
Eragrostis is a large and widespread genus of plants in the grass family, found in many countries on all inhabited continents and many islands.

The Saint Helena olive is an extinct species of flowering plant. It is the only member of the genus Nesiota. It was endemic to the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. Despite its name, it is unrelated to the true olive, but is instead a member of the family Rhamnaceae, the family which contains buckthorns and jujube. The last remaining tree in the wild died in 1994, and the last remaining individual in cultivation died in December 2003, despite conservation efforts. It is thus a prime example of recent plant extinction. The Saint Helena olive belongs to the tribe Phyliceae, which are mostly endemic to Southern Africa.

Lachanodes arborea, the she cabbage tree, is a small tree in the family Asteraceae. It is an endangered endemic of the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is now extinct in the wild.

Melanodendron is a genus of trees in the family Asteraceae, with only one species, Melanodendron integrifolium, native to the island of Saint Helena. It is related to the Saint Helenan gumwoods and is the most common of the remaining cabbage tree species of Saint Helena, although it is considered endangered due to the restricted population size.

Acalypha rubrinervis is an extinct plant in the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae), from the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. It was called string tree on account of the thin pendulous inflorescences which resembled red strings. Disturbance following human settlement on the island destroyed its habitat and it was last seen in the 19th century. It is thus one of a number of island plants to have been driven to extinction by human activity.

Pladaroxylon is a genus of trees in the tribe Senecioneae within the family Asteraceae.

Trochetiopsis ebenus, the dwarf ebony or Saint Helena ebony, is a species of flowering plant that is endemic to the island of Saint Helena in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is not related to the ebony of commerce, but is instead a member of the mallow family, Malvaceae. Saint Helena ebony is now critically endangered in the wild, being reduced to two wild individuals on a cliff, but old roots are sometimes found washed out of eroding slopes. These are collected on the island and used for inlay work, an important craft on Saint Helena. A related species, Trochetiopsis melanoxylon, is now completely extinct.

Commidendrum robustum, the Saint Helena gumwood, is a species of tree endemic to Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. Though it is now comparatively rare, it was once one of the most abundant trees of mid-elevations of the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. A small tree to 7–8 m, it was cut extensively for fuel in the early years of settlement of the island by the English East India Company. It has given its name to certain placenames on the island such as "Gumwoods". It is one of several species in the endemic genus Commidendrum.

Lobelia scaevolifolia is a species of the plant family Campanulaceae. It is endemic to the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. It was at one time placed as the only species, Trimeris scaevolifolia, in the genus Trimeris. Its common name is St. Helena lobelia.

Commidendrum rugosum, known as scrubwood, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae.
Sium burchellii, known commonly as dwarf jellico, is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae. It is endemic to Saint Helena. It grows on steep island cliffs. It is threatened by the fragmentation of its small populations, introduced species of plants, landslides, and possibly hybridization with Sium bracteatum.

Frankenia portulacifolia, also called Saint Helena tea or tea plant, is a species of salt-tolerant plant in the Frankeniaceae family. It is endemic to the islands of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. Its natural habitats are inhospitable, dry and rocky areas and rocky shores, often on weathered volcanic ash. As its total population has been estimated at only around 3,500 individuals, it is currently classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN.

Phylica polifolia, also called rosemary or Saint Helena rosemary, is a species of plant in the family Rhamnaceae. It is endemic to Saint Helena. Its natural habitats are rocky areas and rocky shores.
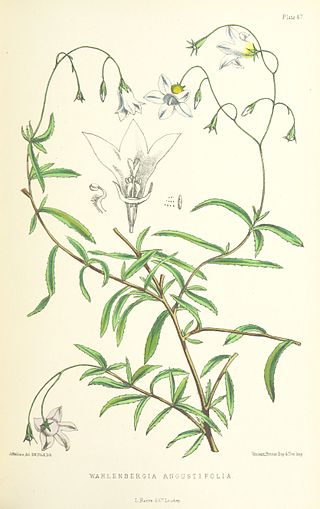
Wahlenbergia angustifolia, also called small bellflower, is a species of plant in the family Campanulaceae. It is endemic to Saint Helena. Its natural habitat is rocky areas. It is endangered because of habitat loss.
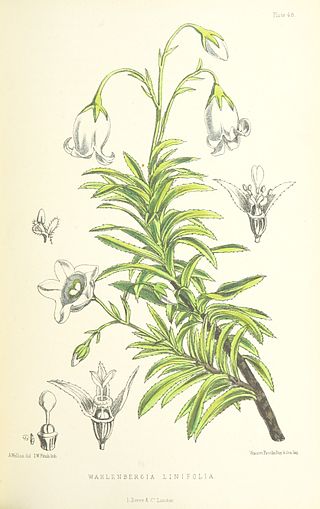
Wahlenbergia linifolia, the large bellflower, is a species of plant in the family Campanulaceae. It is endemic to Saint Helena. Its natural habitat is rocky areas. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Bulbostylis neglecta, neglected tuft sedge locally, is an endemic member of the Cyperaceae of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic.

Eragrostis variabilis is a species of grass known by the common names variable lovegrass, kawelu, emoloa, and kalamalo. It is endemic to Hawaii, where it occurs on all the main islands plus Kure Atoll, Midway Atoll, Pearl and Hermes Atoll, Lisianski Island, Laysan, and Nihoa.
Asplenium haughtonii, also known as the Barn fern, is a species of fern in the family Aspleniaceae. It is native to Saint Helena.

Bulbostylis lichtensteiniana is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae, that is endemic to Saint Helena. Unlike other species native to Saint Helena, such as Bulbostylis neglecta, Bulbostylis lichtensteiniana does not show obvious signs of decline due to the spread of invasive plants. However, the lack of decline is partially attributed to Bulbostylis lichtensteiniana being the only endemic plant to have expanded into new anthropogenic habitats.
Eragrostis ciliaris, the gophertail lovegrass, is a species of grass. It is native to the Old World Tropics; nearly all of Africa, Madagascar, other Indian Ocean islands, the Arabian Peninsula, the Indian Subcontinent, Myanmar, Vietnam, Taiwan and the Philippines and a number of Pacific islands, and has been introduced to the New World Tropics and Subtropics, from the southern United States to Argentina, the Caribbean, and other Pacific islands. Its seeds are edible and nutritious, but quite small and difficult to harvest and handle, so it is usually regarded as a famine food.

















