
China is a country located in East Asia with an area of 9,596,960 km2 (3,705,410 sq mi). The exact land area can sometimes be challenged by border disputes, including those concerning Taiwan, Aksai Chin, the Trans-Karakoram Tract, the South China Sea Islands, the Senkaku Islands, and South Tibet. As sovereignty over Hong Kong and Macau were restored to China in 1997 and 1999, two special administrative regions were established under the One Country, Two Systems policy. The People's Republic of China is either the third or fourth largest country in the world, being either slightly larger or slightly smaller than the United States depending on how the area of the United States is measured.

The Himalayas, or Himalaya are a mountain range in Asia separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding 7,200 m (23,600 ft) in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia is 6,961 m (22,838 ft) tall.

Lieutenant Colonel Sir Francis Edward Younghusband, was a British Army officer, explorer, and spiritual writer. He is remembered for his travels in the Far East and Central Asia; especially the 1904 British expedition to Tibet, led by himself, and for his writings on Asia and foreign policy. Younghusband held positions including British commissioner to Tibet and President of the Royal Geographical Society.

The Karakoram is a mountain range spanning the borders of China, India, and Pakistan, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan; its highest 15 mountains are all based in Pakistan. It begins in the Wakhan Corridor (Afghanistan) in the west, encompasses the majority of Gilgit-Baltistan, and extends into Ladakh and Aksai Chin. It is the second highest mountain range in the world and part of the complex of ranges including the Pamir Mountains, the Hindu Kush and the Himalayan Mountains. The Karakoram has eighteen summits over 7,500 m (24,600 ft) height, with four of them exceeding 8,000 m (26,000 ft): K2, the second highest peak in the world at 8,611 m (28,251 ft), Gasherbrum I, Broad Peak and Gasherbrum II.

The Roof of the World or Top of the World is a metaphoric description of the high region in the world, also known as High Asia. The term usually refers to the mountainous interior of Asia, including the Pamirs, the Himalayas, the Tibet, the Tian Shan, and the Altai Mountains.

The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia, South Asia, and East Asia. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world's highest mountains.

The Tibetan Plateau, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau in Central Asia, South Asia and East Asia, covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, Northwestern Yunnan, Western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti as well as Bhutan. It stretches approximately 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) north to south and 2,500 kilometres (1,600 mi) east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of 2,500,000 square kilometres (970,000 sq mi). With an average elevation exceeding 4,500 metres (14,800 ft) and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World".

The Tibetan sandgrouse is a large bird in the sandgrouse family. The genus name Syrrhaptes is from Ancient Greek surrhaptos, "sewn together" and tibetanus is from the type locality, Tibet.

The Karakoram Pass is a 5,540 m or 18,176 ft mountain pass between India and China in the Karakoram Range. It is the highest pass on the ancient caravan route between Leh in Ladakh and Yarkand in the Tarim Basin. 'Karakoram' literally means 'Black Gravel' in Mongolic.

The Tibetan snowcock is a bird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. This species is found in high-altitude regions of the Western Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau, where it overlaps in part with the larger Himalayan snowcock. The head is greyish and there is a white crescent patch behind the eye and underside is white with black stripes. In flight the secondaries show a broad white trailing edge.

The snow pigeon is a species of bird in the genus Columba in the family Columbidae from hilly regions of central Asia. They are grey, black, pale brown and white birds and two subspecies are recognised: C. l. leuconota occurs in the western Himalayas from western Afghanistan to Sikkum and C. l. gradaria occurs in the mountains of eastern Tibet and from eastern Nan Shan (Qinghai) to Yunnan and extreme northern Myanmar. The birds forage in open country in pairs or small groups, feeding on grain, buds, shoots, berries and seeds. They roost at night on cliffs, breeding in crevices where they build untidy stick nests and lay a clutch of usually two white eggs. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated the bird's conservation status as being of least concern.
Miju, Midžuish, Southern Mishmi, or Geman languages are a small proposed family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken by the Kaman people of southeastern Tibet and Arunachal Pradesh. The languages are Kaman (Midzu/Miju) and Zakhring (Meyor). Although Zakhring appears to be Sino-Tibetan, Kaman may be more divergent. Blench and Post (2011) believe that Zakhring is an East Bodish language that has been influenced by Midzu or other divergent languages of the region, whereas Kaman may be a language isolate.
The Tamangic languages, TGTM languages, or West Bodish languages, are a family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in the Himalayas of Nepal. They are called "West Bodish" by Bradley (1997), from Bod, the native term for Tibet. TGTM stands for Tamang-Gurung-Thakali-Manang.
South Tibet is a literal translation of the Chinese term '藏南', which may refer to different geographic areas:
Arctia intercalaris is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Eduard Friedrich Eversmann in 1843. It is found in Dzhungarian Alatau, Zailiiskii Alatau, Tien Shan, Alai-Pamirs, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, the mountains of Afghanistan, north-western Pakistan and from Kashmir to Kulu.
Callindra principalis is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Vincenz Kollar in 1844. It is found in the Pamir Mountains, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Kashmir, the Himalayas, Nepal and China.
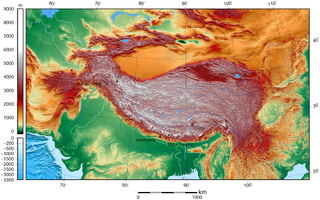
High-Mountain Asia (HMA) is a high-elevation geographic region in Asia that includes numerous cordillera and highland systems around the Tibetan Plateau, encompassing regions of East, Southeast, Central and South Asia. The region was orogenically formed by the continental collision of the Indian Plate into the Eurasian Plate.

Tashkurgan Airport is an under construction airport in Xinjiang scheduled to be operational in mid-2022. At an elevation of 3,200 m, it is Xinjiang's first high plateau airport.













