
Alstom SA is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer which operates worldwide in rail transport markets. It is active in the fields of passenger transportation, signaling, and locomotives, producing high-speed, suburban, regional and urban trains along with trams.

CSX Transportation, known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad company operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. Operating about 21,000 route miles (34,000 km) of track, it is the leading subsidiary of CSX Corporation, a Fortune 500 company headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida.

A railway brake is a type of brake used on the cars of railway trains to enable deceleration, control acceleration (downhill) or to keep them immobile when parked. While the basic principle is similar to that on road vehicle usage, operational features are more complex because of the need to control multiple linked carriages and to be effective on vehicles left without a prime mover. Clasp brakes are one type of brakes historically used on trains.

The British Rail Class 313 was a dual-voltage electric multiple unit (EMU) train built by British Rail Engineering Limited's Holgate Road carriage works between February 1976 and April 1977. They were the first production units that were derived from British Rail's 1971 prototype suburban EMU design which, as the BREL 1972 family, eventually encompassed 755 vehicles over five production classes. They were the first second-generation EMUs to be constructed for British Rail and the first British Rail units with both a pantograph for 25 kV 50 Hz AC overhead lines and contact shoe equipment for 750 V DC third rail supply. They were, additionally, the first units in Britain to employ multi-function automatic Tightlock couplers, which include electrical and pneumatic connections allowing the coupling and uncoupling of units to be performed unassisted by the driver whilst in the cab.
Bombardier Transportation was a Canadian-German rolling stock and rail transport manufacturer, with headquarters in Berlin, Germany. It was one of the world's largest companies in the rail vehicle and equipment manufacturing and servicing industry. Bombardier Transportation had many regional offices, production and development facilities worldwide. It produced a wide range of products including passenger rail vehicles, locomotives, bogies, propulsion and controls. In February 2020, the company had 36,000 employees, and 63 manufacturing and engineering locations around the world. Formerly a division of Bombardier Inc., the company was acquired by French manufacturer Alstom on 29 January 2021.

The Westinghouse Air Brake Technologies Corporation was an American company founded on September 28, 1869 by George Westinghouse in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Earlier in the year he had invented the railway air brake in New York state.

The TGV Duplex is a French high-speed train of the TGV family, manufactured by Alstom, and operated by the French national railway company SNCF. They were the first TGV trainsets to use bi-level passenger carriages with a seating capacity of 508 passengers, increasing capacity on busy high-speed lines. While the TGV Duplex started as a small component of the TGV fleet, it has become one of the system's workhorses.
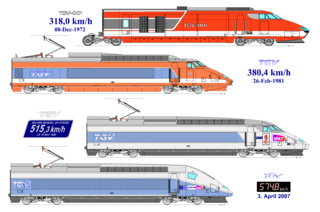
The TGV holds a series of land speed records for rail vehicles achieved by SNCF, the French national railway, and its industrial partners. The high-speed trials are intended to expand the limits of high-speed rail technology, increasing speed and comfort without compromising safety.
Wheel slide protection and wheel slip protection are railway terms used to describe automatic systems used to detect and prevent wheel-slide during braking or wheel-slip during acceleration. This is analogous to ABS and traction control systems used on motor vehicles. It is particularly important in slippery rail conditions.

Knorr-Bremse AG is a German manufacturer of braking systems for rail and commercial vehicles that has operated since 1905. Other products in Group's portfolio include intelligent door systems, control components, air conditioning systems for rail vehicles, torsional vibration dampers, and transmission control systems for commercial vehicles.

The Class 13 are a type of mixed use 200 km/h (124 mph) multivoltage electric locomotive of type Traxis designed by Alstom in the late 1990s for the Belgian and Luxembourgish railways.
Electronically controlled pneumatic brakes are a type of railway braking systems.

Westinghouse Air Brake Technologies Corporation, commonly known as Wabtec, is an American company formed by the merger of the Westinghouse Air Brake Company (WABCO) and MotivePower Industries Corporation in 1999. It is headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.

CSR Corporation Limited (CSR), formerly known as China South Locomotive & Rolling Stock Corp was a Chinese manufacturer of locomotive and rolling stock.

The KTX-Sancheon is a South Korean high-speed train built by Hyundai Rotem in the second half of the 2000s and operated by Korail since March 2010. With a top speed of 305 km/h (189.5 mph), the KTX-Sancheon is the second commercial high-speed train operated in South Korea and the first domestic high-speed train that is designed and developed in South Korea.

The Tyne and Wear Metrocars are a fleet of light rail vehicles manufactured by Metro-Cammell for the Tyne and Wear Metro in North East England between 1978 and 1981. For operation on Network Rail controlled tracks between Pelaw Junction and Sunderland, they are designated on TOPS as the Class 599. Most were refurbished between 2010 and 2015 by Wabtec Rail at Doncaster Works and are scheduled to be replaced by Class 555 rolling stock from 2024.

Saft is a French company involved in the design, the development and the manufacturing of batteries used in transport, industry and defense. Headquartered in France, it has an international presence.

United Wagon Company is Russia's leading and one of the world's biggest manufacturers of freight cars. The company is on the Russian Ministry for Economic Development list of strategically important organizations.

Brecknell Willis is a Wabtec company headquartered in Chard, Somerset, South West England and brand-name of electrification equipment for railways, mostly pantographs and contact shoes.
Track IQ formerly known as Trackside Intelligence, is an international manufacturer and supplier of railway equipment and services for the purpose of measuring operating conditions. After developing the RailBAM and WCM systems, Track IQ formed a partnership with Siemens to install the systems in the United Kingdom and Continental Europe.





















