An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. They convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current (AC) signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices ranging from the simplest clock generators to digital instruments and complex computers and peripherals etc. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by radio and television transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and the sounds produced by electronic beepers and video games.
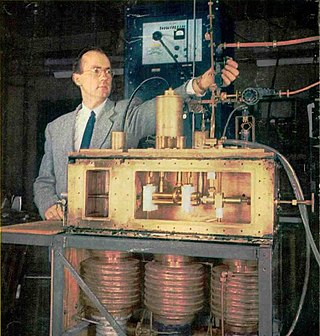
A maser is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves, through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, James P. Gordon, and Herbert J. Zeiger at Columbia University in 1953. Townes, Nikolay Basov and Alexander Prokhorov were awarded the 1964 Nobel Prize in Physics for theoretical work leading to the maser. Masers are also used as the timekeeping device in atomic clocks, and as extremely low-noise microwave amplifiers in radio telescopes and deep-space spacecraft communication ground stations.

The second is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as 1⁄86400 of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each.

A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses a piezoelectric crystal as a frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep track of time, as in quartz wristwatches, to provide a stable clock signal for digital integrated circuits, and to stabilize frequencies for radio transmitters and receivers. The most common type of piezoelectric resonator used is a quartz crystal, so oscillator circuits incorporating them became known as crystal oscillators. However, other piezoelectricity materials including polycrystalline ceramics are used in similar circuits.

A rubidium standard or rubidium atomic clock is a frequency standard in which a specified hyperfine transition of electrons in rubidium-87 atoms is used to control the output frequency.

A radio clock or radio-controlled clock (RCC), and often (incorrectly) referred to as an atomic clock is a type of quartz clock or watch that is automatically synchronized to a time code transmitted by a radio transmitter connected to a time standard such as an atomic clock. Such a clock may be synchronized to the time sent by a single transmitter, such as many national or regional time transmitters, or may use the multiple transmitters used by satellite navigation systems such as Global Positioning System. Such systems may be used to automatically set clocks or for any purpose where accurate time is needed. RC clocks may include any feature available for a clock, such as alarm function, display of ambient temperature and humidity, broadcast radio reception, etc.

In radio, longwave, long wave or long-wave, and commonly abbreviated LW, refers to parts of the radio spectrum with wavelengths longer than what was originally called the medium-wave broadcasting band. The term is historic, dating from the early 20th century, when the radio spectrum was considered to consist of longwave (LW), medium-wave (MW), and short-wave (SW) radio bands. Most modern radio systems and devices use wavelengths which would then have been considered 'ultra-short'.
CHU is the call sign of a shortwave time signal radio station operated by the Institute for National Measurement Standards of the National Research Council. CHU's signal is used for continuous dissemination of official Canadian government time signals, derived from atomic clocks.

DCF77 is a German longwave time signal and standard-frequency radio station. It started service as a standard-frequency station on 1 January 1959. In June 1973 date and time information was added. Its primary and backup transmitter are located at 50°0′56″N9°00′39″E in Mainflingen, about 25 km south-east of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. The transmitter generates a nominal power of 50 kW, of which about 30 to 35 kW can be radiated via a T-antenna.
A variable frequency oscillator (VFO) in electronics is an oscillator whose frequency can be tuned over some range. It is a necessary component in any tunable radio transmitter and in receivers that works by the superheterodyne principle. The oscillator controls the frequency to which the apparatus is tuned.
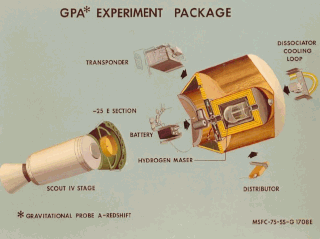
Gravity Probe A (GP-A) was a space-based experiment to test the equivalence principle, a feature of Einstein's theory of relativity. It was performed jointly by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. The experiment sent a hydrogen maser—a highly accurate frequency standard—into space to measure with high precision the rate at which time passes in a weaker gravitational field. Masses cause distortions in spacetime, which leads to the effects of length contraction and time dilation, both predicted results of Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. Because of the bending of spacetime, an observer on Earth should measure a slower rate at which time passes than an observer that is higher in altitude. This effect is known as gravitational time dilation.

