Related Research Articles
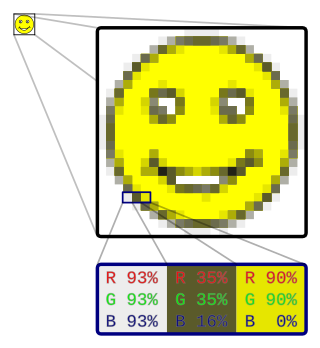
In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.

A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs.
Tag Image File Format or Tagged Image File Format, commonly known by the abbreviations TIFF or TIF, is an image file format for storing raster graphics images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and photographers. TIFF is widely supported by scanning, faxing, word processing, optical character recognition, image manipulation, desktop publishing, and page-layout applications. The format was created by the Aldus Corporation for use in desktop publishing. It published the latest version 6.0 in 1992, subsequently updated with an Adobe Systems copyright after the latter acquired Aldus in 1994. Several Aldus or Adobe technical notes have been published with minor extensions to the format, and several specifications have been based on TIFF 6.0, including TIFF/EP, TIFF/IT, TIFF-F and TIFF-FX.

Exchangeable image file format is a standard that specifies formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras, scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras. The specification uses the following existing encoding formats with the addition of specific metadata tags: JPEG lossy coding for compressed image files, TIFF Rev. 6.0 for uncompressed image files, and RIFF WAV for audio files. It does not support JPEG 2000 or GIF encoded images.
An image server is web server software which specializes in delivering images. However, not all image servers support HTTP or can be used on web sites.
The Cineon System was one of the first computer based digital film systems, created by Kodak in the early 1990s. It was an integrated suite of components consisting a Motion picture film scanner, a film recorder and workstation hardware with software for compositing, visual effects, image restoration and color management.

Photo CD is a system designed by Kodak for digitizing and saving photos onto a CD. Launched in 1991, the discs were designed to hold nearly 100 high quality images, scanned prints and slides using special proprietary encoding. Photo CDs are defined in the Beige Book and conform to the CD-ROM XA and CD-i Bridge specifications as well. They were intended to play on CD-i players, Photo CD players, and any computer with a suitable software.
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency.
A camera raw image file contains unprocessed or minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, a motion picture film scanner, or other image scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed, and contain large amounts of potentially redundant data. Normally, the image is processed by a raw converter, in a wide-gamut internal color space where precise adjustments can be made before conversion to a viewable file format such as JPEG or PNG for storage, printing, or further manipulation. There are dozens of raw formats in use by different manufacturers of digital image capture equipment.

Digital photography uses cameras containing arrays of electronic photodetectors interfaced to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to produce images focused by a lens, as opposed to an exposure on photographic film. The digitized image is stored as a computer file ready for further digital processing, viewing, electronic publishing, or digital printing. It is a form of digital imaging based on gathering visible light.

The Canon EOS 30D is an 8.2-megapixel semi-professional digital single-lens reflex camera, initially announced on February 21, 2006. It is the successor of the Canon EOS 20D, and is succeeded by the EOS 40D. It can accept EF and EF-S lenses, and like its predecessor, it uses an APS-C sized image sensor, so it does not require the larger imaging circle necessary for 35 mm film and 'full-frame' digital cameras.
JPEG XR is an image compression standard for continuous tone photographic images, based on the HD Photo specifications that Microsoft originally developed and patented. It supports both lossy and lossless compression, and is the preferred image format for Ecma-388 Open XML Paper Specification documents.

Kodak Picture Kiosk is a line of self service photo printing kiosks manufactured by the Eastman Kodak company.

ImageMagick, invoked from the command line as magick, is a free and open-source cross-platform software suite for displaying, creating, converting, modifying, and editing raster images. ImageMagick was created by John Cristy in 1987, it can read and write over 200 image file formats. It is widely used in open-source applications.
PGF is a wavelet-based bitmapped image format that employs lossless and lossy data compression. PGF was created to improve upon and replace the JPEG format. It was developed at the same time as JPEG 2000 but with a focus on speed over compression ratio.
In computing, a bitmap graphic is an image formed from rows of different colored pixels. A GIF is an example of a graphics image file that uses a bitmap.

The Kodak DC series was Kodak's pioneering consumer-grade line of digital cameras; as distinct from their much more expensive professional Kodak DCS series. Cameras in the DC series were manufactured and sold during the mid-to-late 1990s and early 2000s. Some were branded as "Digital Science". Most of these early digital cameras supported RS-232 serial port connections because USB hardware was not widely available before 1998. Some models in the DC series ran on the short lived DigitaOS, a camera operating system that allowed third party software to be installed.
WebP is a raster graphics file format developed by Google intended as a replacement for JPEG, PNG, and GIF file formats. It supports both lossy and lossless compression, as well as animation and alpha transparency.
The IVUE file format is an image format used by Live Picture, a discontinued image application. It chunks an image into tiles and stores multiple quarter-downscaled versions of one image. It is supported by Adobe Photoshop 3.0 through 7.0. The image format is extended to FlashPix.
JPEG XL is a royalty-free raster-graphics file format that supports both lossy and lossless compression. It is designed to outperform existing raster formats and thus become their universal replacement.
References
- ↑ "FlashPix Format Specification" (PDF).
- ↑ "TechWeb: TechEncyclopedia". TechWeb. September 1, 2006. Archived from the original on June 9, 2015. Retrieved September 1, 2006.
- ↑ "AI3A Standards - Initiatives- Flashpix". International Imaging Industry Association. September 1, 2006. Archived from the original on April 26, 2008.
- ↑ "ImageMagick/libfpx". ImageMagick Studio LLC. 19 September 2019. license