Related Research Articles

The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails.

The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
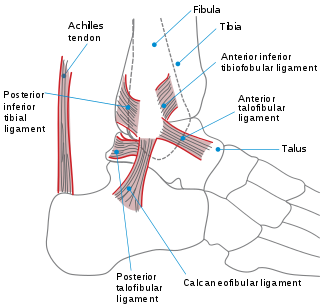
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

Plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain (PHP) is a disorder of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one-third of cases.

A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma on the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any major joint or minor joint. The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.

A cystocele, also known as a prolapsed bladder, is a medical condition in which a woman's bladder bulges into her vagina. Some may have no symptoms. Others may have trouble starting urination, urinary incontinence, or frequent urination. Complications may include recurrent urinary tract infections and urinary retention. Cystocele and a prolapsed urethra often occur together and is called a cystourethrocele. Cystocele can negatively affect quality of life.
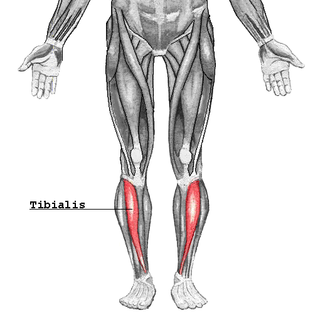
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle in humans that originates along the upper two-thirds of the lateral (outside) surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.

In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
The Broström operation is a repair of ligaments on lateral ankle. It is designed to address ankle instability. More importantly, it is primarily used to repair the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) in the ankle. It is thought that the majority of patients regain most function in their ankles. The recovery time for the procedure varies according to the patient but usually takes a minimum of 3–6 months.

A sprained ankle, also known as a twisted ankle or rolled ankle, is an injury where sprain occurs on one or more ligaments of the ankle. It is the most common injury to occur in ball sports, such as basketball, volleyball, football, and racquet sports.

The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is a complex of three ligaments on the underside of the foot that connect the calcaneus with the navicular bone.

The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is formed by the triangular fibrocartilage discus (TFC), the radioulnar ligaments (RULs) and the ulnocarpal ligaments (UCLs).

Cuboid syndrome or cuboid subluxation describes a condition that results from subtle injury to the calcaneocuboid joint and ligaments in the vicinity of the cuboid bone, one of seven tarsal bones of the human foot.

Laminoplasty is an orthopaedic/neurosurgical surgical procedure for treating spinal stenosis by relieving pressure on the spinal cord. The main purpose of this procedure is to provide relief to patients who may have symptoms of numbness, pain, or weakness in arm movement. The procedure involves cutting the lamina on both sides of the affected vertebrae and then "swinging" the freed flap of bone open thus relieving the pressure on the spinal cord. The spinous process may be removed to allow the lamina bone flap to be swung open. The bone flap is then propped open using small wedges or pieces of bone such that the enlarged spinal canal will remain in place.
A high ankle sprain, also known as a syndesmotic ankle sprain (SAS), is a sprain of the syndesmotic ligaments that connect the tibia and fibula in the lower leg, thereby creating a mortise and tenon joint for the ankle. High ankle sprains are described as high because they are located above the ankle. They comprise approximately 15% of all ankle sprains. Unlike the common lateral ankle sprains, when ligaments around the ankle are injured through an inward twisting, high ankle sprains are caused when the lower leg and foot externally rotates.
Posterolateral corner injuries of the knee are injuries to a complex area formed by the interaction of multiple structures. Injuries to the posterolateral corner can be debilitating to the person and require recognition and treatment to avoid long term consequences. Injuries to the PLC often occur in combination with other ligamentous injuries to the knee; most commonly the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). As with any injury, an understanding of the anatomy and functional interactions of the posterolateral corner is important to diagnosing and treating the injury.

Medial knee injuries are the most common type of knee injury. The medial ligament complex of the knee is composed of the superficial medial collateral ligament (sMCL), deep medial collateral ligament (dMCL), and the posterior oblique ligament (POL). These ligaments have also been called the medial collateral ligament (MCL), tibial collateral ligament, mid-third capsular ligament, and oblique fibers of the sMCL, respectively. This complex is the major stabilizer of the medial knee. Injuries to the medial side of the knee are most commonly isolated to these ligaments. A thorough understanding of the anatomy and function of the medial knee structures, along with a detailed history and physical exam, are imperative to diagnosing and treating these injuries.

Syndesmosis procedure is one of the more than 20 bunion surgeries currently being performed. While the majority of bunion surgeries involve the breaking and shifting of bones, syndesmosis procedure is one of few surgical techniques that use a soft tissue or non-osteotomy (non-bone-breaking) approach to afford the same correction. More than 130 different surgical techniques have been described for correction of one single condition of the foot: the bunion deformity.
References
- ↑ Tindall, S. F., and S. H. Heaney. "Repair of the lateral ligaments of the ankle by the Evans technique." J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 58 (1976): S133.
- ↑ EVANS DL (May 1953). "Recurrent instability of the ankle; a method of surgical treatment". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine . 46 (5): 343–4. doi:10.1177/003591575304600507. PMC 1918639 . PMID 13055916.
- ↑ Ateşalp, S.; Demiralp, B.; Ozkal, U. B.; Uğurlu, M.; Bozkurt, M.; Başbozkurt, M. (2009). "Modified Evans technique improves plantar pressure distribution in lateral ankle instability". Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 20 (1): 41–6. PMID 19522690.
- ↑ Peters, J. W.; Trevino, S. G.; Renstrom, P. A. (1991). "Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability". Foot & Ankle International. 12 (3): 182–191. doi:10.1177/107110079101200310. ISSN 1071-1007. PMID 1791012. S2CID 23889509.
- ↑ Rosenbaum, D.; Becker, H.-P.; Sterk, J.; Gerngross, H.; Claes, L. (1997). "Functional Evaluation of the 10-Year Outcome after Modified Evans Repair for Chronic Ankle Instability". Foot & Ankle International. 18 (12): 765–771. doi:10.1177/107110079701801202. ISSN 1071-1007. PMID 9429877. S2CID 21849001.