
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.
Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyquinol (1,2,4-benzenetriol) and pyrogallol (1,2,3-benzenetriol). Phloroglucinol, and its benzenetriol isomers, are still defined as "phenols" according to the IUPAC official nomenclature rules of chemical compounds. Many such monophenolics are often termed polyphenols.

Propyl gallate, or propyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate, is an ester formed by the condensation of gallic acid and propanol. Since 1948, this antioxidant has been added to foods containing oils and fats to prevent oxidation. As a food additive, it is used under the E number E310.
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus is a bacterial species of the genus Acinetobacter. It is a nonmotile, Gram-negative coccobacillus. It grows under aerobic conditions, is catalase positive and oxidase negative. A. calcoaceticus is a part of the A. calcoaceticus-A. baumannii complex together with Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter nosocomialis, Acinetobacter pitti and Acinetobacter seifertii.
In enzymology, a phloroglucinol reductase (EC 1.3.1.57) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyrogallol hydroxytransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme gallate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.59) catalyzes the chemical reaction

Flopropione is a spasmolytic or antispasmodic agent. It acts as a COMT inhibitor.
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.
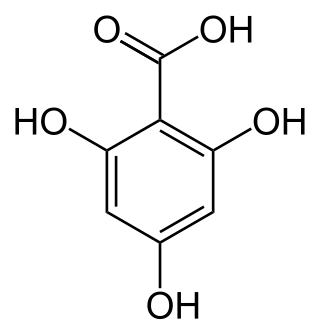
Phloroglucinol carboxylic acid is a trihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid.

The trihydroxybenzenes (or benzenetriols) are organic compounds with the formula C6H3(OH)3. Also classified as polyphenols, they feature three hydroxyl groups substituted onto a benzene ring. They are white solids with modest solubility in water.
Pelobacter acidigallici is the type species in the bacterial genus Pelobacter.

1,2,3,5-Tetrahydroxybenzene is a benzenetetrol.

Tetrahydroxybenzenes or Benzenetetrols are a group of organic compounds which are tetrahydroxy derivatives of benzene. Tetrahydroxybenzene comes in three isomers:
The 2008 WGC-Bridgestone Invitational was a golf tournament that was contested from July 31 – August 3, 2008 over the South Course at Firestone Country Club in Akron, Ohio. It was the tenth WGC-Bridgestone Invitational tournament, and the third of three World Golf Championships events held in 2008.
The 2010 WGC-Bridgestone Invitational was a golf tournament held August 5–8 over the South Course at Firestone Country Club in Akron, Ohio. It was the 12th WGC-Bridgestone Invitational tournament, and the third of four World Golf Championships events held in 2010.
Trihydroxybenzoic acid may refer to the following phenolic acids:

Humulone, a vinylogous type of organic acid, is a bitter-tasting chemical compound found in the resin of mature hops. Humulone is a prevalent member of the class of compounds known as alpha acids, which collectively give hopped beer its characteristic bitter flavor.

Dihydrophloroglucinol is a chemical compound found in the pathway of the microbial degradation of phloroglucinol and other phenolic compounds.
Peptoclostridium acidaminophilum is a Gram-positive bacterium species in the family Peptostreptococcaceae, notable for being an amino acid-degrading obligate anaerobe producing or utilizing H2 or formate. It is rod-shaped and motile by a polar to subpolar flagellum. Its type strain is al-2. It produces several relevant enzymes.









