
A cantilever bridge is a bridge built using structures that project horizontally into space, supported on only one end. For small footbridges, the cantilevers may be simple beams; however, large cantilever bridges designed to handle road or rail traffic use trusses built from structural steel, or box girders built from prestressed concrete.

A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements, typically straight, may be stressed from tension, compression, or sometimes both in response to dynamic loads. There are several types of truss bridges, including some with simple designs that were among the first bridges designed in the 19th and early 20th centuries. A truss bridge is economical to construct primarily because it uses materials efficiently.

The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond to the Ohio River by 1873, where the railroad town of Huntington, West Virginia, was named for him.

Gustav Lindenthal was a civil engineer who designed the Queensboro and Hell Gate bridges in New York City, among other bridges. Lindenthal's work was greatly affected by his pursuit for perfection and his love of art. Having received little formal education and no degree in civil engineering, Lindenthal based his work on his prior experience and techniques used by other engineers of the time.

The High Bridge is a railroad bridge crossing the Kentucky River Palisades, that rises approximately 275 feet from the river below and connects Jessamine and Mercer counties in Kentucky. Formally dedicated in 1879, it is the first cantilever bridge constructed in the United States. It has a three-span continuous under-deck truss used by Norfolk Southern Railway to carry trains between Lexington and Danville. It has been designated as a National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark.

The C&O Railroad bridge is a cantilever truss bridge carrying the CSX Transportation Cincinnati Terminal Subdivision over the Ohio River. It was the first railroad bridge connecting Cincinnati, Ohio, and Covington, Kentucky.

The Cincinnati Southern Bridge, originally the Cincinnati Southern Railroad Swinging Truss Bridge, is a vertical lift bridge that carries the Norfolk Southern Railway's Cincinnati, New Orleans and Texas Pacific Railway over the Ohio River between Cincinnati, Ohio, and Ludlow, Kentucky in the United States.
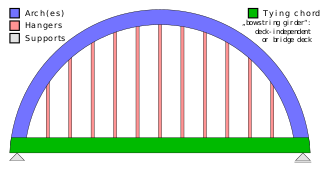
A tied-arch bridge is an arch bridge in which the outward horizontal forces of the arch(es) caused by tension at the arch ends to a foundation are countered by equal tension of its own gravity plus any element of the total deck structure such great arch(es) support. The arch(es) have strengthened chord(s) that run to a strong part of the deck structure or to independent tie-rods below the arch ends.

The West End Bridge is a steel tied-arch bridge over the Ohio River in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) below the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela Rivers. It connects the West End to the Chateau neighborhood on the North Side of Pittsburgh.

The Cape Girardeau Bridge was a continuous through truss bridge connecting Missouri's Route 34 with Illinois Route 146 across the Mississippi River between Cape Girardeau, Missouri, and East Cape Girardeau, Illinois. It was replaced in 2003 with the Bill Emerson Memorial Bridge.

A continuous truss bridge is a truss bridge that extends without hinges or joints across three or more supports. A continuous truss bridge may use less material than a series of simple trusses because a continuous truss distributes live loads across all the spans; in a series of simple trusses, each truss must be capable of supporting the entire load.

Matthew E. Welsh Bridge is a two-lane, single-pier cantilever bridge on the Ohio River. The bridge connects Kentucky Route 313 and Indiana State Road 135, as well as the communities of Brandenburg, Kentucky and Mauckport, Indiana.

The Fourteenth Street Bridge, also known as the Ohio Falls Bridge, Pennsylvania Railroad Bridge, Conrail Railroad Bridge or Louisville and Indiana (L&I) Bridge, is a truss drawbridge that spans the Ohio River, between Louisville, Kentucky and Clarksville, Indiana.

The Hawkesbury River railway bridge is a heritage-listed railway bridge in New South Wales, Australia that carries the Main North railway line across the Hawkesbury River. The bridge crosses between Brooklyn on the northern outskirts of Sydney and Cogra Bay in the Central Coast region. The railway bridge was to be the last link in a railway network that linked the state capitals Adelaide, Melbourne, Sydney and Brisbane and was a major engineering feat at the time. The original railway bridge was built in 1889 and replaced by the current bridge in 1946. The 1946 bridge was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.

The bridges and tunnels across the Yangtze River carry rail and road traffic across China's longest and largest river and form a vital part of the country's transportation infrastructure. The river bisects China proper from west to east, and every major north–south bound highway and railway must cross the Yangtze. Large urban centers along the river such as Chongqing, Wuhan, and Nanjing also have urban mass transit rail lines crossing the Yangtze.

Sadliers Crossing Railway Bridge is a heritage-listed railway bridge at over Bremer River between Tallon Street, Sadliers Crossing and Dixon Street, Wulkuraka, Queensland, Australia on the Main Line (this section is now the Ipswich and Rosewood railway line. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 13 November 2008.
The Fink truss is a commonly used truss in residential homes and bridge architecture. It originated as a bridge truss although its current use in bridges is rare.


















