
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term family is a metaphor borrowed from biology, with the tree model used in historical linguistics analogous to a family tree, or to phylogenetic trees of taxa used in evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists thus describe the daughter languages within a language family as being genetically related. The divergence of a proto-language into daughter languages typically occurs through geographical separation, with different regional dialects of the proto-language undergoing different language changes and thus becoming distinct languages over time.

A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative body, a stage in the process of legislation. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are laws made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, regulations issued by government agencies, and oral or customary law. Statutes may originate with the legislative body of a country, state or province, county, or municipality.

Sicyon or Sikyōn was an ancient Greek city state situated in the northern Peloponnesus between Corinth and Achaea on the territory of the present-day regional unit of Corinthia. The ruins lie just west of the modern village of Sikyona. An ancient monarchy at the times of the Trojan War, the city was ruled by a number of tyrants during the Archaic and Classical period and became a democracy in the 3rd century BC. Sicyon was celebrated for its contributions to ancient Greek art, producing many famous painters and sculptors. In Hellenistic times it was also the home of Aratus of Sicyon, the leader of the Achaean League.

Nabis was the last king of independent Sparta. He was probably a member of the Heracleidae, and he ruled from 207 BC to 192 BC, during the years of the First and Second Macedonian Wars and the eponymous "War against Nabis", i.e. against him. After taking the throne by executing two claimants, he began rebuilding Sparta's power. During the Second Macedonian War, Nabis sided with King Philip V of Macedon and in return he received the city of Argos. However, when the war began to turn against the Macedonians, he defected to Rome. After the war, the Romans, urged by the Achaean League, attacked Nabis and defeated him. He then was assassinated in 192 BC by the Aetolian League. He represented the last phase of Sparta's reformist period.

Alexandria Eschate was a city founded by Alexander the Great, at the south-western end of the Fergana Valley in August 329 BC. It was the most northerly outpost of Alexander's Empire in Central Asia. Alexandria Eschate was established on the south bank of the river Jaxartes, at or close to the site of modern Khujand. According to the Roman writer Curtius, Alexandria Ultima retained its Greek culture as late as 30 BC.

Areus I was Agiad King of Sparta from 309 to 265 BC. His reign is noted for his attempts to transform Sparta into a Hellenistic kingdom and to recover its former pre-eminence in Greece, notably against the kings Antigonos Gonatas of Macedonia and Pyrrhus of Epirus.

Eutychides of Sicyon in Corinthia, Greek sculptor of the early part of the 3rd century BC, was a pupil of Lysippus. His most noted work was a statue of the Tyche of Antioch, a goddess who embodied the idea of the then newly founded city of Antioch. The Tyche was seated on a rock, crowned with towers, and having the river Orontes at her feet. There is a small copy of the statue in the Vatican. It was imitated by a number of Asiatic cities; and indeed most statues since created that commemorate cities borrow something from the work of Eutychides.

Aquarius (♒︎) is the eleventh astrological sign in the zodiac, originating from the constellation Aquarius. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun is in the Aquarius sign between about January 20 and February 18. Aquarius is one of the three air signs, alongside Gemini and Libra. The ruling planets of Aquarius are Saturn, and Uranus in modern astrology. It is a fixed Air Sign. The opposite sign of Aquarius is Leo.

The Hesperiini or branded grass skippers are a tribe in the Hesperiinae subfamily of skipper butterflies. They are known as branded grass skippers because all the males in this tribe feature a black diagonal brand of scales on their forewings that exude pheromones to attract females.
Alexis was an ancient Greek sculptor mentioned by Pliny as one of the pupils of Polykleitos. Pausanias mentions an artist of the same name, a native of Sicyon, and father of the sculptor Cantharus. It cannot be satisfactorily settled whether these are the same, or different persons. Pliny's account implies that he had the elder Polykleitos in mind, in which case Alexis could not have flourished later than Olympiad 95 in 400 BC, whereas Eutychides, under whom Cantharus studied, flourished about Olympiad 120 in 300. If the two were identical, as German classicist Friedrich Thiersch thinks, we must suppose either that Pliny made a mistake, and that Alexis studied instead under Polykleitos the Younger, or else that Eutychides, whose date is given by Pliny, was not the artist under whom Cantharus studied.
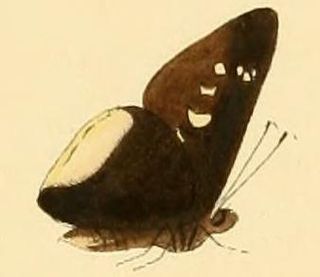
Eutychide is a genus of skippers in the family Hesperiidae.
An earthquake occurred in Antioch on 13 December 115 AD. It had an estimated magnitude of 7.5 on the surface wave magnitude scale and an estimated maximum intensity of XI (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. Antioch and surrounding areas were devastated with a great loss of life and property. It triggered a local tsunami that badly damaged the harbour at Caesarea Maritima. The Roman Emperor Trajan was caught in the earthquake, as was his successor Hadrian. Although the consul Marcus Pedo Vergilianus was killed, they escaped with only slight injuries and later began a program to rebuild the city.
Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 252 is a fragment of a notice of removal, in Greek. It was discovered in Oxyrhynchus. The manuscript was written on papyrus in the form of a sheet. It is dated to the year 19-20. Current location of fragment is unknown.
Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 253 is a fragment of a notice of removal, in Greek. It was discovered in Oxyrhynchus. The manuscript was written on papyrus in the form of a sheet. It is dated to 25 July - 23 August 19. Currently it is housed in the Universitätsbibliothek Graz in Graz.

Moncina is a subtribe of butterflies in the skipper subfamily Hesperiinae.












