Eunomia is one of the Horae, goddesses of Greek mythology. Eunomia may also refer to:
S-type asteroids are asteroids with a spectral type that is indicative of a siliceous mineralogical composition, hence the name. They have relatively high density. Approximately 17% of asteroids are of this type, making it the second-most common after the carbonaceous C-type.

Eunomia is a very large asteroid in the middle asteroid belt. It is the largest of the stony (S-type) asteroids, with 3 Juno as a close second. It is quite a massive asteroid, in 6th to 8th place. It is the largest Eunomian asteroid, and is estimated to contain 1% of the mass of the asteroid belt.
The Eunomia or Eunomian family is a large asteroid family of S-type asteroids named after the asteroid 15 Eunomia. It is the most prominent family in the intermediate asteroid belt and the 6th-largest family with nearly six thousand known members, or approximately 1.4% of all asteroids in the asteroid belt.
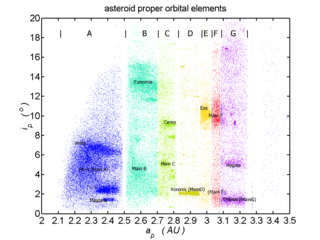
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be fragments of past asteroid collisions. An asteroid family is a more specific term than asteroid group whose members, while sharing some broad orbital characteristics, may be otherwise unrelated to each other.
In Greek mythology, Dysnomia was the daemon of "lawlessness", who shares her nature with Atë ("ruin"). She was a companion of the latter deity, Adikia (Injustice), and Hybris (insolence). Dysnomia makes rare appearances among other personifications in poetical contexts that are marginal in ancient Greek religion but become central to Greek philosophy: see Plato's Laws.

1050 Meta, provisional designation 1925 RC, is a stony Eunomia asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 10 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 14 September 1925, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. The meaning of the asteroids's name is unknown. The presumably S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 6.14 hours and possibly an elongated shape.
Fifteen or 15 may refer to:

The Ctenuchina are a subtribe of moths in the family Erebidae.

Eirene or Irene, more commonly known in English as Peace, is one of the Horae, the personification and goddess of peace in Greek mythology and ancient religion. She was depicted in art as a beautiful young woman carrying a cornucopia, sceptre, and a torch or rhyton. She is usually said to be the daughter of Zeus and Themis and thus sister of Dike and Eunomia. Her Roman equivalent is the goddess Pax.
Eunomia is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1818.

Callicore is a genus of nymphalid butterfly found in the Neotropical realm. This genus, like some related ones, was formerly lumped together as the paraphyletic Catagramma assemblage.

In Greek mythology, Eunomia was a minor goddess of law and legislation, as well as the spring-time goddess of green pastures. She is by most accounts the daughter of Themis and Zeus. Her opposite number was Dysnomia (Lawlessness).

Boloria eunomia, the bog fritillary or ocellate bog fritillary is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae.

Callicore eunomia, the Eunomia eighty-eight or Eunomia numberwing, is a species of butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in the upper Amazonian region, from Colombia and Guyana to Brazil, Peru, and Bolivia.
Eunomia insularis is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1866. It is found on Cuba.
Eunomia nitidula is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1866. It is found on Cuba.
Eunomia colombina is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1793. It is found on the Antilles and possibly in Honduras and Brazil.
Eunomia rubripunctata is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1876. It is found on Jamaica and Puerto Rico.
Eunomia caymanensis is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by George Hampson in 1911. It is found on the Cayman Islands and Cuba.









