
The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes.
Notacanthidae, the deep-sea spiny eels, are a family of fishes found worldwide below 125 m (410 ft), and as deep as 3,500 m (11,500 ft).

Anthias are members of the family Anthiadidae in the order Perciformes. The group has also been called Anthiidae or Anthiinae, but these names are preoccupied by a subfamily of ground beetles in the family Carabidae erected by Bonelli in 1813.

Grunters or tigerperches are ray-finned fishes in the family Terapontidae. This family is part of the superfamily Percoidea of the order Perciformes.

Haemulidae is a family of fishes in the order Perciformes known commonly as grunts. It is made up of the two subfamilies Haemulinae (grunters) and Plectorhynchinae (sweetlips), which in turn contain about 133 species in 19 genera. These fish are found in tropical fresh, brackish, and salt waters around the world. They are bottom-feeding predators, and named for the ability of Haemulinae to produce sound by grinding their teeth. They also engage in mutualistic relationship with cleaner gobies of genus Elacatinus, allowing them to feed on ectoparasites on their bodies.

The sea chubs, also known as rudderfish and pilot fish and in Hawaiian as enenue or nenue, are a family, Kyphosidae, of fishes in the order Perciformes native to the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans usually close to shore in marine waters.

Pentacerotidae or armourheads are a small family of ray-finned fishes in the order Acropomatiformes. They are native to the Indian Ocean, western and central Pacific, and southwestern Atlantic. They are generally found at rocky reefs below normal scuba diving depths, although several species occur in low densities at shallower depths.
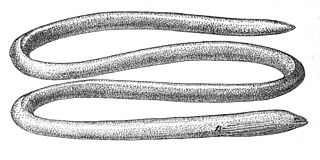
The Moringuidae are a small family of eels commonly known as spaghetti eels or worm eels, although the latter name is also shared with other families of eels.

Botiidae, the pointface loaches, is a family of cypriniform ray-finned fishes from South, Southeast, and East Asia. Until recently they were placed in the true loach family Cobitidae, until Maurice Kottelat revised the loaches and re-elevated this taxon to family rank in 2012. The family includes about 56 species.

Serpenticobitis, popularly known as serpent loaches, is a small genus of loaches found in the Mekong River Basin in Southeast Asia. It is the only genus in the family Serpenticobitidae.

The Nemacheilidae, or stone loaches, are a family of cypriniform fishes that inhabit stream environments, mostly in Eurasia, with one genus, Afronemacheilus found in Africa. The family includes about 790 species.

Parabembras is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bembridae, the deepwater flatheads, although they are sufficiently different from the other genera in that family to be classified as their own family, Parabembradidae, by some authorities. These fishes are found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Plectorhinchinae, is one of two subfamilies of the family Haemulidae, some known colloquially as sweetlips. This subfamily is regarded as having an Old World origin.

Naucratinae is a subfamily of ray-finned fish from the family Carangidae which consists of five genera and 13 species.

Luciocephalinae is a subfamily of the gourami family Osphronemidae. The members of this subfamily differ from the other groups within the gourami family by having a reduced number of rays supporting the branchiostegal membrane, five rather than six, and in the possession of a median process of the basioccipital which reaches the first vertebra and which has an attachment to the Baudelot's ligament.

Paradicichthyinae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes, one of four subfamilies classified within the family Lutjanidae, the snappers.

Scorpaeninae is a subfamily of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae in the order Scorpaeniformes, it includes the scorpionfishes, the lionfishes and turkeyfishes. They bear venomous spines in the anal, dorsal and pelvic fins which can cause severe pain in envenomated humans. The subfamily is distributed in the tropical and temperate seas around the world.

Spratelloididae is a small family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the suborder Clupeoidei of the order Clupeiformes, which also includes the anchovies and herrings. The taxa in this family were previously classified within the family Clupeidae but are now considered to be a valid family. One genus, Jenkinsia is found in the Western Atlantic, the other, Spratelloides, in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Dorosomatidae is a family of clupeiform fishes. It is now recognized by FishBase as a family in its own right; it had been considered to be a subfamily of Clupeidae. It contains 31 extant genera.
Chedrinae, the troutbarbs, is a subfamily of freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Danionidae, the danionins or danios. The fishes in thus subfamily are found in Asia and Africa.


















