
The Bromeliaceae are a family of monocot flowering plants of about 80 genera and 3700 known species, native mainly to the tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, Pitcairnia feliciana.

Gonatodes is a genus of New World dwarf geckos of the family Sphaerodactylidae.

Albizia is a genus of more than 160 species of mostly fast-growing subtropical and tropical trees and shrubs in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the family Fabaceae. The genus is pantropical, occurring in Asia, Africa, Madagascar, America and Australia, but mostly in the Old World tropics. In some locations, some species are considered weeds.

Xanthosoma is a genus of flowering plants in the arum family, Araceae. The genus is native to tropical America but widely cultivated and naturalized in other tropical regions. Several are grown for their starchy corms, an important food staple of tropical regions, known variously as malanga, otoy, otoe, cocoyam, tannia, tannier, yautía, macabo, ocumo, macal, taioba, dasheen, quequisque, ʻape and as Singapore taro. Many other species, including especially Xanthosoma roseum, are used as ornamental plants; in popular horticultural literature these species may be known as ‘ape due to resemblance to the true Polynesian ʻape, Alocasia macrorrhizos, or as elephant ear from visual resemblance of the leaf to an elephant's ear. Sometimes the latter name is also applied to members in the closely related genera Caladium, Colocasia (taro), and Alocasia.

Hevea is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, with about ten members. It is also one of many names used commercially for the wood of the most economically important rubber tree, H. brasiliensis. The genus is native to tropical South America but is widely cultivated in other tropical countries and naturalized in several of them. It was first described in 1775.

Ochnaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Malpighiales. In the APG III system of classification of flowering plants, Ochnaceae is defined broadly, to include about 550 species, and encompasses what some taxonomists have treated as the separate families Medusagynaceae and Quiinaceae. In a phylogenetic study that was published in 2014, Ochnaceae was recognized in the broad sense, but two works published after APG III have accepted the small families Medusagynaceae and Quiinaceae. These have not been accepted by APG IV (2016).

Caladium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. They are often known by the common name elephant ear, heart of Jesus, and angel wings. There are over 1000 named cultivars of Caladium bicolor from the original South American plant.

Pouteria is a genus of flowering trees in the gutta-percha family, Sapotaceae. The genus is widespread throughout the tropical Americas, with outlier species in Cameroon and Malesia. It includes the canistel, the mamey sapote, and the lucuma. Commonly, this genus is known as pouteria trees, or in some cases, eggfruits.

Caryocar is a genus of flowering plants, in the South American family Caryocaraceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1771. It is native primarily to South America with a few species extending into Central America and the West Indies.

Calycolpus is a genus of the botanical family Myrtaceae, first described as a genus in 1856. It is native to the South America, Central America, and the West Indies.
Corythophora is a genus of woody plant in the Lecythidaceae family first described as a genus in 1939. It is native to northeastern South America.
- Corythophora altaR.Knuth - Pará, Amazonas
- Corythophora amapaensisPires ex S.A.Mori & Prance - French Guiana, Amapá
- Corythophora labriculata(Eyma) S.A.Mori & Prance - Suriname
- Corythophora rimosaW.A.Rodrigues - French Guiana, Amazonas, Amapá, Suriname

Couratari guianensis, the fine-leaf wadara, cachimbo caspi, cachimbo, capa de tabaco, coco cabuyo, or tauari, is a species of woody plant in the family Lecythidaceae. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Lecythis is a genus of woody plant in the Lecythidaceae family first described as a genus in 1758. It is native to Central America and South America. Several species produce edible seeds and referred to by a variety of common names including paradise nut, monkey pot, cream nut, and sapucaia nut.

Gustavia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lecythidaceae described by Linnaeus in 1775. It is native to tropical Central America and South America. Many of the species are threatened; some are critically endangered Gustavia superba, though, is actually abundant in re-growing secondary forests. It grows in northern South America, from Panama south through the Andes as far as Ecuador, and along the Caribbean coast and in the Amazon basin. Gustavia flowers have numerous stamens, in some species as many as 1,200 in a single flower.

Monotagma is a genus of plant in family Marantaceae described as a genus in 1902. It is native to tropical America.

Pradosia is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1872.
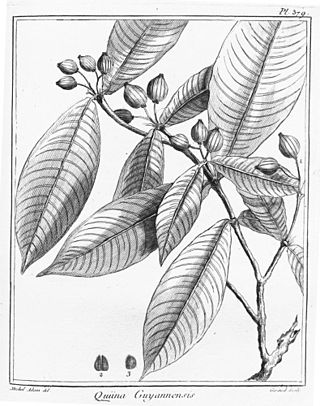
Quiina is a genus of plant in family Ochnaceae. It contains the following species :

Rhodospatha is a genus of plant in family Araceae. It is native to South America, Central America, and southern Mexico.

Stenospermation is a genus of plant in family Araceae native to South America and Central America.
Froesia gereauana is a plant species endemic to the State of Amazonas in southern Venezuela.

