A crystal oven is a temperature-controlled chamber used to maintain the quartz crystal in electronic crystal oscillators at a constant temperature, in order to prevent changes in the frequency due to variations in ambient temperature. An oscillator of this type is known as an oven-controlled crystal oscillator This type of oscillator achieves the highest frequency stability possible with a crystal. They are typically used to control the frequency of radio transmitters, cellular base stations, military communications equipment, and for precision frequency measurement.

A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) is a compact, low-power atomic clock fabricated using techniques of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and incorporating a low-power semiconductor laser as the light source. The first CSAC physics package was demonstrated at NIST in 2003, based on an invention made in 2001. The work was funded by the US Department of Defense's Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) with the goal of developing a microchip-sized atomic clock for use in portable equipment. In military equipment it is expected to provide improved location and battlespace situational awareness for dismounted soldiers when the global positioning system is not available, but many civilian applications are also envisioned. Commercial manufacturing of these atomic clocks began in 2011. The CSAC, the world's smallest atomic clock, is 4 x 3.5 x 1 cm in size, weighs 35 grams, consumes only 115 mW of power, and can keep time to within 100 microseconds per day after several years of operation. A more stable design based on the vibration of rubidium atoms was demonstrated by NIST in 2019. The new design has yet to be commercialized.
Atomic Clock Ensemble in Space (ACES) is a project led by the European Space Agency which will place ultra-stable atomic clocks on the International Space Station. Operation in the microgravity environment of the ISS will provide a stable and accurate time base for different areas of research, including general relativity and string theory tests, time and frequency metrology, and very long baseline interferometry.

Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 3,000 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.
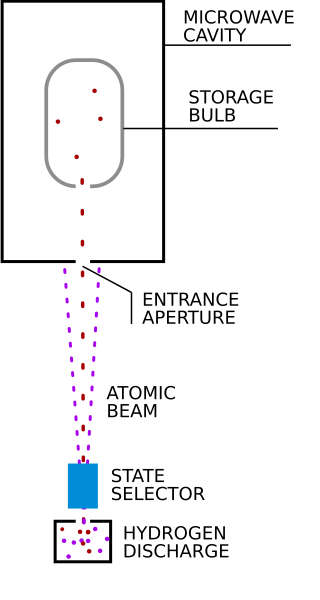
A hydrogen maser, also known as hydrogen frequency standard, is a specific type of maser that uses the intrinsic properties of the hydrogen atom to serve as a precision frequency reference.

In physics, time is defined by its measurement: time is what a clock reads. In classical, non-relativistic physics, it is a scalar quantity and, like length, mass, and charge, is usually described as a fundamental quantity. Time can be combined mathematically with other physical quantities to derive other concepts such as motion, kinetic energy and time-dependent fields. Timekeeping is a complex of technological and scientific issues, and part of the foundation of recordkeeping.
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes some unwanted components or features from a signal. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal. Most often, this means removing some frequencies or frequency bands. However, filters do not exclusively act in the frequency domain; especially in the field of image processing many other targets for filtering exist. Correlations can be removed for certain frequency components and not for others without having to act in the frequency domain. Filters are widely used in electronics and telecommunication, in radio, television, audio recording, radar, control systems, music synthesis, image processing, computer graphics, and structural dynamics.

An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions between such states they interact with a very specific frequency of electromagnetic radiation. This phenomenon serves as the basis for the International System of Units' (SI) definition of a second:
The second, symbol s, is the SI unit of time. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, , the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be 9192631770 when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1.

A GPS clock, or GPS disciplined oscillator (GPSDO), is a combination of a GPS receiver and a high-quality, stable oscillator such as a quartz or rubidium oscillator whose output is controlled to agree with the signals broadcast by GPS or other GNSS satellites. GPSDOs work well as a source of timing because the satellite time signals must be accurate in order to provide positional accuracy for GPS in navigation. These signals are accurate to nanoseconds and provide a good reference for timing applications.















