The excretory system of gastropods removes nitrogenous waste and maintains the internal water balance of these creatures, commonly referred to as snails and slugs. The primary organ of excretion is a nephridium.
Contents

The excretory system of gastropods removes nitrogenous waste and maintains the internal water balance of these creatures, commonly referred to as snails and slugs. The primary organ of excretion is a nephridium.

The most primitive gastropods retain two nephridia, but in the great majority of species, the right nephridium has been lost, leaving a single excretory organ, located in the anterior part of the visceral mass. The nephridium projects into the main venous sinus in the animal's foot. The circulatory fluid of gastropods, known as haemolymph directly bathes the tissues, where it supplies them with oxygen and absorbs carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste, a necessary waste product of metabolism. From the arterial sinuses bathing the tissues, it drains into the venous sinus, and thus flows past the nephridium.
The main body cavity of most aquatic gastropods also includes pericardial glands, often located above the heart. These secrete waste into the haemolymph, prior to further filtration in the nephridium. Pulmonates lack these glands, so that the nephridium is the only major organ of excretion.
In some gastropods, the nephridium opens directly into the sinus, but more usually, there is a small duct, referred to as the renopericardial canal. In aquatic gastropods, the nephridium is drained by a ureter that opens near the rear of the mantle cavity. This allows the flow of water through the cavity to flush out the excreta. Terrestrial pulmonates instead have a much longer ureter, that opens near the anus.
In addition to the pericardial glands and nephridium, excretory cells are also present in the digestive glands opening into the stomach. These glands have a metabolic function, somewhat similar to that of the vertebrate liver, and excrete waste products directly into the digestive system, where it is voided with the faeces.
In aquatic gastropods, the waste product is invariably ammonia, which rapidly dissolves in the surrounding water. In the case of freshwater species, the nephridium also resorbs a significant amount of salt in order to prevent its loss through osmosis into the surrounding water.
Terrestrial species instead excrete insoluble uric acid, which allows them to maintain their internal water balance. Even so, most species require a somewhat humid environment, and secrete a considerable amount of water in their slime trail. Those few species that dwell in arid environments typically hibernate or aestivate during dry periods to preserve moisture.

The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about 12 centimetres in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder.
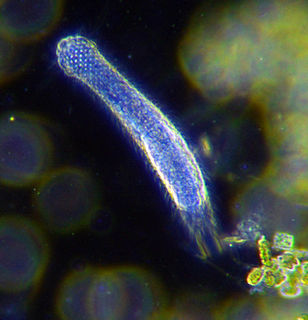
The gastrotrichs, commonly referred to as hairybellies or hairybacks, are a group of microscopic (0.06-3.0 mm), worm-like, acoelomate animals, and are widely distributed and abundant in freshwater and marine environments. They are mostly benthic and live within the periphyton, the layer of tiny organisms and detritus that is found on the seabed and the beds of other water bodies. The majority live on and between particles of sediment or on other submerged surfaces, but a few species are terrestrial and live on land in the film of water surrounding grains of soil. Gastrotrichs are divided into two orders, the Macrodasyida which are marine, and the Chaetonotida, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Nearly 800 species of gastrotrich have been described.

The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin.
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The dual function of excretory systems is the elimination of the waste products of metabolism and to drain the body of used up and broken down components in a liquid and gaseous state. In humans and other amniotes most of these substances leave the body as urine and to some degree exhalation, mammals also expel them through sweating.
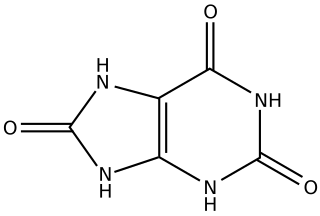
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after leaving the cell. Excretion is an essential process in all forms of life. For example, in mammals, urine is expelled through the urethra, which is part of the excretory system. In unicellular organisms, waste products are discharged directly through the surface of the cell.

