Related Research Articles
Absolute magnitude is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object, on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it were viewed from a distance of exactly 10 parsecs, without extinction of its light due to absorption by interstellar matter and cosmic dust. By hypothetically placing all objects at a standard reference distance from the observer, their luminosities can be directly compared among each other on a magnitude scale.

A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing — no particles or even electromagnetic radiation such as light — can escape from it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has an enormous effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, it has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly.

Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in California. With a 2020 population of 3,898,747, it is the second-largest city in the United States, following New York City. Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic and cultural diversity, Hollywood film industry and sprawling metropolitan area.
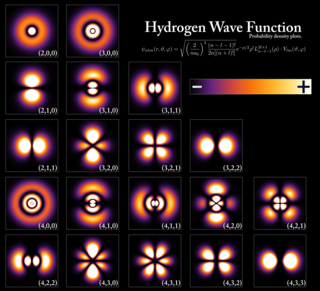
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.

Sex is a trait that determines an individual's reproductive function, male or female, in animals and plants that propagate their species through sexual reproduction. The type of gametes produced by an organism defines its sex. Commonly in plants and animals, male organisms produce smaller gametes while female organisms produce larger gametes. Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes that develop into offspring that inherit a selection of the traits of each parent.
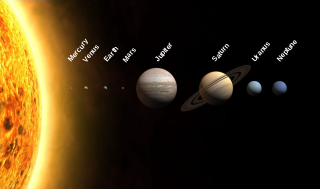
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. Of the bodies that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the four gas and ice giants and the four terrestrial planets, followed by an unknown number of dwarf planets and innumerable small Solar System bodies. Of the bodies that orbit the Sun indirectly—the natural satellites—two are larger than Mercury, the smallest terrestrial planet, and one is nearly as large.

The lion is a large cat of the genus Panthera native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, deep-chested body, short, rounded head, round ears, and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on large ungulates. The lion is an apex and keystone predator; although some lions scavenge when opportunities occur and have been known to hunt humans, the species typically does not.

In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances. However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables.

Leif Erikson, Leiv Eiriksson or Leif Ericson, also known as Leif the Lucky, was a Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to have set foot on continental North America, approximately half a millennium before Christopher Columbus. According to the sagas of Icelanders, he established a Norse settlement at Vinland, which is usually interpreted as being coastal North America. There is ongoing speculation that the settlement made by Leif and his crew corresponds to the remains of a Norse settlement found in Newfoundland, Canada, called L'Anse aux Meadows and which was occupied 1,000 years ago.
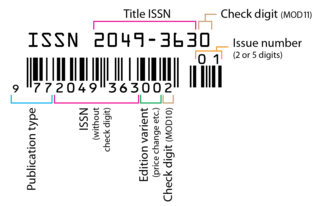
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication, such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature.

HSL and HSV are alternative representations of the RGB color model, designed in the 1970s by computer graphics researchers to more closely align with the way human vision perceives color-making attributes. In these models, colors of each hue are arranged in a radial slice, around a central axis of neutral colors which ranges from black at the bottom to white at the top.

Quebec is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States.
Pedomicrobium is a ubiquitous bacterium dominant in biofilms of man-made aquatic environments such as water distribution systems and bioreactors. Due to their abilities to oxidise manganese (Mn), they are found to be the main culprits of Mn related “dirty water”.
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, originally spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated from Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea, to the area of Great Britain later named after them: England. The closest living relatives of English include Scots, followed by the Low Saxon and Frisian languages. While English is genealogically West Germanic, its vocabulary is also hugely influenced by Old Norman French and Latin, as well as by Old Norse.
The Richter scale – also called the Richter magnitude scale and Richter's magnitude scale – is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 paper, where he called it the "magnitude scale". This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale, denoted as ML or ML .

PageRank (PR) is an algorithm used by Google Search to rank web pages in their search engine results. It is named after both the term "web page" and co-founder Larry Page. PageRank is a way of measuring the importance of website pages. According to Google:
PageRank works by counting the number and quality of links to a page to determine a rough estimate of how important the website is. The underlying assumption is that more important websites are likely to receive more links from other websites.
Filomicrobium fusiforme is a Gram-negative, aerobic, motile bacteria from the genus of Filomicrobium which was isolated from brackish water in Germany.
Filomicrobium insigne is a Gram-negative, aerobic, motile bacteria from the genus of Filomicrobium which was isolated from soil in the coastal Shengli Oilfield in Shandong Province in eastern China.

Hyphomicrobium is a genus of Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped bacteria from the family of Hyphomicrobiaceae. It has a large polar or sub-polar filiform prostheca very similar to that of Caulobacter. In addition to having a nutritional function, the prostheca also plays a role in the initiation of DNA replication.
Hyphomicrobium aestuarii is a Gram-negative bacteria from the genus of Hyphomicrobium.
References
- 1 2 3 LSPN lpsn.dsmz.de
- ↑ UniProt
- ↑ Wu, X. -L.; Yu, S. -L.; Gu, J.; Zhao, G. -F.; Chi, C. -Q. (2009). "Filomicrobium insigne sp. nov., isolated from an oil-polluted saline soil". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 59 (2): 300–5. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65758-0 . PMID 19196769.