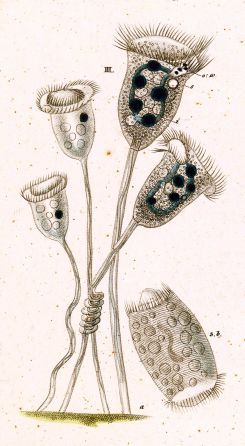
Vorticella is a genus of bell-shaped ciliates that have stalks to attach themselves to substrates. The stalks have contractile myonemes, allowing them to pull the cell body against substrates. The formation of the stalk happens after the free-swimming stage.
Giovanolaia is a subgenus of the genus Plasmodium created by Corradetti et al. in 1963. The parasites within this subgenus infect birds.
Plasmodium eylesi is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Plasmodium.
Plasmodium lemuris is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Vinckeia.
Plasmodium basilisci is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Carinamoeba.
Plasmodium juxtanucleare is a species of parasite in the family Plasmodiidae. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are birds.
Plasmodium fieldi is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium sub genus Plasmodium found in Malaysia. This species is related to Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium simiovale. As in all Plasmodium species, P. fieldi has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are primates.
Karyolysus is a genus of coccidia. With the exception of K. sonomae whose vertebrate host is the yellow-legged frog, species in this genus only infect lizards of the genus Lacerta.
Plasmodium vaughani is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium, and the type species of the subgenus Novyella. As in all Plasmodium species, P. vaughani has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are birds.
Plasmodium alaudae is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium.
Acroeimeria is a genus of parasites that contains those species which initially develop immediately beneath the brush-border of the intestinal epithelium, but the meronts and gamonts of which are early on extruded to form a layer on the surface of the gut mucosa. Morphologically they are similar to the Eimeria to which they are closely related. The genus was described in 1989 by Paperna and Landsberg.
Polychromophilus is a genus of obligate intracellular eukaryotic parasites that infect bats from every continent except Antarctica. They are transmitted by bat flies, which act as an insect vector as well as the parasite’s site of sporogeny. Polychromophilus follows a fairly typical Haemospororidian lifecycle, with gametocytes and gametes restricted to the bloodstream of the host and meronts infecting organs – most notably the lungs and the liver. The type species is Polychromophilus melanipherus, and was described by Dionisi in 1898.
Hepatocystis is a genus of parasites transmitted by midges of the genus Culicoides. Hosts include Old World primates, bats, hippopotamus and squirrels. This genus is not found in the New World. The genus was erected by Levaditi and Schoen, 1932, as Hepatocystes.
Haemosporidiasina (Haemosporidia) is a subclass of apicomplexans described by Jacques Euzéby in 1988. The taxon is very similar to Aconoidasida.
Nycteria is a genus of protozoan parasites that belong to the phylum Apicomplexa. It is composed of vector-borne haemosporidian parasites that infect a wide range of mammals such as primates, rodents and bats. Its vertebrate hosts are bats. First described by Garnham and Heisch in 1953, Nycteria is mostly found in bat species where it feeds off the blood of their hosts and causes disease. Within the host, Nycteria develops into peculiar lobulated schizonts in parenchyma cells of the liver, similarly to the stages of Plasmodium falciparum in the liver. The vector of Nycteria has been hard to acquire and identify. Because of this, the life cycle of Nycteria still remains unknown and understudied. It has been suggested that this vector could be an arthropod other than a mosquito or the vector of most haemosporidian parasites.
Sauroplasma is a genus of parasites of the phylum Apicomplexa.
The genus Schellackia comprises obligate unicellular eukaryotic parasites within the phylum Apicomplexa, and infects numerous species of lizards and amphibians worldwide. Schellackia is transmitted via insect vectors, primarily mites and mosquitoes, which take up the parasite in blood meals. These vectors then subsequently infect reptilian and amphibian which consume the infected insects. The parasites deform erythrocytes of the host into crescents, and can be visualized using a blood smear.
Haematractidium is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. It infects the Atlantic mackerel.
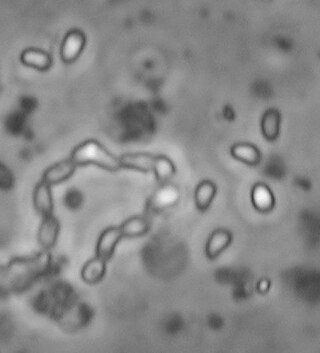
Ordospora colligata is an intracellular parasite belonging to the Microsporidia. It is an obligatory gut parasite with the crustacean Daphnia magna as its only host. So far it has been reported from Europe and Asia.
Monocercomonas is a Parabasalian genus belonging to the order Trichomonadida. It presents four flagella, three forward-facing and one trailing, without the presence of a costa or any kind of undulating membrane. Monocercomonas is found in animal guts. and is susceptible to cause Monocercomoniasis in reptiles

