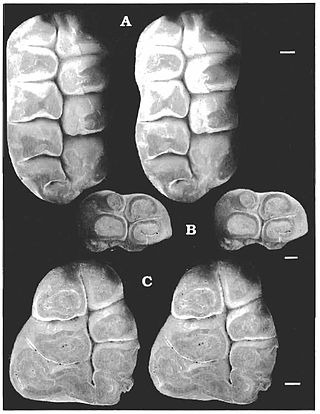
Catopsalis is a genus of extinct mammal from the Paleocene of North America. This animal was a relatively large member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. Most Multituberculates were much smaller.

Fissidens adianthoides, the maidenhair pocketmoss, is a moss in the family Fissidentaceae. It was first collected by Hedwig in 1801.
Maiden's hair or maidenhair may refer to:

Johann Hedwig, also styled as Johannes Hedwig, was a German botanist notable for his studies of mosses. He is sometimes called the "father of bryology". He is known for his particular observations of sexual reproduction in the cryptogams. Many of his writings were in Latin, and his name is rendered in Latin as Ioannis Hedwig or Ioanne Hedwig. The standard author abbreviation Hedw. is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.
Fissidens hydropogon is a species of moss in the family Fissidentaceae. It is endemic to Ecuador. Its natural habitat is rivers. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Fissidens is a genus of haplolepideous mosses (Dicranidae) in the family Fissidentaceae.
Ilma Grace Stone, née Balfe, was an Australian botanist who specialised in bryology. She was an author, collector, and researcher of Australian mosses, a subject on which she lectured and wrote.
Astroblepus fissidens is a species of catfish of the family Astroblepidae. It can be found on Ecuador.

Fissidens limbatus commonly known as Herzog's pocket-moss, is a moss in the family Fissidentaceae. This species is found growing in high elevations in tropical America in addition to the US, Mexico and Canada. Montagne first collected F. crispus in 1838.
Fissidens arnoldii is a species of moss belonging to the family Fissidentaceae.

Fissidens dubius is a species of moss belonging to the family Fissidentaceae.
Fissidens exilis is a species of moss belonging to the family Fissidentaceae.
Fissidens elegans is a species of moss belonging to the family Fissidentaceae.
Fissidens serratus is a species of moss belonging to the family Fissidentaceae.
Fissidens usambaricus is a species of moss belonging to the family Fissidentaceae. It is known from Sub-Saharan Africa. In Angola, it has been reported to grow in lowland rainforests.

Fissidens taxifolius is a species of moss in the Fissidentaceae family. It has a cosmopolitan distribution.

Coniophanes fissidens, the yellowbelly snake, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species is native to Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, Belize, Nicaragua, El Salvador, Costa Rica, Panama, Ecuador, Peru, and Colombia.
Fissidens celticus, also known by its common name Welsh pocket-moss, is a species of moss in the family Fissidentaceae. It was discovered in 1958 in Pembrokeshire by A.H. Norkett and was first described as a new species by Jean Paton in 1965.