The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids and tardigrades.
The nephridium is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys. Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia come in two basic categories: metanephridia and protonephridia. All nephridia- and kidney- having animals belong to the clade Nephrozoa.
A nephridiopore is part of the nephridium, an excretory organ found in many organisms, such as flatworms and annelids. Polychaetes typically release their gametes into the water column using nephridiopores.
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, water, CO2, phosphates, sulphates, etc. Animals treat these compounds as excretes. Plants have chemical "machinery" which transforms some of them (primarily the nitrogen compounds) into useful substances.
Merriam-Webster defines chemotaxonomy as the method of biological classification based on similarities and dissimilarity in the structure of certain compounds among the organisms being classified. Advocates argue that, as proteins are more closely controlled by genes and less subjected to natural selection than the anatomical features, they are more reliable indicators of genetic relationships. The compounds studied most are proteins, amino acids, nucleic acids, peptides etc.

The common octopus is a mollusc belonging to the class Cephalopoda. Octopus vulgaris is one of the most studied of all octopus species, and also one of the most intelligent. It ranges from the eastern Atlantic, extends from the Mediterranean Sea and the southern coast of England, to the southern coast of South Africa. It also occurs off the Azores, Canary Islands, and Cape Verde Islands. The species is also common in the Western Atlantic. The common octopus hunts at dusk. Crabs, crayfish, and bivalve molluscs are preferred, although the octopus eats almost anything it can catch. It is able to change colour to blend in with its surroundings, and is able to jump upon any unwary prey that strays across its path. Using its beak, it is able to break into the shells of shelled molluscs. Training experiments have shown the common octopus can distinguish the brightness, size, shape, and horizontal or vertical orientation of objects.
Insect physiology includes the physiology and biochemistry of insect organ systems.
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration of electrolytes to keep the body fluids from becoming too diluted or concentrated. Osmotic pressure is a measure of the tendency of water to move into one solution from another by osmosis. The higher the osmotic pressure of a solution, the more water tends to move into it. Pressure must be exerted on the hypertonic side of a selectively permeable membrane to prevent diffusion of water by osmosis from the side containing pure water.

Tomigerus clausus is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Odontostomidae.
The digestive system of gastropods has evolved to suit almost every kind of diet and feeding behavior. Gastropods as the largest taxonomic class of the mollusca are very diverse: the group includes carnivores, herbivores, scavengers, filter feeders, and even parasites.

As in other molluscs, the circulatory system of gastropods is open, with the fluid, or haemolymph, flowing through sinuses and bathing the tissues directly. The haemolymph typically contains haemocyanin, and is blue in colour.

In pharmacology the elimination or excretion of a drug is understood to be any one of a number of processes by which a drug is eliminated from an organism either in an unaltered form or modified as a metabolite. The kidney is the main excretory organ although others exist such as the liver, the skin, the lungs or glandular structures, such as the salivary glands and the lacrimal glands. These organs or structures use specific routes to expel a drug from the body, these are termed elimination pathways:
The tissues that are concerned with the secretion of gums, resins, volatile oils, nectar latex, and other substances in plants are called secretory tissues. These tissues are classified as either laticiferous tissues or glandular tissues.
The rock dove, Columbia livia, has a number of special adaptations for regulating water uptake and loss.
The kidney is a paired organ of the excretory system in vertebrates, which maintains the balance of water and electrolytes in the body (osmoregulation), filters the blood, removes metabolic waste products, and in many vertebrates also produces hormones and maintains blood pressure. In healthy vertebrates, the kidneys maintain homeostasis of extracellular fluid in the body. When the blood is being filtered, the kidneys form urine, which consists of water and excess or unnecessary substances, the urine is then excreted from the body through other organs, which in vertebrates, depending on the species, may include the ureter, urinary bladder, cloaca, and urethra.
Barnes, Robert D. (1982). Invertebrate Zoology. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 364–365. ISBN 0-03-056747-5.