Related Research Articles
A stenosis is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture.

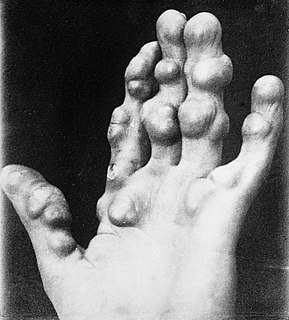
Osler's nodes are painful, red, raised lesions found on the hands and feet. They are associated with a number of conditions, including infective endocarditis, and are caused by immune complex deposition. Their presence is one definition of Osler's sign.
A chondroma is a benign cartilaginous tumor, which is encapsulated with a lobular growing pattern.

Thymidine monophosphate (TMP), also known as thymidylic acid, deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP), or deoxythymidylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in DNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside thymidine. dTMP consists of a phosphate group, the pentose sugar deoxyribose, and the nucleobase thymine. Unlike the other deoxyribonucleotides, thymidine monophosphate often does not contain the "deoxy" prefix in its name; nevertheless, its symbol often includes a "d" ("dTMP"). Dorland’s Illustrated Medical Dictionary provides an explanation of the nomenclature variation at its entry for thymidine.

In anatomy, a process is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body. For instance, in a vertebra, a process may serve for muscle attachment and leverage, or to fit, with another vertebra. The word is used even at the microanatomic level, where cells can have processes such as cilia or pedicels. Depending on the tissue, processes may also be called by other terms, such as apophysis, tubercle, or protuberance.
A lemniscus is a bundle of secondary sensory fibers in the brainstem. The medial lemniscus and lateral lemniscus terminate in specific relay nuclei of the diencephalon. The trigeminal lemniscus is sometimes considered as the cephalic part of the medial lemniscus.
Bruit, also called vascular murmur, is the abnormal sound generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery due to either an area of partial obstruction or a localized high rate of blood flow through an unobstructed artery.
Dysgammaglobulinemia is a type of immune disorder characterized by a reduction in some types of gamma globulins, resulting in heightened susceptibility to some infectious diseases where primary immunity is antibody based.
Tympanites is a medical condition in which excess gas accumulates in the gastrointestinal tract and causes abdominal distension. The term is from the Greek τύμπανο, "drum".
A medical dictionary is a lexicon for words used in medicine. The three major medical dictionaries in the United States are Stedman's, Taber's, and Dorland's. Other significant medical dictionaries are distributed by Elsevier. Dictionaries often have multiple versions, with content adapted for different user groups. For example Stedman's Concise Medical Dictionary and Dorland's are for general use and allied health care, while the full text editions are reference works used by medical students, doctors, and health professionals. Medical dictionaries are commonly available in print, online, or as downloadable software packages for personal computers and smartphones.
Hypersalivation, or ptyalism, also known as Hypersialorrhea or hypersialosis is the excessive production of saliva. It has also been defined as increased amount of saliva in the mouth, which may also be caused by decreased clearance of saliva.
Dorland's is the brand name of a family of medical reference works in various media spanning printed books, CD-ROMs, and online content. The flagship products are Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary and Dorland's Pocket Medical Dictionary. The principal dictionary was first published in 1890 as the American Illustrated Medical Dictionary, including 770 pages. The pocket edition, called the American Pocket Medical Dictionary, was first published in 1898, consisting of just over 500 pages.

The biliary tract, refers to the liver, gall bladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and conjugated bilirubin. Some components are synthesised by hepatocytes, the rest are extracted from the blood by the liver.

Foster Kennedy syndrome is a constellation of findings associated with tumors of the frontal lobe.
Glomerulopathy is a set of diseases affecting the glomeruli of the nephron.
Microcheilia is a congenital disorder where one's lips are unusually small.
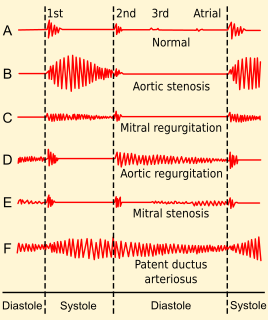
Diastolic heart murmurs are heart murmurs heard during diastole, i.e. they start at or after S2 and end before or at S1. Many involve stenosis of the atrioventricular valves or regurgitation of the semilunar valves.

Systolic heart murmurs are heart murmurs heard during systole, i.e. they begin and end between S1 and S2. Many involve stenosis of the semilunar valves or regurgitation of the atrioventricular valves.

Heart murmurs are most frequently organized by timing, into systolic heart murmurs and diastolic heart murmurs. However, continuous murmurs can not be directly placed into either category.

A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms have hemoglobin-containing cells in their blood, and with the exception of mammals, all of these red blood cells are nucleated. In mammals, NRBCs occur in normal development as precursors to mature red blood cells in erythropoiesis, the process by which the body produces red blood cells. NRBCs are normally found in the bone marrow of humans of all ages and in the blood of fetuses and newborn infants. After infancy, RBCs normally contain a nucleus only during the very early stages of the cell's life, and the nucleus is ejected as a normal part of cellular differentiation before the cell is released into the bloodstream. Thus, if NRBCs are identified on an adult's complete blood count or peripheral blood smear, it suggests that there is a very high demand for the bone marrow to produce RBCs, and immature RBCs are being released into circulation. Possible pathologic causes include anemia, myelofibrosis, thalassemia, miliary tuberculosis, cancers involving bone marrow, and in chronic hypoxemia.