
The James River and Kanawha Canal was a partially built canal in Virginia intended to facilitate shipments of passengers and freight by water between the western counties of Virginia and the coast. Ultimately its towpath became the roadbed for a rail line following the same course.
The Bluegrass Railroad and Museum is a railroad museum and heritage railroad in Versailles, Kentucky, United States.

Crescent Hill is a neighborhood four miles (6 km) east of downtown Louisville, Kentucky USA. This area was originally called "Beargrass" because it sits on a ridge between two forks of Beargrass Creek. The boundaries of Crescent Hill are N Ewing Ave to the St. Matthews city limit by Brownsboro Road to Lexington Road. Frankfort Avenue generally bisects the neighborhood.
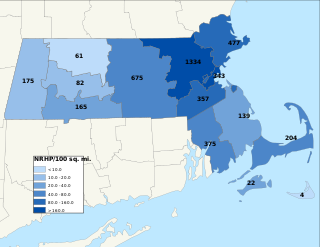
This is a list of properties and districts in Massachusetts listed on the National Register of Historic Places. There are over 4,300 listings in the state, representing about 5% of all NRHP listings nationwide and the second-most of any U.S. state, behind only New York. Listings appear in all 14 Massachusetts counties.
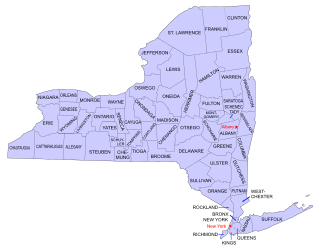
Buildings, sites, districts, and objects in New York listed on the National Register of Historic Places:

The Flim-Flam Man is a 1967 American comedy film directed by Irvin Kershner, featuring George C. Scott, Michael Sarrazin, and Sue Lyon, based on the 1965 novel The Ballad of the Flim-Flam Man by Guy Owen. The movie has well-known character actors in supporting roles, including Jack Albertson, Slim Pickens, Strother Martin, Harry Morgan, and Albert Salmi.

This is a list of properties and historic districts in Kentucky that are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. There are listings in all of Kentucky's 120 counties.

Tunkhannock Creek Viaduct is a concrete deck arch bridge on the Nicholson Cutoff rail segment of the Norfolk Southern Railway Sunbury Line that spans Tunkhannock Creek in Nicholson, Pennsylvania. Measuring 2,375 feet (724 m) long and towering 240 feet (73.15 m) when measured from the creek bed, it was the largest concrete structure in the world when completed in 1915 and still merited "the title of largest concrete bridge in America, if not the world" 50 years later.

The Fitchburg Cutoff was a rail line running 2.8 miles (4.5 km) from Brighton Street in Belmont, Massachusetts, to Somerville Junction in Somerville, Massachusetts. It was constructed in two segments in 1870 and 1881 to connect the Lexington Branch and Central Massachusetts Railroad to the Boston and Lowell Railroad. Passenger service lasted until 1927. Freight service ended in 1979–80 to allow construction of the Red Line Northwest Extension; the line was abandoned in three sections in 1979, 1983, and 2007.

The Whitewater Canal, which was built between 1836 and 1847, spanned a distance of 76 miles (122 km) and stretched from Lawrenceburg, Indiana on the Ohio River to Hagerstown, Indiana near the West Fork of the White River.

The Kinzua Bridge or the Kinzua Viaduct was a railroad trestle that spanned Kinzua Creek in McKean County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The bridge was 301 feet (92 m) tall and 2,052 feet (625 m) long. Most of its structure collapsed during a tornado in July 2003.

Fresh Pond Parkway is a historic park and parkway on the western end of Cambridge, Massachusetts, part of the Metropolitan Park System of Greater Boston. The parkway was built in 1899 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2005.

The Blackstone Viaduct, or the New York & New England Railroad Viaduct is a historic viaduct in Blackstone, Massachusetts. The viaduct was built in 1872 by the Boston, Hartford and Erie Railroad and the American Bridge Company. The viaduct is 1,600 feet (490 m) long structure, consisting of masonry arches and earthen embankments in the Massachusetts portion of the village of Waterford. It runs from the Blackstone River in the east to a still-watered section of the defunct Blackstone Canal to the west. The most prominent portion of the structure is an 800-foot earthen embankment running west from the river that is 25 feet (7.6 m) high, and then a 375-foot (114 m) multiple-arch masonry bridge constructed out of granite which was sheathed in concrete in 1918. The structure was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2002.
The Lyman Viaduct is a buried railroad trestle built over Dickinson Creek in Colchester, Connecticut in 1873. Along with the nearby Rapallo Viaduct, it is one of the few surviving wrought iron railroad trestles from the first generation of such structures. It was built for the Boston and New York Air-Line Railroad, whose successor, the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (NYNH&H), buried it in sand rather than replacing it with a stronger structure. The viaduct was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1986, since it is capable of providing detailed information about construction methods of the period. The viaduct now carries the multiuse Air Line State Park Trail.

The Rapallo Viaduct is a buried railroad trestle in East Hampton, Connecticut which carries the Air Line Trail across Flat Brook.

Young's High Bridge, also known as the Jo Blackburn Bridge, is a former railroad bridge near Tyrone, Kentucky, USA, that spans the Kentucky River between Anderson County, Kentucky and Woodford County, Kentucky for the Louisville Southern Railroad. The cantilever bridge, named in honor of William Bennett Henderson Young, was constructed in 1889, and the first train crossed over on August 24, 1889. The bridge is 1,659 feet in length, is 283 feet above the river, and includes a 551 foot long cantilever span.

The Louisville Southern Railroad was a 19th-century railway company in the U.S. state of Kentucky. It operated from 1884 until 1894, when it was incorporated into the Southern Railway in Kentucky.

The Long Key Bridge, officially known as the Dante B. Fascell Bridge, is a bridge in the Florida Keys connecting Long Key and Conch Key, roughly halfway between Miami and Key West. At a length of nearly two and a half miles, it is the second longest bridge on the Overseas Highway after the Seven Mile Bridge. The current bridge opened in 1982, replacing the parallel Long Key Viaduct, which carried the Overseas Railroad from 1907 to 1935 and was repurposed for highway use shortly after.

The Simpsonville Stone Arch Bridge is a historic stone arch bridge, carrying Vermont Route 35 across Simpson Brook, north of the village of Townshend, Vermont. Built about 1909, it is one of a few surviving bridges in the region built by local mason James Otis Follett. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977.


















