Related Research Articles

The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid.

The gastrointestinal tract is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as faeces. Gastrointestinal is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines.

Acanthuridae are the family of surgeonfishes, tangs, and unicornfishes. The family includes about 86 extant species of marine fish living in tropical seas, usually around coral reefs. Many of the species are brightly colored and popular in aquaria.

A dik-dik is the name for any of four species of small antelope in the genus Madoqua that live in the bushlands of eastern and southern Africa.

Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.

The crop is a thin-walled, expanded portion of the alimentary tract, which is used for the storage of food before digestion. The gizzard is an anatomical structure in vertebrate animals, such as birds, and invertebrate animals, such as gastropods, earthworms, leeches, and insects.
Candidatus Epulopiscium is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria that have a symbiotic relationship with surgeonfish. These bacteria are known for their unusually large size, many ranging from 0.2 - 0.7 mm in length. Until the discovery of Thiomargarita namibiensis in 1999, Epulonipiscium species were thought to be the largest bacteria. They are still the largest known heterotrophic bacteria.

The term coldwater fish can have different meanings in different contexts.

The Sacramento blackfish is a species of freshwater fish in central California. A cyprinid, the blackfish is the sole member of its genus.
Abrothrix andina, also known as the Andean Altiplano mouse or Andean akodont, is a species of rodent in the genus Abrothrix of family Cricetidae. It is found in the Altiplano habitat of the Andes from central Peru through Bolivia, south to Argentina and Chile.

Arhynchobdellida, the proboscisless leeches, are a monophyletic order of leeches. They are defined by the lack of the protrusible proboscis that defines their sister taxon, the Rhynchobdellida. Arhynchobdellida is a diverse order, compromising both aquatic and terrestrial, besides sanguivorous and predatory, leeches. The order is divided into two suborders, Erpobdelliformes and Hirudiniformes.

Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodies that can lengthen and contract. Both groups are hermaphrodites and have a clitellum, but leeches typically differ from the oligochaetes in having suckers at both ends and in having ring markings that do not correspond with their internal segmentation. The body is muscular and relatively solid, and the coelom, the spacious body cavity found in other annelids, is reduced to small channels.

Naso lituratus, the clown unicornfish, orangespined unicornfish, black-finned unicornfish, Pacific orangespined unicornfish, blackfinned unicornfish or stripefaced unicornfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This fish is found in the eastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean.

Erpobdella is a genus of leeches in the family Erpobdellidae. Members of the genus have three or four pairs of eyes, but never have true jaws, and are typically 20–50 millimetres (0.8–2.0 in) long. All members do not feed on blood, but instead are predators of small aquatic invertebrates, which they often swallow whole.
Holotrichius is a genus of assassin bugs.

Eucidaris thouarsii, the slate pencil urchin, is a species of cidaroid sea urchins that inhabits littoral regions of the East Pacific Ocean.

Erpobdellidae is a family of leeches. It is one of the four families belonging to the suborder Erpobdelliformes of the proboscisless leeches order, Arhynchobdellida.
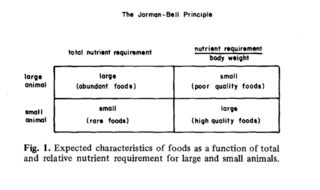
The Jarman–Bell principle is a concept in ecology that the food quality of a herbivore's intake decreases as the size of the herbivore increases, but the amount of such food increases to counteract the low quality foods. It operates by observing the allometric properties of herbivores. The principle was coined by P.J Jarman (1968.) and R.H.V Bell (1971).
Barbara Hibbs Blake was an American mammalogist and college professor.

The femoral chordotonal organ is a group of mechanosensory neurons found in an insect leg that detects the movements and the position of the femur/tibia joint. It is thought to function as a proprioceptor that is critical for precise control of leg position by sending the information regarding the femur/tibia joint to the motor circuits in the ventral nerve cord and the brain
References
- ↑ Mark E. Siddall (2002). "Phylogeny of the leech family Erpobdellidae (Hirudinida : Oligochaeta)" (PDF). Invertebrate Systematics. 16: 1–6. doi:10.1071/IT01011.
- ↑ Mas, IG; Lopez, FM; Mora, AMP; Ortega, GT (1998). "The freshwater leeches (Annelida, Hirudinea) of Valencian Community (Spain)". Boletin de la Real Sociedad Espanola de Historia Natural (Seccion Biologica). 94 (1–2): 149–161.
- ↑ Oka, Kazuyuki; Takeda, Naokuni (1986-01-01). "Relationship between neurosecretion and spermatogenesis in the leech, Erpobdella lineata". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology. 84 (3): 421–425. doi:10.1016/0300-9629(86)90340-3. ISSN 0300-9629.
- ↑ Chang, N. S. (1994). "Ultrastructure of the digestive tract of Korean Leech (Erpobdella lineata)". Applied Microscopy. 24 (3): 34–45. ISSN 2287-5123.