
Clupeiformes is the order of ray-finned fish that includes the herring family, Clupeidae, and the anchovy family, Engraulidae. The group includes many of the most important forage and food fish.

Sprat is the common name applied to a group of forage fish belonging to the genus Sprattus in the family Clupeidae. The term also is applied to a number of other small sprat-like forage fish. Like most forage fishes, sprats are highly active, small, oily fish. They travel in large schools with other fish and swim continuously throughout the day.

Alosa is a genus of fish, the river herrings, in the family Alosidae. Along with other genera in the subfamily Alosinae, they are generally known as shads. They are distinct from other herrings by having a deeper body and spawning in rivers. Several species can be found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Also, several taxa occur in the brackish-water Caspian Sea and the Black Sea basin. Many are found in fresh water during spawning and some are only found in landlocked fresh water.

The Caspian seal is one of the smallest members of the earless seal family and unique in that it is found exclusively in the brackish Caspian Sea. It lives along the shorelines, but also on the many rocky islands and floating blocks of ice that dot the Caspian Sea. In winter and cooler parts of the spring and autumn season, it populates the northern Caspian coastline. As the ice melts in the summer and warmer parts of the spring and autumn season, it also occurs in the deltas of the Volga and Ural Rivers, as well as the southern latitudes of the Caspian where the water is cooler due to greater depth.

The European sprat, also known as brisling, brisling sardine, bristling, garvie, garvock, Russian sardine, russlet, skipper or whitebait, is a species of small marine fish in the herring family Clupeidae. Found in European, West Asian and North African waters, it has silver grey scales and white-grey flesh. Specific seas in which the species occurs include the Irish Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea and Sea of the Hebrides. The fish is the subject of fisheries, particularly in Scandinavia, and is made into fish meal, as well as being used for human consumption. When used for food it can be canned, salted, breaded, fried, boiled, grilled, baked, deep fried, marinated, broiled, and smoked.

The Black Sea sprat or Pontic sprat, Clupeonella cultriventris, is a small fish of the herring family, Clupeidae. It is found in the Black Sea and Sea of Azov and rivers of its basins: Danube, Dnister, Dnipro (Ukraine), Southern Bug, Don, Kuban. It has white-grey flesh and silver-grey scales. A typical size is 10 cm. The life span is up to 5 years. The peak of its spawning is in April and it can be found in enormous shoals in sea-shores, filled all-round coastal shallows, moving quickly back into the sea at a depth of 6–30 metres. Used for food; it has around 12% fat in flesh.

The Russian sturgeon, also known as the diamond sturgeon or Danube sturgeon, is a species of fish in the family Acipenseridae. It is found in Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Georgia, Iran, Kazakhstan, Romania, Russia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, and Ukraine. It is also found in the Caspian Sea. This fish can grow up to about 235 cm (93 in) and weigh 115 kg (254 lb). Russian sturgeon mature and reproduce slowly, making them highly vulnerable to fishing. It is distinguished from other Acipenser species by its short snout with a rounded tip as well as its lower lip which is interrupted at its center.

Clupeoides is a genus of sprats that occur in rivers in Southeast Asia. There are currently four recognized species in the genus.
The Abrau sprat is a species of freshwater fish in the family Clupeidae. It is found landlocked in Russia in a single locality, Lake Abrau, located at 70 m above sea level near the Black Sea coast close to Novorossiysk. The lake is small and has been stocked by several alien species, whence the Abrau sprat is considered critically endangered. As a result of the 2019 expedition, several individuals of the Abrau sprat were caught and their mitocondrial genome were sequenced, which showed their identity with the museum specimens. This confirmed that the C. abrau is present in the fish community and is capable of reproducing in the Lake Abrau.
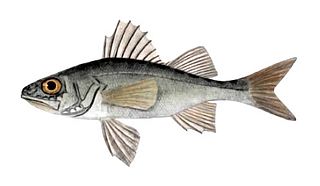
Common percarina is a species of fish in the family Percidae. It is found in northwestern Black Sea basin in estuaries and coastal lakes, and in the lower reaches of the rivers that drain into that part of the Black Sea. It is a carnivorous species.

Alosa caspia is a species of alosid fish, one of the species of shad endemic to the Caspian Sea basin.

Alosa braschnikowi, the Caspian marine shad or Brazhnikov's shad, is one of the alosid fish species endemic to the Caspian Sea.

The tadpole-gobies (Benthophilus), also called pugolovkas, are a genus of Ponto-Caspian fish in the family Gobiidae.
Sundasalanx, the Sundaland noodlefishes, is a genus of ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ehiravidae. This genus of extremely small, sprat-like fishes is restricted to freshwater environments of Southeast Asia with Indonesia being home to the majority of species. The seven currently recognized species in this genus are:
Caspian tyulka, Clupeonella caspia, is a species of fish in the family Clupeidae. It is found in the Caspian Sea, also in the lower reaches of the rivers Volga, Ural, and possibly Terek. This is a brackishwater pelagic-neritic fish, up to 12 cm maximum length.
The freshwater tyulka is a species of fish in the herring family Clupeidae. It is found in the Caspian Sea watersheds, including the lower reaches of the rivers Volga and Ural. It was introduced to the Don River basin and is also invasive upstream in the Volga drainage. It is a small freshwater pelagic fish, up to 10 cm maximal length, inhabiting large lakes and reservoirs, and breeding in open water. Earlier it was considered to be a part of the species Clupeonella cultriventris.
Anchovy sprat, Clupeonella engrauliformis, is a species of fish in the family Clupeidae. It is one of the several species of Clupeonella found in the Caspian Sea It lives pelagically in the central and southern parts of this brackishwater lake. It is typically 12 cm (4.7 in) long, and up to 16.5 cm (6.5 in) maximum. May be found down to 78 m (256 ft) depth.
Southern Caspian sprat, Clupeonella grimmi, is a species of fish in the family Clupeidae. It is found in the brackishwater Caspian Sea, in its central and southern parts in the pelagic zone. It is a small fish, typically 11 cm length, and up to 14.5 cm maximum. Occurs not deeper that 32 m depth.
Clupeonella muhlisi is a species of clupeid fish endemic to Lake Uluabat in Turkey, linked to the Sea of Marmara.

Ehiravidae is a family of clupeiform fishes. It is now recognized by FishBase as a family in its own right; it had been considered to be a subfamily of Clupeidae. It contains eleven extant genera.












