
José Gervasio Artigas Arnal was a soldier and statesman who is regarded as a national hero in Uruguay and the father of Uruguayan nationhood.

The national flag of Uruguay, officially known as the National Pavilion, is one of the three official flags of Uruguay along with the Artigas flag and the flag of the Treinta y Tres. It has a field of nine equal horizontal stripes alternating white and blue. The canton is white, charged with the Sun of May, from which 16 rays extend, alternating between triangular and wavy. The flag was first adopted by law on 18 December 1828, and had 19 alternating stripes of white and blue until 11 July 1830, when a new law reduced the number of alternating stripes to nine. The flag was designed by Joaquín Suárez.

Juan Antonio Lavalleja y de la Torre was an Uruguayan revolutionary, military general, and political figure. He was born in Minas, in a region now named after him as the Lavalleja Department of Uruguay.

The coat of arms of Uruguay was first adopted by law on March 19, 1829, and later on had some minor modification in 1906 and 1908. It was supposedly designed by Juan Manuel Besnes Irigoyen.

José Fructuoso Rivera y Toscana was a Uruguayan general and patriot who fought for the liberation of Banda Oriental from Brazilian rule, thrice served as President of Uruguay and was one of the instigators of the long Uruguayan Civil War. He is also considered to be the founder of the Colorado Party, which ruled Uruguay without interruption from 1865 until 1958. He made a controversial decision to almost completely eliminate the native Charrúa during the 1831 Massacre of Salsipuedes.

Treinta y Tres is the capital city of the Treinta y Tres Department in eastern Uruguay. It is known for its role in the development of folk music.
Banda Oriental, or more fully Banda Oriental del Río Uruguay, was the name of the South American territories east of the Uruguay River and north of Río de la Plata that comprise the modern nation of Uruguay, the modern state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, and part of the modern state of Santa Catarina, Brazil. It was the easternmost territory of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata.

The United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, earlier known as the United Provinces of South America, was a name adopted in 1816 by the Congress of Tucumán for the region of South America that declared independence in 1816, with the Sovereign Congress taking place in 1813, during the Argentine War of Independence (1810–1818) that began with the May Revolution in 1810. It originally comprised rebellious territories of the former Spanish Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata dependencies and had Buenos Aires as its capital.

The Cisplatine War was an armed conflict fought in the 1820s between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata over control of Brazil's Cisplatina province. It was fought in the aftermath of the United Provinces' and Brazil's independence from Spain and Portugal, respectively, and resulted in the independence of Cisplatina as the Oriental Republic of Uruguay.
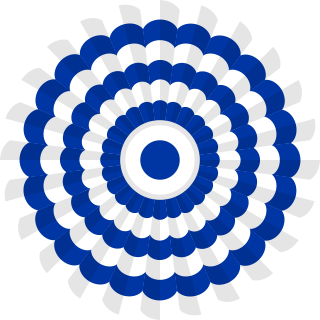
The National Cockade of Uruguay was first adopted by law on December 22, 1828. It features the colours of the national flag, blue and white.

The Treinta y Tres Orientales was a revolutionary group led by Juan Antonio Lavalleja and Manuel Oribe against the Empire of Brazil. Their actions culminated in the foundation of modern Uruguay. They became famous by the name of the Treinta y Tres Orientales when, in 1825, they began an insurrection for the independence of Oriental Province, a historical territory encompassing modern Uruguay and part of modern Brazilian Rio Grande do Sul State, from Brazilian control.

Cisplatina was a Brazilian province in existence from 1821 to 1828 created by the Luso-Brazilian invasion of the Banda Oriental. From 1815 until 1822 Brazil was a constituent kingdom of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. After the independence of Brazil and the formation of the Empire of Brazil the Cisplatina province remained part of it. In 1828, following the Preliminary Peace Convention, the Cisplatina province became independent as Uruguay.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Uruguay:

The Portuguese conquest of the Banda Oriental was the armed-conflict that took place between 1816 and 1820 in the Banda Oriental, for control of what today comprises the whole of the Republic of Uruguay, the northern part of the Argentine Mesopotamia and southern Brazil. The four-year armed-conflict resulted in the annexation of the Banda Oriental into the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves as the Brazilian province of Cisplatina.

Spain–Uruguay relations are the current and historical relations between Spain and Uruguay. There is community of 67,000 Spanish nationals residing in Uruguay and 33,000 Uruguayan nationals residing in Spain. Both nations are members of the Association of Spanish Language Academies, Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.
Agraciada Beach is a historic beach area in Uruguay.
Claudia Josefa Palacios González (?–1881) was an Uruguayan painter and miniaturist of the nineteenth century. She is best known for creating the first visual representation of Uruguayan independence episode known as Desembarco de los Treinta y Tres Orientales.
The provisional governorship of José Rondeau was the pre-Constitution government period of Uruguay which began with his oath and inauguration as the Governor and Captain General of Uruguay, recently becoming independent and also known as the State of Montevideo, after being summoned by the Constitutional and Legislative General Assembly to take office, and lasted until 17 April 1830 with his resignation.
The interim governorship of Joaquín Suárez was the pre-Constitution government period of Uruguay which began after his appointment by the Constitutional Assembly as the interim substitute Governor and Captain General from 2nd December until 22nd December 1828 when the elected Governor and Captain General José Rondeau assumed his charge. During the twenty days of this brief period the cessation of all foreign authorities on the territory was ordered and several national symbols were established.

The flag represents the Argentine province of Corrientes was adopted in 1986. The flag features a horizontal triband of light blue-white-light blue, with a small blue triangle, motto and coat of arms on a white stripe.















