, golden-brown algae or golden algae. It was first identified and defined by Adolf Pascher (1881–1945) in 1910.
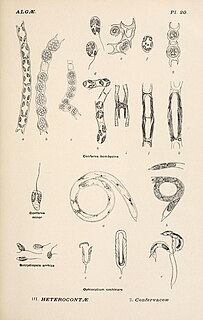
Yellow-green algae or the Xanthophyceae (xanthophytes) are an important group of heterokont algae. Most live in fresh water, but some are found in marine and soil habitats. They vary from single-celled flagellates to simple colonial and filamentous forms. Xanthophyte chloroplasts contain the photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll a, chlorophyll c, β-carotene, and the carotenoid diadinoxanthin. Unlike other heterokonts, their chloroplasts do not contain fucoxanthin, which accounts for their lighter colour. Their storage polysaccharide is chrysolaminarin. Xanthophyte cell walls are produced of cellulose and hemicellulose. They appear to be the closest relatives of the brown algae.

Eustigmatophytes are a small group of eukaryotic algae that includes marine, freshwater and soil-living species.
Pyramimonadales are an order of green algae in the Chlorophyta. The chloroplasts of phototrophic euglenids probably came from endosymbiosis with a member of this order.
Oocystaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlorellales. The type genus is Oocystis.
The Tetrasporaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales.
Chlorococcum is a genus of green algae, in the family Chlorococcaceae. The alga may be useful in the flocculation of lipids from wastewater.
Elakatothrix is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Klebsormidiophyceae.

Kirchneriella is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae.
Oltmannsiellopsis is a genus of marine colonial flagellate green algae in the Oltmannsiellopsidaceae family of Chlorophyta. It was named in reference to the similar genus Oltmannsiella. It has three species, O. viridis, which forms four-celled colonies, O. unicellularis, which is single celled, and O. geminata, which forms two-celled colonies. In Japanese it is called ウミイカダモ.
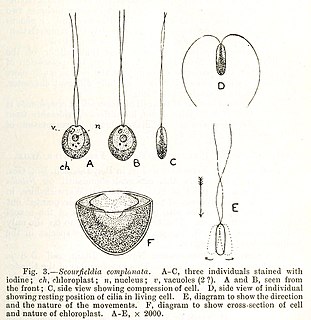
Scourfieldia is a genus of green algae in the family Scourfieldiaceae. Cardiomona Korshikov is an invalid synonym.
Actinochloridaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales.
Characiaceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales.
Radiococcaceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales.
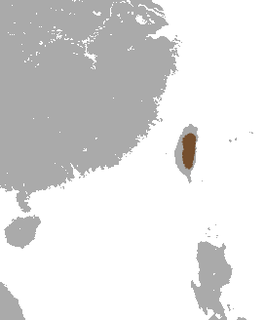
The lesser Taiwanese shrew is a rare species of shrew in the Soricomorpha order.
Cryptochrysis is a formerly recognized genus of cryptomonads first proposed by Adolf Pascher in 1911. He initially treated it as the sole genus in family Cryptochrysidaceae, but later treated it as a member of the Cryptochrysideae subfamily of Cryptomonadaceae, along with Rhodomonas, Chroomonas, and Cyanomonas. In 1967, R.W. Butcher relegated the group to a subgenus within Chroomonas.
Coenococcus is a genus of green algae belonging to the family Radiococcaceae.
Hyaloraphidium is a genus of fungi belonging to the class Chytridiomycetes, unknown order and family.








