Related Research Articles
Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated way to decrease, maintain, or increase body weight, or to prevent and treat diseases such as diabetes and obesity. As weight loss depends on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasising particular macronutrients, have been shown to be no more effective than one another. As weight regain is common, diet success is best predicted by long-term adherence. Regardless, the outcome of a diet can vary widely depending on the individual.

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.

Human nutrition deals with the provision of essential nutrients in food that are necessary to support human life and good health. Poor nutrition is a chronic problem often linked to poverty, food security, or a poor understanding of nutritional requirements. Malnutrition and its consequences are large contributors to deaths, physical deformities, and disabilities worldwide. Good nutrition is necessary for children to grow physically and mentally, and for normal human biological development.
Life extension is the concept of extending the human lifespan, either modestly through improvements in medicine or dramatically by increasing the maximum lifespan beyond its generally-settled limit of 125 years.
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight, or to the metabolic state achieved after complete digestion and absorption of a meal. Metabolic changes in the fasting state begin after absorption of a meal.

Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat, or lean mass. Weight loss can either occur unintentionally because of malnourishment or an underlying disease, or from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. "Unexplained" weight loss that is not caused by reduction in calorific intake or exercise is called cachexia and may be a symptom of a serious medical condition.

Low-carbohydrate diets restrict carbohydrate consumption relative to the average diet. Foods high in carbohydrates are limited, and replaced with foods containing a higher percentage of fat and protein, as well as low carbohydrate foods.

The Okinawa diet describes the traditional dietary practices of indigenous people of the Ryukyu Islands, which were believed to have contributed to their relative longevity over a period of study in the 20th century.
A low-protein diet is a diet in which people decrease their intake of protein. A low-protein diet is used as a therapy for inherited metabolic disorders, such as phenylketonuria and homocystinuria, and can also be used to treat kidney or liver disease. Low protein consumption appears to reduce the risk of bone breakage, presumably through changes in calcium homeostasis. Consequently, there is no uniform definition of what constitutes low-protein, because the amount and composition of protein for an individual with phenylketonuria would differ substantially from one with homocystinuria or tyrosinemia.
Calorie restriction is a dietary regimen that reduces intake of energy from caloric foods & beverages without incurring malnutrition. "Reduce" can be defined relative to the subject's previous intake before intentionally restricting food or beverage consumption, or relative to an average person of similar body type.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
The CRON-diet is a nutrient-rich, reduced calorie diet developed by Roy Walford, Lisa Walford, and Brian M. Delaney. The CRON-diet involves calorie restriction in the hope that the practice will improve health and retard aging, while still attempting to provide the recommended daily amounts of various nutrients. Other names include CR-diet, Longevity diet, and Anti-Aging Plan. The Walfords and Delaney, among others, founded the CR Society International to promote the CRON-diet.

A very-low-calorie diet (VLCD), also known as semistarvation diet and crash diet, is a type of diet with very or extremely low daily food energy consumption. Often described as a fad diet, it is defined as a diet of 800 kilocalories (3,300 kJ) per day or less. Modern medically supervised VLCDs use total meal replacements, with regulated formulations in Europe and Canada which contain the recommended daily requirements for vitamins, minerals, trace elements, fatty acids, protein and electrolyte balance. Carbohydrates may be entirely absent, or substituted for a portion of the protein; this choice has important metabolic effects. Medically supervised VLCDs have specific therapeutic applications for rapid weight loss, such as in morbid obesity or before a bariatric surgery, using formulated, nutritionally complete liquid meals containing 800 kilocalories or less per day for a maximum of 12 weeks.
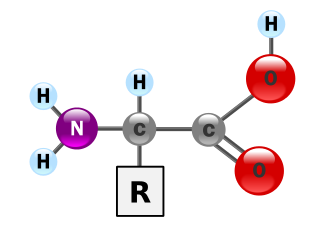
Proteins are essential nutrients for the human body. They are one of the building blocks of body tissue and can also serve as a fuel source. As a fuel, proteins provide as much energy density as carbohydrates: 4 kcal per gram; in contrast, lipids provide 9 kcal per gram. The most important aspect and defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is its amino acid composition.
A diabetic diet is a diet that is used by people with diabetes mellitus or high blood sugar to minimize symptoms and dangerous complications of long-term elevations in blood sugar.

The Western pattern diet is a modern dietary pattern that is generally characterized by high intakes of pre-packaged foods, refined grains, red meat, processed meat, high-sugar drinks, candy and sweets, fried foods, conventionally-raised animal products, butter and other high-fat dairy products, eggs, potatoes, corn, and low intakes of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, pasture-raised animal products, fish, nuts, and seeds.

Intermittent fasting is any of various meal timing schedules that cycle between voluntary fasting and non-fasting over a given period. Methods of intermittent fasting include alternate-day fasting, periodic fasting, and daily time-restricted feeding.
Diet plays an important role in the genesis of obesity. Personal choices, food advertising, social customs and cultural influences, as well as food availability and pricing all play a role in determining what and how much an individual eats.

Weight management refers to behaviors, techniques, and physiological processes that contribute to a person's ability to attain and maintain a healthy weight. Most weight management techniques encompass long-term lifestyle strategies that promote healthy eating and daily physical activity. Moreover, weight management involves developing meaningful ways to track weight over time and to identify ideal body weights for different individuals.

Luigi Fontana, M.D., PhD, FRACP is an internationally recognized physician scientist who studies healthy longevity, with a focus on calorie restriction, endurance exercise and metabolism. He is currently the Leonard P Ullmann Chair in Translational Metabolic Health at the Charles Perkins Centre, where he directs the Healthy Longevity Research and Clinical Program. He is also a Professor of Medicine and Nutrition in the Faculty of Medicine and Health at the University of Sydney and a Clinical Academic in the Department of Endocrinology at the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney, Australia. Fontana is an Adjunct Professor of Medicine at Washington University School of Medicine.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Lee MB, Hill CM, Bitto A, Kaeberlein M (November 2021). "Antiaging diets: Separating fact from fiction". Science. 374 (6570): eabe7365. doi:10.1126/science.abe7365. PMC 8841109 . PMID 34793210.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Flanagan, Emily W.; Most, Jasper; Mey, Jacob T.; Redman, Leanne M. (2020-09-23). "Calorie restriction and aging in humans". Annual Review of Nutrition. 40 (1): 105–133. doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-122319-034601. ISSN 0199-9885. PMC 9042193 . PMID 32559388.
- ↑ "Fasting". Encyclopedia Britannica. 2023. Retrieved 2023-03-22.
- ↑ Longo, Valter D.; Anderson, Rozalyn M. (2022). "Nutrition, longevity and disease: From molecular mechanisms to interventions". Cell. 185 (9): 1455–1470. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.002. PMC 9089818. PMID 35487190.
| Library resources about Fasting and longevity |