The Cleveland, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railway, also known as the Big Four Railroad and commonly abbreviated CCC&StL, was a railroad company in the Midwestern United States. It operated in affiliation with the New York Central system.

The Monon Railroad, also known as the Chicago, Indianapolis, and Louisville Railway from 1897 to 1971, was an American railroad that operated almost entirely within the state of Indiana. The Monon was merged into the Louisville and Nashville Railroad in 1971, and much of the former Monon right of way is owned today by CSX Transportation. In 1970, it operated 540 miles (870 km) of road on 792 miles (1,275 km) of track; that year it reported 1320 million ton-miles of revenue freight and zero passenger-miles.

The Louisville and Nashville Railroad, commonly called the L&N, was a Class I railroad that operated freight and passenger services in the southeast United States.

The Union Station of Louisville, Kentucky is a historic railroad station that serves as offices for the Transit Authority of River City (TARC), as it has since mid-April 1980 after receiving a year-long restoration costing approximately $2 million. It was one of at least five union stations in Kentucky, amongst others located in Lexington, Covington, Paducah and Owensboro. It was one of three stations serving Louisville, the others being Central Station and Southern Railway Station. It superseded previous, smaller, railroad depots located in Louisville, most notably one located at Tenth and Maple in 1868-1869, and another L&N station built in 1858. The station was formally opened on September 7, 1891 by the Louisville and Nashville Railroad. There was a claim made at the time that it was the largest railroad station in the Southern United States, covering forty acres. The other major station in Louisville was Central Station, serving the Baltimore and Ohio, the Illinois Central and other railroads.

The Kentucky Railway Museum, now located in New Haven, Kentucky, United States, is a non-profit railroad museum dedicated to educating the public regarding the history and heritage of Kentucky's railroads and the people who built them. Originally created in 1954 in Louisville, Kentucky, the museum is at its third location, in extreme southern Nelson County. It is one of the oldest railroad stations in the United States.

The Wiregrass Central Railroad is a shortline railroad operating 19.5 miles (31.4 km) of track from a CSX Transportation connection at Waterford, near Newton, to Enterprise, Alabama via the south side of Fort Rucker. The company was initially a subsidiary of Gulf and Ohio Railways and began operations in 1987 following the purchase of the Enterprise Subdivision branch line of CSX Transportation.

The Flim-Flam Man is a 1967 American comedy film directed by Irvin Kershner, featuring George C. Scott, Michael Sarrazin, and Sue Lyon, based on the 1965 novel The Ballad of the Flim-Flam Man by Guy Owen. The movie has well-known character actors in supporting roles, including Jack Albertson, Slim Pickens, Strother Martin, Harry Morgan, and Albert Salmi.

The George Washington was a named passenger train of the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway running between Cincinnati, Ohio and Washington, D.C. A section divided from the main train at Gordonsville, Virginia and operated through Richmond to Phoebus, Virginia. From the west, a section originated in Louisville and joined at Ashland. The train began service in 1932 to mark the 200th anniversary of the birth of the first president of the United States.

James Edwards Cantrill was elected the 22nd Lieutenant Governor of Kentucky serving from 1879 to 1883 under Governor Luke P. Blackburn. He also served as a circuit court judge starting in 1892, and in 1898 was elected to the Court of Appeals bench.

Central Railroad of Indianapolis is a Class III short-line railroad that operates approximately 39 miles (63 km) miles of rail line in north central Indiana.

The Historic Railpark and Train Museum, formerly the Louisville and Nashville Railroad Station in Bowling Green, Kentucky, is located in the historic railroad station. The building was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on December 18, 1979. Opened in 1925, the standing depot is the third Louisville & Nashville Railroad depot that served Bowling Green.
A shortline railroad is a small or mid-sized railroad company that operates over a relatively short distance relative to larger, national railroad networks. The term is used primarily in the United States and Canada. In the U.S., railroads are categorized by operating revenue, and most shortline railroads fall into the Class III or Class II categorization defined by the Surface Transportation Board. Shortlines generally exist for one of three reasons: to link two industries requiring rail freight together ; to interchange revenue traffic with other, usually larger, railroads; or to operate a tourist passenger train service. Often, short lines exist for all three of these reasons.

Louisville & Nashville 152 is a preserved K-2a class 4-6-2 "Pacific" type steam locomotive listed on the National Register of Historic Places, currently homed at the Kentucky Railway Museum at New Haven, Kentucky in southernmost Nelson County, Kentucky. It is the oldest known remaining 4-6-2 "Pacific" type locomotive to exist. It is also the "Official State Locomotive of Kentucky", designated as such on March 6, 2000. The locomotive is currently owned and being restored back to operating condition by the Kentucky Railway Museum.

The Louisville and Nashville Combine Car Number 665, also known as the "Jim Crow Car", is a historic railcar on the National Register of Historic Places, currently at the Kentucky Railway Museum at New Haven, Kentucky, in southernmost Nelson County, Kentucky.
The Mt. Broderick Pullman Car is a historic railcar on the National Register of Historic Places, currently at the Kentucky Railway Museum at New Haven, Kentucky, in southernmost Nelson County, Kentucky. It has been described as a "four-star hotel" on rails.
The Frankfort and Cincinnati Model 55 Rail Car is a historic railcar on the National Register of Historic Places. The railcar currently resides at the Kentucky Railway Museum in New Haven, Nelson County, Kentucky.
The Western Kentucky Railway was a shortline railroad in Kentucky, that connected coal mines with CSX Transportation at Providence. The lines were part of the Illinois Central Gulf Railroad until March 1982, when Costain Coal, Inc. bought the trackage and set up the Tradewater Railway to operate it. In January 1995, the Rail Management and Consulting Corporation acquired the property and transferred it to the new Western Kentucky Railway. Genesee & Wyoming Inc. acquired it from the Rail Management Corporation in 2005. In 2010, WKRL abandoned all of its remaining lines north of Providence, and the rails were removed shortly after. The only remaining tracks that were originally owned by WKRL are operated by Martin Marrieta Aggregates' Fredonia Valley Railroad from Princeton to Fredonia.
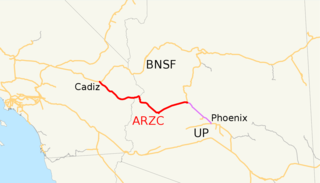
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.

The Ripley & New Albany Railroad is a 27-mile long (43 km) shortline railroad that runs from New Albany to Falkner, Mississippi, and previously extended from Houston, Mississippi, to Middleton, Tennessee, along former Gulf, Mobile and Ohio Railroad trackage. RNA interchanges with the BNSF Railway in New Albany, Mississippi. It primarily hauls lumber products and Oil-Dri.

Tulsa-Sapulpa Union Railway Company, L.L.C. is a Class III shortline rail carrier which operates freight service between Tulsa, Oklahoma and Sapulpa, Oklahoma over 10 miles of track known as the Sapulpa Lead, as well as leases and operates a 12.9 mile section of Union Pacific track known as the Jenks Industrial Lead between Tulsa and Jenks, Oklahoma. The line connects with two Class I railroads, being the Union Pacific at Tulsa and the BNSF at Sapulpa, and additionally connects to its fellow Class III shortline, the Sand Springs Railway, in Tulsa. It is owned by the Collins Family Trust. Major customers on the Sapulpa Lead include Technotherm, Prescor, and Ardagh Glass, and on the Jenks Industrial Lead, the Sinclair Oil Refinery, Kentube, Word Industries, Pepsi Cola, and Kimberly-Clark.















