
The Great Artesian Basin (GAB), located in Australia, is the largest and deepest artesian basin in the world, stretching over 1,700,000 square kilometres (660,000 sq mi), with measured water temperatures ranging from 30 to 100 °C. The basin provides the only source of fresh water through much of inland Australia.

The Lake Eyre basin is a drainage basin that covers just under one-sixth of all Australia. It is the largest endorheic basin in Australia and amongst the largest in the world, covering about 1,200,000 square kilometres (463,323 sq mi), including much of inland Queensland, large portions of South Australia and the Northern Territory, and a part of western New South Wales. The basin is also one of the largest, least-developed arid zone basins with a high degree of variability anywhere. It supports only about 60,000 people and has no major irrigation, diversions or flood-plain developments. Low density grazing that sustains a large amount of wildlife is the major land use, occupying 82% of the total land within the basin. The Lake Eyre basin of precipitation to a great extent geographically overlaps the Great Artesian Basin underneath.

The Channel Country is a region of outback Australia mostly in the state of Queensland but also in parts of South Australia, Northern Territory and New South Wales. The name comes from the numerous intertwined rivulets that cross the region, which cover 150,000 km². The Channel Country is over the Cooper and Eromanga geological basins and the Lake Eyre Basin drainage basin. Further to the east is the less arid Maranoa district.
The Surat Basin is a geological basin in eastern Australia. It is part of the Great Artesian Basin drainage basin of Australia. The Surat Basin extends across an area of 270,000 square kilometres and the southern third of the basin occupies a large part of northern New South Wales, the remainder is in Queensland. It comprises Jurassic through to Cretaceous aged sediments derived from Triassic and Permian arc rocks of the Hunter-Bowen orogeny. Towns situated above the basin, once dominated by agriculture, are experiencing a boom as mines and infrastructure in the area are expanded.
The Cooper Basin is a Permian-Triassic sedimentary geological basin in Australia. The intracratonic rift basin is located mainly in the southwestern part of Queensland and extends into northeastern South Australia. It is named after the Cooper Creek which is an ephemeral river that runs into Lake Eyre. For most of its extent, it is overlain by the Eromanga Basin. It covers 130,000 km².

Queensland's energy policy is based on the year 2000 document called the Queensland Energy Policy: A Cleaner Energy Strategy. The Queensland Government assists energy development through the Department of Energy and Water Supply. The state is noted for its significant contribution to coal mining in Australia. The primary fuel for electricity generation in the state is coal with coal seam gas becoming a significant fuel source. Queensland has 98% of Australia's reserves of coal seam gas. An expansion of energy-intensive industries such as mining, economic growth and population growth have created increased demand for energy in Queensland.

The geography of Australia encompasses a wide variety of biogeographic regions being the world's smallest continent, while comprising the territory of the sixth-largest country in the world. The population of Australia is concentrated along the eastern and south-eastern coasts. The geography of the continent is extremely diverse, ranging from the snow-capped mountains of the Australian Alps and Tasmania to large deserts, tropical and temperate forests, grasslands, heathlands and woodlands.
The Toolebuc Formation is a geological formation that extends from Queensland across South Australia and the Northern Territory in Australia, whose strata date back to the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Dinosaurs, pterosaurs, plesiosaurs, ichthyosaurs, protostegid turtles, sharks, chimaeroids and bony fish remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

Energy in Australia is the production in Australia of energy and electricity, for consumption or export. Energy policy of Australia describes the politics of Australia as it relates to energy.

The geography of Queensland in the north-east of Australia, is varied. It includes tropical islands, sandy beaches, flat river plains that flood after monsoon rains, tracts of rough, elevated terrain, dry deserts, rich agricultural belts and densely populated urban areas.
Geologically the Australian state of New South Wales consists of seven main regions: Lachlan Fold Belt, the Hunter-Bowen Orogeny or New England Orogen (NEO), the Delamerian Orogeny, the Clarence Moreton Basin, the Great Artesian Basin, the Sydney Basin, and the Murray Basin.

The geology of Queensland can be subdivided into several regions with different histories. Along the east coast is a complex of Palaezoic to Cainozoic rocks while much of the rest of the state is covered by Cretaceous and Cainozoic rocks. A Precambrian basement is found in the north west and Cape York regions. The Thomson Orogen occurs in the central and southern parts of Queensland, but is mostly covered by younger basins.
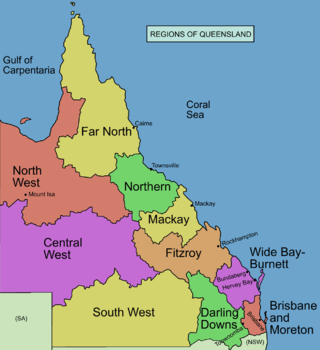
South West Queensland is a remote region in the Australian state of Queensland which covers 319,808 km2 (123,479 sq mi). The region lies to the south of Central West Queensland and west of the Darling Downs and includes the Maranoa district and parts of the Channel Country. The area is noted for its cattle grazing, cotton farming, opal mining and oil and gas deposits.

The Galilee Basin is a large inland geological basin in the western Queensland region of Australia. The Galilee Basin is part of a larger Carboniferous to Mid-Triassic basin system that contains the Cooper Basin, situated towards the south-west of the Galilee Basin, and the Bowen Basin to the east. The Galilee Basin covers a total area of approximately 247,000 square kilometres (95,000 sq mi). The basin is underlain by the Carboniferous Drummond Basin and overlain by the Cretaceous – Jurassic Eromanga Basin. The Triassic and younger sediments of the Galilee Basin form the basal sequence of the Great Artesian Basin drainage basin.
There are oil shale deposits in Australia which range from small deposits to large reserves. Deposits, varying by their age and origin, are located in about a third of eastern Australia. In 2012, the demonstrated oil shale reserves were estimated at 58 billion tonnes. The easiest to recover deposits are located in Queensland.

Mainland Australia is the main landmass of the Australian continent, excluding the Aru Islands, New Guinea, Tasmania, and other Australian offshore islands. The landmass also constitutes the mainland of the territory governed by the Commonwealth of Australia, and the term, along with continental Australia, can be used in a geographic sense to exclude surrounding continental islands and external territories. Generally, the term is applied to the states of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia, as well as the Australian Capital Territory, Jervis Bay Territory, and Northern Territory.

Elizabeth Springs is a heritage-listed artesian springs in Diamantina Lakes, Shire of Diamantina, Queensland, Australia. It is one of the springs of the Great Artesian Basin (GAB). It was added to the Australian National Heritage List on 4 August 2009.
Helmut (Heli) Wopfner was an Austrian geologist and professor at the University of Cologne.

The Eromanga Sea was an inland sea across what would be Australia that formed in the Early Cretaceous. The sea reached the Eromanga Basin from the north via the Carpentarian Basin. The southern end of the sea comprised lagoons and rivers, and to the east in Surat Basin a bay.












