An octopus is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda. The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates.

A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology.
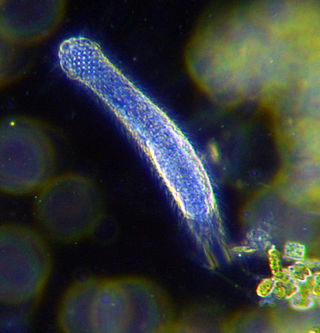
The gastrotrichs, commonly referred to as hairybellies or hairybacks, are a group of microscopic (0.06–3.0 mm), cylindrical, acoelomate animals, and are widely distributed and abundant in freshwater and marine environments. They are mostly benthic and live within the periphyton, the layer of tiny organisms and detritus that is found on the seabed and the beds of other water bodies. The majority live on and between particles of sediment or on other submerged surfaces, but a few species are terrestrial and live on land in the film of water surrounding grains of soil. Gastrotrichs are divided into two orders, the Macrodasyida which are marine, and the Chaetonotida, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Nearly 800 species of gastrotrich have been described.

Bobtail squid are a group of cephalopods closely related to cuttlefish. Bobtail squid tend to have a rounder mantle than cuttlefish and have no cuttlebone. They have eight suckered arms and two tentacles and are generally quite small.

Myopsida is one of the four orders of squid. It consists of two families: the monotypic Australiteuthis and the diverse and commercially important Loliginidae. Some taxonomists classify this taxon as a suborder of the order Teuthida, in which case it is known as Myopsina. This reclassification is due to Myopsina and Oegopsina not being demonstrated to form a clade.

The giant cuttlefish, also known as the Australian giant cuttlefish, is the world's largest cuttlefish species, growing to 50 cm (20 in) in mantle length and up to 100 cm (39 in) in total length. They can be over 10.5 kg (23 lb) in weight. Like all cuttlefish species, the giant cuttlefish has 8 arms and 2 feeding tentacles, as well as blue blood and 3 hearts. Using cells known as chromatophores, the cuttlefish can put on spectacular displays, changing colour in an instant. The giant cuttlefish is native to temperate and subtropical waters of Australia, from Brisbane in Queensland to Shark Bay in Western Australia and Tasmania to the south. It occurs on rocky reefs, seagrass beds, and sand and mud seafloor to a depth of 100 m (330 ft). In 2009 the species was listed at Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species due to an observed declining trend at that time.

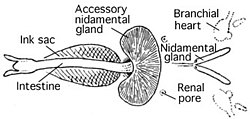
An ink sac is an anatomical feature that is found in many cephalopod mollusks used to produce the defensive cephalopod ink. With the exception of nocturnal and very deep water cephalopods, all Coleoidea which dwell in light conditions have an ink sac, which can be used to expel a cloud of dark ink in order to confuse predators.

The paintpot cuttlefish is a small, poorly researched species of cuttlefish found in the Indo-Pacific, between Japan and Hong Kong. It is one of the two species classified in the genus Metasepia. Metasepia cuttlefish are characterized by their small, thick, diamond-shaped cuttlebone, and distinctive body coloration.

Idiosepius paradoxus, also known as the northern pygmy squid, is a species of pygmy squid native to the western Pacific Ocean. This species can be found inhabiting shallow, inshore waters around central China, South Korea, and Japan.

Thysanoteuthis rhombus, also known as the diamond squid,diamondback squid, or rhomboid squid, is a large species of squid from the family Thysanoteuthidae which is found worldwide, throughout tropical and subtropical waters. T. rhombus is given its name for the appearance of the fins that run the length of the mantle. They are a fast growing species with a lifespan of approximately 1 year. The diamond squid is the only cephalopod species known to be monogamous. T. rhombus often preys on fish and other small cephalopods at varying water depths. This species is commercially fished in Japan, specifically in the Sea of Japan and Okinawa.

Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous ink released into water by most species of cephalopod, usually as an escape mechanism. All cephalopods, with the exception of the Nautilidae and the Cirrina, are able to release ink to confuse predators.
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.

Cuttlefish, or cuttles, are marine molluscs of the suborder Sepiina. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of buoyancy.

Branchial hearts are accessory pumps that supplement the action of the systemic heart in a cephalopod's body. They are myogenic in nature. Branchial hearts are always in pairs located at the base of the gills. Each branchial heart consists of a single chamber. They pump blood through the gills via the afferent branchial veins. Since they only circulate venous blood, branchial hearts function under predominantly anaerobic conditions. Branchial hearts also appear to be involved in hemocyanin synthesis.

Sepioteuthis lessoniana, commonly known as the bigfin reef squid, tiger squid, glitter squid, oval squid, or northern calamari, is a species of loliginid squid. It is one of the three currently recognized species belonging to the genus Sepioteuthis. Studies in 1993, however, have indicated that bigfin reef squids may comprise a cryptic species complex. The species is likely to include several very similar and closely related species.

Sepiella inermis is a species of cuttlefish in the family Sepiidae. It is indigenous to the Indo-Pacific region. In this region, S. inermis is an economically important species, and is sold and eaten.
The hypobranchial gland is a glandular structure which is part of the anatomy of many mollusks, including several different families of gastropods, and also many protobranch bivalves. This gland produces mucus as well as biologically active compounds. The cephalopod ink sac is a modified hypobranchial gland.

Sepioloidea lineolata or more commonly known as the striped pyjama squid or the striped dumpling squid is a type of bottletail squid that inhabits the Indo-Pacific Oceans of Australia. The striped pyjama squid lives on the seafloor, often hiding in the sand. When fully mature, a striped pyjama squid will only be about 7 to 8 centimetres in length. Baby striped pyjama squid can be smaller than 10 millimetres (0.39 in).

The dwarf cuttlefish (Sepia bandensis), also known as the stumpy-spined cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish native to the shallow coastal waters of the Central Indo-Pacific. The holotype of the species was collected from Banda Neira, Indonesia. It is common in coral reef and sandy coast habitats, usually in association with sea cucumbers and sea stars. Sepia baxteri and Sepia bartletti are possible synonyms.