
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths.

Psilocybe quebecensis is a moderately active hallucinogenic mushroom in the section Aztecorum, having psilocybin and psilocin as main active compounds. Native to Quebec, it is the most northern known psilocybin mushroom after Psilocybe semilanceata in northern Scandinavia. Macroscopically this mushroom somewhat resembles Psilocybe baeocystis.

Psilocybe ovoideocystidiata is a psilocybin mushroom, having psilocybin and/or psilocin as main active compounds. It is closely related to P. subaeruginascens from Java, P. septentrionalis from Japan, and P. wayanadensis from India. This mushroom was first documented by Richard V. Gaines in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania in June 2003. Although it is sometimes confused with Psilocybe caerulipes, it can be distinguished by its rhomboid spores, larger stature, earlier fruiting season and membranous annulus.
Psilocybe galindoi is a psychedelic mushroom in the section Mexicana, having psilocybin and psilocin as its main active compounds. It is also known as Psilocybe galindii. The species was named in honor of Mr. Carlos Galindo Arias and his family by Dr. Gastón Guzmán.
Psilocybe graveolens is an extremely rare psilocybin mushroom which has psilocybin and psilocin as main active compounds, discovered in the salt marshes or "meadows" of Hackensack, New Jersey. This mushroom is known for its strong and persistent odor.

Psilocybe stuntzii, also known as Stuntz's blue legs and blue ringers it is a psilocybin mushroom of the family Hymenogastraceae, having psilocybin and psilocin as main active compounds.

Gymnopilus luteoviridis is a widely distributed mushroom-forming fungus of the Eastern United States that contains the hallucinogens psilocybin and psilocin.
Psilocybe plutonia is a small psilocybin mushroom of the family Hymenogastraceae, believed to contain psilocybin and psilocin. It was first documented from Cuba. An older synonym is Agaricus plutonia.

Bromus catharticus is a species of brome grass known by the common names rescuegrass, grazing brome, prairie grass, and Schrader's bromegrass. The specific epithet catharticus is Latin, meaning cathartic. The common name rescuegrass refers to the ability of the grass to provide forage after harsh droughts or severe winters. The grass has a diploid number of 42.

Coprinopsis lagopus is a species of fungus in the family Psathyrellaceae. Until 2001, the species was known as Coprinus lagopus; advances in the understanding of phylogenetic relationships between the various coprinoid species led to a major reorganization of that genus. It is a delicate and short-lived fungus, the fruit bodies lasting only a few hours before dissolving into a black ink – a process called deliquescence. The vague resemblance of the young fruit body to the paw of a white rabbit has earned this species the common name harefoot mushroom.

Amanita abrupta, commonly known as the American abrupt-bulbed amanita or the American abrupt-bulbed lepidella, is a possibly toxic species of fungus in the family Amanitaceae. Named for the characteristic shape of its fruit bodies, this white Amanita has a slender stem, a cap covered with conical white warts, and an "abruptly enlarged" swollen base. This terrestrial species grows in mixed woods in eastern North America and eastern Asia, where it is thought to exist in a mycorrhizal relationship with a variety of both coniferous and deciduous tree species.
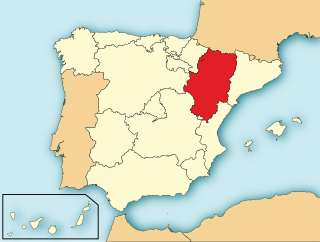
Psilocybe hispanica is a species of fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. It produces small brown mushrooms with conical to convex caps up to 10 mm (0.4 in) in diameter and stems 16 to 25 mm long by 0.5 to 1 mm thick. Reported as new to science in 2000, it is only known from the Pyrenees mountain range in northern Spain and southwestern France, where it grows on horse dung in grass fields at elevations of 1,700 to 2,300 m. The mushroom contains the psychoactive compound psilocybin. The possible depiction of this species in the 6,000-year-old Selva Pascuala rock art suggests that it might have been used in ancient religious rituals—the oldest evidence of such usage in prehistoric Europe.
Psilocybe tasmaniana is a species of coprophilous agaric fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. It was described by Gastón Guzmán and Roy Watling in 1978 as a small tawny orange mushroom that grows on dung, with a slight blueing reaction to damage, known only from Tasmania and southeastern Australia. It was likened to Psilocybe subaeruginosa although characteristics, appearance, and the association with dung were not typical for that species. As a blueing member of the genus Psilocybe it contains the psychoactive compounds psilocin and psilocybin.

Adiantum viridimontanum, commonly known as Green Mountain maidenhair fern, is a fern found only in outcrops of serpentine rock in New England and Eastern Canada. The leaf blade is cut into finger-like segments, themselves once-divided, which are borne on the outer side of a curved, dark, glossy rachis. These finger-like segments are not individual leaves, but parts of a single compound leaf. The "fingers" may be drooping or erect, depending on whether the individual fern grows in shade or sunlight. Spores are borne under false indusia at the edge of the subdivisions of the leaf, a characteristic unique to the genus Adiantum.

Morchella punctipes is a species of morel fungus in the family Morchellaceae. It is native to North America, found widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains. It is edible when cooked.
Pannaria phyllidiata is a species of lichen in the family Pannariaceae. Known from Australia, it was described as new to science in 2011. It is characterised by its unique phyllidia and distinct distribution.

Mycena crocea, commonly known as the walnut mycena, is a species of mushroom in the family Mycenaceae. The small mushroom has a bright yellow, conical to broadly convex cap up to 15 mm (0.6 in) in diameter. The stem is tough and thin, up to 20 mm (0.8 in) tall, bright yellow at the top becoming progressively orange towards the base. The gills are adnate, subdistant, and yellowish, becoming lighter in age; and the spore print is white. This mushroom is saprobic and found exclusively on hickory nuts and walnuts in eastern North America. The specific epithet crocea refers to the orange color. The mushroom is commonly known as the "walnut mycena" and was previously and commonly misidentified as Mycena luteopallens.
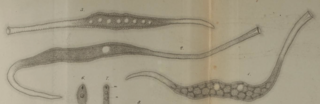
Tracheloraphis is a genus of ciliates in the family Trachelocercidae.

Psilocybe angulospora is a species of agaric fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. The species was described from Taiwan in 2015 and is also present in New Zealand, where it is considered introduced. As a blueing member of the genus Psilocybe it contains the psychoactive compounds psilocin and psilocybin.

Filoboletus is a genus of fungi in the family Mycenaceae.














