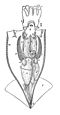
Grimalditeuthis bonplandi paralarva
Paralarvae (sg.: paralarva) are young cephalopods in the planktonic stages between hatchling and subadult. This stage differs from the larval stage of animals that undergo true metamorphosis. [1] Paralarvae have been observed only in members of the orders Octopoda and Teuthida. [2]
Contents
The term was introduced by Richard E. Young and Robert F. Harman in 1988. [2]
Paralarvae usually spend an uncertain amount of time in the plankton and then typically descend to an adult habitat in the mesopelagic or bathypelagic zone. Their population abundance is dependent on the variation of mortality rates during the planktonic period.