
The Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China, as well as Buryatia and Kalmykia republics of Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats and the Buryats are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols.

Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of 1,564,116 square kilometres, with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's most sparsely populated sovereign state. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border a closed sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population.

Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained de facto independence from Qing China during the Xinhai Revolution.

Mongolian is the principal language of the Mongolic language family that originated in the Mongolian Plateau. It is spoken by ethnic Mongols and other closely related Mongolic peoples who are native to modern Mongolia and surrounding parts of East and North Asia. Mongolian is the official language of Mongolia and Inner Mongolia and a recognized language of Xinjiang and Qinghai.

The Mongolic languages are a language family spoken by the Mongolic peoples in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, North Asia and East Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas and in Kalmykia and Buryatia. The best-known member of this language family, Mongolian, is the primary language of most of the residents of Mongolia and the Mongol residents of Inner Mongolia, with an estimated 5.7+ million speakers.

A kurultai was a political and military council of ancient Mongol and Turkic chiefs and khans. The root of the term is from the Proto-Mongolic verb *kura-, *kurija- 'to collect, to gather' whence khural 'meeting, assembly' in Mongolic languages. From this same root arises the Mongolian word хурим khurim 'feast', which originally referred to large festive gatherings on the steppe, but it is now used mainly in the sense of 'wedding'.

A yurt or ger (Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and insulated with skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct nomadic groups in the steppes and mountains of Inner Asia. The structure consists of a flexible angled assembly or latticework of wood or bamboo for walls, a door frame, ribs, and a wheel possibly steam-bent as a roof. The roof structure is sometimes self-supporting, but large yurts may have interior posts or columns supporting the crown. The top of the wall of self-supporting yurts is prevented from spreading by means of a tension band which opposes the force of the roof ribs. Yurts take between 30 minutes and 3 hours to set up or take down, and are generally used by between five and 15 people. Nomadic farming with yurts as housing has been the primary life style in Central Asia, particularly Mongolia, for thousands of years.

Tuvan, sometimes spelt Tyvan, is a Turkic language spoken in the Republic of Tuva in South Central Siberia, Russia. The language has borrowed a certain number of roots from Mongolian, Tibetan and Russian. There are small groups of Tuvans that speak distinct dialects of Tuvan in China and Mongolia.
Tarkhan is an ancient Central Asian title used by various Turkic, Hungarian, Mongolic, and Iranian peoples. Its use was common among the successors of the Mongol Empire and Turkic Khaganate.
The Yassa was the oral law code of the Mongols, gradually built up through the reign of Genghis Khan. It was the de facto law of the Mongol Empire, even though the "law" was kept secret and never made public. The Yassa seems to have its origin in wartime decrees, which were later codified and expanded to include cultural and lifestyle conventions. By keeping the Yassa secret, the decrees could be modified and used selectively. It is believed that the Yassa was supervised by Genghis Khan himself and his adopted son Shigi Qutuqu, then the high judge of the Mongol Empire. Genghis Khan appointed his second son, Chagatai, to oversee the laws' execution.
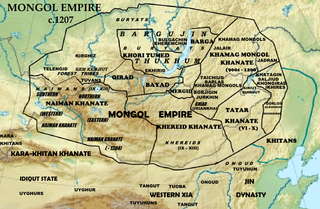
The Merkit was one of the five major tribal confederations of Mongol or Turkic origin in the 12th century Mongolian Plateau.

The tögrög or tugrik is the official currency of Mongolia. It was historically subdivided into 100 möngö. Currently, the lowest denomination in regular use is the 10-tögrög note, and the highest is the 20,000-tögrög note. In Unicode, the currency sign is U+20AE₮TUGRIK SIGN.

Buryat or Buriat, known in foreign sources as the Bargu-Buryat dialect of Mongolian, and in pre-1956 Soviet sources as Buryat-Mongolian, is a variety of the Mongolic languages spoken by the Buryats and Bargas that is classified either as a language or major dialect group of Mongolian.
Mongolian names have undergone a number of changes in the history of Mongolia, both with regard to their meaning and their source languages. In Inner Mongolia, naming customs are now similar to Mongolia but with some differences.
Noyan, or Toyon, was a Central Asian title of authority which was used to refer to civil-military leaders of noble ancestry in the Central Asian Khanates with origins in Noyon, which was used as a title of authority in the Chagatai Khanate of the Mongol Empire. In modern times, Noyan is used as a given name or surname in Asia meaning "the lord", "the prince", "the protector", "the commander-in-chief".

The traditional Mongolian script, also known as the Hudum Mongol bichig, was the first writing system created specifically for the Mongolian language, and was the most widespread until the introduction of Cyrillic in 1946. It is traditionally written in vertical lines Top-Down, right across the page. Derived from the Old Uyghur alphabet, it is a true alphabet, with separate letters for consonants and vowels. It has been adapted for such languages as Oirat and Manchu. Alphabets based on this classical vertical script continue to be used in Mongolia and Inner Mongolia to write Mongolian, Xibe and, experimentally, Evenki.
Elsornis is a genus of enantiornithine bird. Only one species is known, Elsornis keni. It lived during the Late Cretaceous. It is known from a partially articulated fossil skeleton found in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia.

A deel is an item of traditional clothing commonly worn by [Mongols and can be made from cotton, silk, wool, or brocade.

The Mongolian passport is a passport issued to Mongolian citizens for purposes of travel outside Mongolia. Mongolian citizens have visa-free or visa on arrival access to 62 countries and territories. Passports are issued by the General Authority for State Registration, an implementing agency of the Mongolian government.
Ordos Mongolian is a variety of Central Mongolic spoken in the Ordos City region in Inner Mongolia and historically by Ordos Mongols. It is alternatively classified as a language within the Mongolic language family or as a dialect of the standard Mongolian language. Due to the research of Antoine Mostaert, the development of this dialect can be traced back 100 years.













