
The Hudson Strait links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Resolution Island off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km long with an average width of 125 km, varying from 70 km at the eastern entrance to 240 km at Deception Bay.

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi) with a population density of 0.03/km²; the population was 13,039 according to the 2021 Canadian census; and it is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, which is the capital of Nunavut.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.
A fox is small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammal.

Melville Peninsula is a large peninsula in the Canadian Arctic north of Hudson Bay. To the east is Foxe Basin and to the west the Gulf of Boothia. To the north the Fury and Hecla Strait separates it from Baffin Island. To the south Repulse Bay and Frozen Strait separate it from Southampton Island at the north end of Hudson Bay. On the southwest it is connected to the mainland by the Rae Isthmus, named after the Arctic explorer John Rae.

Russell Island is an uninhabited island of the Arctic Archipelago in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the Parry Channel, separated from the northern tip of Prince of Wales Island by the narrow Baring Channel. The western third of the island is separated from the other two thirds by a narrow lake and its outlet. At the northern end of the lake there is an isthmus just 1.1 km (0.68 mi) wide and this joins the two parts of the island. With a total area of 940 km2 (360 sq mi), it is the largest island offshore of Prince of Wales Island.

Bray Island is one of the Canadian Arctic islands located in Nunavut, Canada along the southern coast of Baffin Island. It is located in Foxe Basin, at 69°16′N77°00′W, and has an area of 689 km2 (266 sq mi).

Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.

Luke Foxe was an English explorer, born in Kingston-upon-Hull, Yorkshire, who searched for the Northwest Passage across North America. In 1631, he sailed much of the western Hudson Bay before concluding no such passage was possible. Foxe Basin, Foxe Channel and Foxe Peninsula were named after him.

Fury and Hecla Strait is a narrow Arctic seawater channel located in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
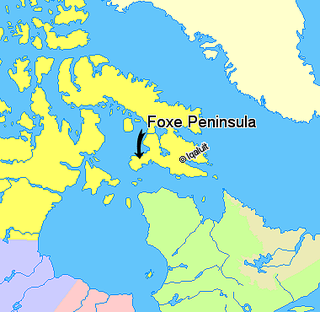
Foxe Peninsula is a peninsula found at the southern end of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It juts out from the southern end of the island in a southwestern direction, dividing Foxe Basin and Hudson Strait. Its western extremity is Cape Queen; to the southeast lies the Inuit hamlet of Kinngait. At the western coast is Inuksuk Point, which contains more than 100 inuksuit.

Captain Thomas James (1593–1635) was a Welsh sea captain, notable as a navigator and explorer, who set out to discover the Northwest Passage, the hoped for ocean route around the top of North America to Asia.
The Ottawa Islands are a group of currently uninhabited islands situated in the eastern edge of Canada's Hudson Bay. The group comprises 24 small islands, located at approximately 60N 80W. The main islands include Booth Island, Bronson Island, Eddy Island, Gilmour Island, J. Gordon Island, Pattee Island, and Perley Island. The highest point is on Gilmour Island, which rises to over 1,800 ft (550 m). Located a short distance off the northwest coast of Quebec's Ungava Peninsula, they, like the other coastal islands in Hudson Bay, were historically part of the Northwest Territories, and became Crown Land upon the creation of Nunavut in 1999. Nunavik Inuit have occupied these islands since time immemorial and gained constitutionally-protected harvest and access rights under the Nunavik Inuit Land Claim Agreement signed in 2007.
Frozen Strait is a waterway in Nunavut just north of Hudson Bay between the Melville Peninsula to the north and Southampton Island to the south. It connects Repulse Bay to the west with Foxe Basin to the east. The strait is 80 km (50 mi) long, and 19 to 32 km wide.
Roes Welcome Sound is a long channel at the northwest end of Hudson Bay in the Kivalliq Region, Nunavut, Canada between the mainland on the west and Southampton Island on the east. It opens south into Hudson Bay. Its north end joins Repulse Bay which is connected east through Frozen Strait to Foxe Basin, thereby making Southampton Island an island. Wager Bay is a western branch. It is situated 200 km (120 mi) north of Marble Island. Roes Welcome Sound measures 290 km (180 mi) long, and 24 to 113 km wide.
Mill Island is an uninhabited Arctic island located in Hudson Bay between Foxe Channel and Hudson Strait. It is south of Baffin Island's Foxe Peninsula, and north of Nottingham and Salisbury islands. Mill Island is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Morrissey Harbour is a bay on the island's north coast.
The Back Peninsula is a cape located on eastern Bell Peninsula, Southampton Island, in the Kivalliq Region, Nunavut, Canada. Its southern shore is part of the northern boundary of Hudson Bay. Foxe Basin is to the north. There are two large bays, Gorden Bay and Junction Bay. Bowhead whale frequent the area. The Bell Peninsula's irregular coastline is marked by Seashore Point and Expectation Point.

Dorset Island or Cape Dorset Island is one of the Canadian Arctic islands located in Hudson Strait, Nunavut, Canada. It lies off the Foxe Peninsula area of southwestern Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region. It is serviced by an airport and a harbour.
New Britain as a historical term of limited usage referred in its day to the poorly mapped lands of North America north of 17th-century New France. The name applied primarily to today's Nunavik and Labrador interiors, though in the 18th century this had grown to include all of the mainland shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay north of the Canadas. British visitors came to sub-divide the district loosely into the territories of New South Wales, New North Wales and Labrador. The name Labrador predates mention of the other names by more than a century.












