
Plagiaulacida is a group of extinct multituberculate mammals. Multituberculates were among the most common mammals of the Mesozoic, "the age of the dinosaurs". Plagiaulacids are a paraphyletic grouping, containing all multituberculates that lie outside of the advanced group Cimolodonta. They ranged from the Middle Jurassic Period to the early Late Cretaceous of the northern hemisphere. During the Cenomanian, they were replaced by the more advanced cimolodontans.
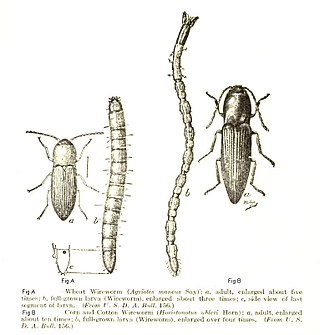
Elateridae or click beetles are a family of beetles. Other names include elaters, snapping beetles, spring beetles or skipjacks. This family was defined by William Elford Leach (1790–1836) in 1815. They are a cosmopolitan beetle family characterized by the unusual click mechanism they possess. There are a few other families of Elateroidea in which a few members have the same mechanism, but most elaterid subfamilies can click. A spine on the prosternum can be snapped into a corresponding notch on the mesosternum, producing a violent "click" that can bounce the beetle into the air. Clicking is mainly used to avoid predation, although it is also useful when the beetle is on its back and needs to right itself. There are about 9300 known species worldwide, and 965 valid species in North America.

The Microhylidae, commonly known as narrow-mouthed frogs, are a geographically widespread family of frogs. The 683 species are in 57 genera and 11 subfamilies.

Meloe is a genus of blister beetles commonly referred to as oil beetles. The name derives from their defensive strategy: when threatened by collectors or predators they release oily droplets of hemolymph from their joints. This fluid is bright orange and contains cantharidin, a poisonous chemical compound. Wiping the chemical on skin can cause blistering and painful swelling of the skin. This defensive strategy is not exclusive to this genus; all meloids possess and exude cantharidin upon threat.

Hydroscapha is a genus of beetles endemic to Europe and the United States. It contains these species:

Alviniconcha is a genus of deep water sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Provannidae. These snails are part of the fauna of the hydrothermal vents in the Indian and Western Pacific Ocean. These and another genus and species within the same family are the only known currently existing animals whose nutrition is derived from an endosymbiotic relationship with a member of bacteria from phylum Campylobacterota occurs as an endosymbiont of the gills of Alviniconcha hessleri.
Figaro is a genus of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae. Until 2008, Figaro was generally considered to be a subgenus of Galeus. The two known species are found off Australia, inhabiting deep, offshore waters on or near the bottom. Figaro contains small, slender, firm-bodied sharks that bear distinctive crests of enlarged, spiny dermal denticles along the dorsal and ventral edges of their short caudal fins. The caudal peduncle is relatively long, such as that the anal and caudal fins are some distance apart. In adult males, the inner margins of the pelvic fins are fused together to form a subtle "apron" over the claspers. F. boardmani is a predator of fishes, crustaceans, and cephalopods, and is oviparous; less is known about the F. striatus. Both are harmless and are of no economic importance.

Coraebus is a genus of beetles in the family Buprestidae, containing the following species:
Paracylindromorphus is a genus of beetles in the family Buprestidae, containing the following species:

Iridotaenia is a genus of beetles in the family Buprestidae, containing the following species:

Anoplius is a genus of spider wasps in the family Pompilidae, called the blue-black spider wasps.

Actenicerus is a genus of click beetle belonging to the family Elateridae, subfamily Dendrometrinae.

Athous is a genus of click beetles belonging to the family Elateridae.

Hemicrepidius is a genus of click beetle belonging to the family Elateridae.

Lacon is a genus of click beetle belonging to the family Elateridae and the subfamily Agrypninae.

Doliops is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Scaphidium is a genus of shining fungus beetles belonging to the family Staphylinidae, subfamily Scaphidiinae.

Glyphonyx is a genus of click beetles in the family Elateridae. There are at least 50 described species in Glyphonyx.
Homalocnemis is a genus of flies which is placed in a family of its own, the Homalocnemidae. There are about seven species in the genus found in the Afrotropical, Neotropical, and Australasian regions, suggestive of a Gondwanan origin. The genus was formerly considered a primitive empidoid and placed variously in the Hybotidae or in the empidid subfamily Brachystomatinae. They are recognized by their wing venation which includes a long anal cell and a long basal segment of the antennal style.
Oedostethus is a genus of beetles belonging to the family Elateridae.















