
An epiphysis is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from a secondary center of ossification. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate. At the joint, the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage; below that covering is a zone similar to the epiphyseal plate, known as subchondral bone. In evolution, reptiles do not have epiphyses and diaphyses, being restricted to mammals.
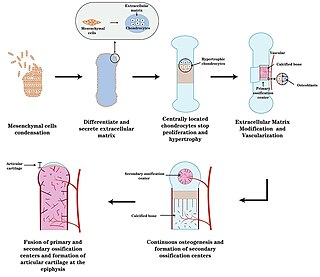
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossification. Both endochondral and intramembranous processes initiate from a precursor mesenchymal tissue, but their transformations into bone are different. In intramembranous ossification, mesenchymal tissue is directly converted into bone. On the other hand, endochondral ossification starts with mesenchymal tissue turning into an intermediate cartilage stage, which is eventually substituted by bone.

A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize. Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.
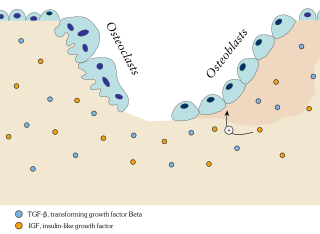
Ossification in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor.

Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw than the upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack. This type of odontogenic neoplasm was designated as an adamantinoma in 1885 by the French physician Louis-Charles Malassez. It was finally renamed to the modern name ameloblastoma in 1930 by Ivey and Churchill.

Enchondroma is a type of benign bone tumor belonging to the group of cartilage tumors. There may be no symptoms, or it may present typically in the short tubular bones of the hands with a swelling, pain or pathological fracture.

Osteochondromas are the most common benign tumors of the bones. The tumors take the form of cartilage-capped bony projections or outgrowth on the surface of bones exostoses. It is characterized as a type of overgrowth that can occur in any bone where cartilage forms bone. Tumors most commonly affect long bones about the knee and in the forearm. Additionally, flat bones such as the pelvis and scapula may be affected. Hereditary multiple exostoses usually present during childhood. Yet, the vast majority of affected individuals become clinically manifest by the time they reach adolescence. Osteochondromas occur in 3% of the general population and represent 35% of all benign tumors and 8% of all bone tumors. The majority of these tumors are solitary non-hereditary lesions and approximately 15% of osteochondromas occur as hereditary multiple exostoses preferably known as hereditary multiple osteochondromas (HMOs). Osteochondromas do not result from injury and the exact cause remains unknown. Recent research has indicated that multiple osteochondromas is an autosomal dominant inherited disease. Germ line mutations in EXT1 and EXT2 genes located on chromosomes 8 and 11 have been associated with the cause of the disease. The treatment choice for osteochondroma is surgical removal of solitary lesion or partial excision of the outgrowth, when symptoms cause motion limitations or nerve and blood vessel impingements. In hereditary multiple exostoses the indications of surgery are based upon multiple factors that are taken collectively, namely: patient's age, tumor location and number, accompanying symptomatology, esthetic concerns, family history and underlying gene mutation. A variety of surgical procedures have been employed to remedy hereditary multiple exostoses such as osteochondroma excision, bone lengthening, corrective osteotomy and hemiepiphysiodesis. Sometimes a combination of the previous procedures is used. The indicators of surgical success in regard to disease and patient characteristics are greatly disputable. Because most studies of hereditary multiple exostoses are retrospective and of limited sample size with missing data, the best evidence for each of the currently practiced surgical procedures is lacking.

Myositis ossificans comprises two syndromes characterized by heterotopic ossification (calcification) of muscle. The World Health Organization, 2020, has grouped myositis ossificans together with fibro-osseous pseudotumor of digits as a single specific entity in the category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.

Giant-cell tumor of the bone (GCTOB), is a relatively uncommon tumor of the bone. It is characterized by the presence of multinucleated giant cells. Malignancy in giant-cell tumor is uncommon and occurs in about 2% of all cases. However, if malignant degeneration does occur, it is likely to metastasize to the lungs. Giant-cell tumors are normally benign, with unpredictable behavior. It is a heterogeneous tumor composed of three different cell populations. The giant-cell tumour stromal cells (GCTSC) constitute the neoplastic cells, which are from an osteoblastic origin and are classified based on expression of osteoblast cell markers such as alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin. In contrast, the mononuclear histiocytic cells (MNHC) and multinucleated giant cell (MNGC) fractions are secondarily recruited and comprise the non-neoplastic cell population. They are derived from an osteoclast-monocyte lineage determined primarily by expression of CD68, a marker for monocytic precursor cells. In most patients, the tumors are slow to develop, but may recur locally in as many as 50% of cases.

Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) is a non-cancerous bone tumor composed of multiple varying sizes of spaces in a bone which are filled with blood. The term is a misnomer, as the lesion is neither an aneurysm nor a cyst. It generally presents with pain and swelling in the affected bone. Pressure on neighbouring tissues may cause compression effects such as neurological symptoms.

The epiphyseal plate, epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with maintenance remodeling throughout its existing bone tissue, but the growth plate is the place where the long bone grows longer.

Ollier disease is a rare sporadic nonhereditary skeletal disorder in which typically benign cartilaginous tumors (enchondromas) develop near the growth plate cartilage. This is caused by cartilage rests that grow and reside within the metaphysis or diaphysis and eventually mineralize over time to form multiple enchondromas. Key signs of the disorder include asymmetry and shortening of the limb as well as an increased thickness of the bone margin. These symptoms are typically first visible during early childhood with the mean age of diagnosis being 13 years of age. Many patients with Ollier disease are prone to develop other malignancies including bone sarcomas that necessitate treatment and the removal of malignant bone neoplasm. Cases in patients with Ollier disease has shown a link to IDH1, IDH2, and PTH1R gene mutations. Currently, there are no forms of treatment for the underlying condition of Ollier disease but complications such as fractures, deformities, malignancies that arise from it can be treated through surgical procedures. The prevalence of this condition is estimated at around 1 in 100,000. It is unclear whether the men or women are more affected by this disorder due to conflicting case studies.

Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC) is a rare developmental lesion that comes from odontogenic epithelium. It is also known as a calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor, which is a proliferation of odontogenic epithelium and scattered nest of ghost cells and calcifications that may form the lining of a cyst, or present as a solid mass.

An ameloblastic fibroma is a fibroma of the ameloblastic tissue, that is, an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. It may be either truly neoplastic or merely hamartomatous. In neoplastic cases, it may be labeled an ameloblastic fibrosarcoma in accord with the terminological distinction that reserves the word fibroma for benign tumors and assigns the word fibrosarcoma to malignant ones. It is more common in the first and second decades of life, when odontogenesis is ongoing, than in later decades. In 50% of cases an unerupted tooth is involved.
The calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (CEOT), also known as a Pindborg tumor, is an odontogenic tumor first recognized by the Danish pathologist Jens Jørgen Pindborg in 1955. It was previously described as an adenoid adamantoblastoma, unusual ameloblastoma and a cystic odontoma. Like other odontogenic neoplasms, it is thought to arise from the epithelial element of the enamel origin. It is a typically benign and slow growing, but invasive neoplasm.

Pseudoachondroplasia is an inherited disorder of bone growth. It is a genetic autosomal dominant disorder. It is generally not discovered until 2–3 years of age, since growth is normal at first. Pseudoachondroplasia is usually first detected by a drop of linear growth in contrast to peers, a waddling gait or arising lower limb deformities.
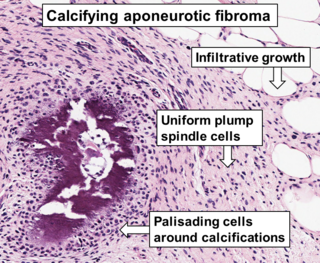
Aponeurotic fibroma, also known as calcifying aponeurotic fibroma, and juvenile aponeurotic fibroma is characterized by a lesion that usually presents as a painless, solitary, deep fibrous nodule, often adherent to tendon, fascia, or periosteum, on the hands and feet. The World Health Organization in 2020 reclassified aponeurotic fibroma nodules as a specific benign type of the fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. Aponeurotic fibromas are diagnosed based on histopathology and treated by surgical excision. They are more common in males than females.
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (EMC) is a rare low-grade malignant mesenchymal neoplasm of the soft tissues, that differs from other sarcomas by unique histology and characteristic chromosomal translocations. There is an uncertain differentiation and neuroendocrine differentiation is even possible.
Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma of bone (FCMB) is an extremely rare tumor first described in 1984. About 26 cases have been reported in literature, with patient ages spanning from 9 to 25 years, though a case in a male infant aged 1 year and 7 months has been reported. Quick growth and bulky size are remarkable features of this tumor.
A juvenile active ossifying fibroma is a benign fibro-osseous neoplasm composed of mixture of stroma and bone characterized by rapid and destructive growth.
















