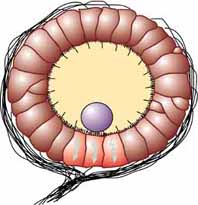

The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, [1] cnidarians, [2] ctenophores, [3] echinoderms, [4] cephalopods, [5] [6] crustaceans, [7] Proseriata [8] and Catenulida [9] (both are taxonomic groups of flatworms),and gastropods, [10] A similar structure is also found in Xenoturbella . [11] The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs (setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained.
Contents
In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance.
It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians.[ citation needed ]