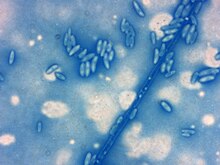
Fusarium oxysporum, an ascomycete fungus, comprises all the species, varieties and forms recognized by Wollenweber and Reinking within an infrageneric grouping called section Elegans. It is part of the family Nectriaceae.

Fusarium wilt is a common vascular wilt fungal disease, exhibiting symptoms similar to Verticillium wilt. This disease has been investigated extensively since the early years of this century. The pathogen that causes Fusarium wilt is Fusarium oxysporum. The species is further divided into formae speciales based on host plant.

Panama disease is a plant disease that infects banana plants. It is a wilting disease caused by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc). The pathogen is resistant to fungicides and its control is limited to phytosanitary measures.

Fusarium is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health if they enter the food chain. The main toxins produced by these Fusarium species are fumonisins and trichothecenes. Despite most species apparently being harmless, some Fusarium species and subspecific groups are among the most important fungal pathogens of plants and animals.

Gibberella zeae, also known by the name of its anamorph Fusarium graminearum, is a fungal plant pathogen which causes fusarium head blight (FHB), a devastating disease on wheat and barley. The pathogen is responsible for billions of dollars in economic losses worldwide each year. Infection causes shifts in the amino acid composition of wheat, resulting in shriveled kernels and contaminating the remaining grain with mycotoxins, mainly deoxynivalenol (DON), which inhibits protein biosynthesis; and zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin. These toxins cause vomiting, liver damage, and reproductive defects in livestock, and are harmful to humans through contaminated food. Despite great efforts to find resistance genes against F. graminearum, no completely resistant variety is currently available. Research on the biology of F. graminearum is directed towards gaining insight into more details about the infection process and reveal weak spots in the life cycle of this pathogen to develop fungicides that can protect wheat from scab infection.
Ceratocystis paradoxa or Black Rot of Pineapple is a plant pathogen that is a fungus, part of the phylum Ascomycota. It is characterized as the teleomorph or sexual reproduction stage of infection. This stage contains ascocarps, or sacs/fruiting bodies, which contain the sexually produced inoculating ascospores. These are the structures which are used primarily to survive long periods of time or overwinter to prepare for the next growing season of its host. Unfortunately, the sexual stage is not often seen in the natural field but instead the anamorph, or asexual stage is more commonly seen. This asexual stage name is Thielaviopsis paradoxa and is the common cause of Black rot or stem-end rot of its hosts.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. asparagi is a fungal plant pathogen infecting asparagus.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. betae is a destructive fungal plant pathogen. It causes Fusarium yellows or fusarium wilt, characterized by yellowing and dwarfing.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. carthami is a fungal plant pathogen.

Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. ciceris is a fungal plant pathogen that causes fusarium wilt of chickpea.
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. spinacia is a fungal plant pathogen. It is a forma specialis of F. o. on spinach.
Fusarium redolens is a species of fungus in the genus Fusarium and family Nectriaceae. This species is a soil-borne plant pathogen in temperate prairies. It causes diseases such as root, crown, and spear rot, seedling damping-off, and wilting disease. It is a known producer of the alkaloids peimisine and imperialine-3β-d-glucoside, which has implications for traditional Chinese medicine.

Fusarium subglutinans is a fungal plant pathogen.

Fusarium solani is a species complex of at least 26 closely related filamentous fungi in the division Ascomycota, family Nectriaceae. It is the anamorph of Nectria haematococca. It is a common soil fungus and colonist of plant materials. Fusarium solani is implicated in plant disease as well as human disease notably infection of the cornea of the eye.

Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense is a fungal plant pathogen that causes Panama disease of banana, also known as fusarium wilt of banana. The fungi and the related disease are responsible for widespread pressure on banana growing regions, destroying the economic viability of several commercially important banana varieties.

Marine fungi are species of fungi that live in marine or estuarine environments. They are not a taxonomic group, but share a common habitat. Obligate marine fungi grow exclusively in the marine habitat while wholly or sporadically submerged in sea water. Facultative marine fungi normally occupy terrestrial or freshwater habitats, but are capable of living or even sporulating in a marine habitat. About 444 species of marine fungi have been described, including seven genera and ten species of basidiomycetes, and 177 genera and 360 species of ascomycetes. The remainder of the marine fungi are chytrids and mitosporic or asexual fungi. Many species of marine fungi are known only from spores and it is likely a large number of species have yet to be discovered. In fact, it is thought that less than 1% of all marine fungal species have been described, due to difficulty in targeting marine fungal DNA and difficulties that arise in attempting to grow cultures of marine fungi. It is impracticable to culture many of these fungi, but their nature can be investigated by examining seawater samples and undertaking rDNA analysis of the fungal material found.
Bayoud disease is an epiphytic fungal disease of date palm. The pathogen responsible for the disease is Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. albedinis.
Harold Corby Kistler is an American Adjunct Professor of biology and plant pathology at the University of Minnesota and a fellow of the American Phytopathological Society and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Hemibiotrophs are the spectrum of plant pathogens, including bacteria, oomycete and a group of plant pathogenic fungi that keep its host alive while establishing itself within the host tissue, taking up the nutrients with brief biotrophic-like phase. It then, in later stages of infection switches to a necrotrophic life-style, where it rampantly kills the host cells, deriving its nutrients from the dead tissues.
John Colhoun was a British mycologist, phytopathologist, and professor of cryptogamic botany. For a one-year term from 1963 to 1964 he was the president of the British Mycological Society.