
The globins are a superfamily of heme-containing globular proteins, involved in binding and/or transporting oxygen. These proteins all incorporate the globin fold, a series of eight alpha helical segments. Two prominent members include myoglobin and hemoglobin. Both of these proteins reversibly bind oxygen via a heme prosthetic group. They are widely distributed in many organisms.

α2-Macroglobulin (α2M), or alpha-2-macroglobulin, is a large plasma protein found in the blood. It is mainly produced by the liver, and also locally synthesized by macrophages, fibroblasts, and adrenocortical cells. In humans it is encoded by the A2M gene.
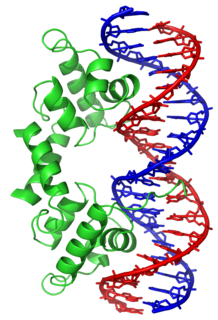
In proteins, the helix-turn-helix (HTH) is a major structural motif capable of binding DNA. Each monomer incorporates two α helices, joined by a short strand of amino acids, that bind to the major groove of DNA. The HTH motif occurs in many proteins that regulate gene expression. It should not be confused with the helix–loop–helix motif.

A basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) is a protein structural motif that characterizes one of the largest families of dimerizing transcription factors. The word "basic" does not refer to complexity but to the chemistry of the motif because transcription factors in general contain basic amino acid residues in order to facilitate DNA binding.
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure.

Human serum albumin is the serum albumin found in human blood. It is the most abundant protein in human blood plasma; it constitutes about half of serum protein. It is produced in the liver. It is soluble in water, and it is monomeric.

Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called albuminoids.
A helix bundle is a small protein fold composed of several alpha helices that are usually nearly parallel or antiparallel to each other.

The EF hand is a helix–loop–helix structural domain or motif found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins.
Protein G is an immunoglobulin-binding protein expressed in group C and G Streptococcal bacteria much like Protein A but with differing binding specificities. It is a ~60-kDA cell surface protein that has found application in purifying antibodies through its binding to the Fab and Fc region. The native molecule also binds albumin, but because serum albumin is a major contaminant of antibody sources, the albumin binding site has been removed from recombinant forms of Protein G. This recombinant Protein G, either labeled with a fluorophore or a single-stranded DNA strand, was used as a replacement for secondary antibodies in immunofluorescence and super-resolution imaging.
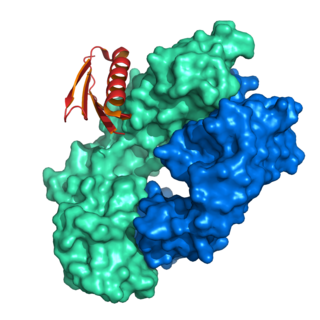
Protein L was first isolated from the surface of bacterial species Peptostreptococcus magnus and was found to bind immunoglobulins through L chain interaction, from which the name was suggested. It consists of 719 amino acid residues. The molecular weight of Protein L purified from the cell walls of Peptostreptoccus magnus was first estimated as 95kD by SDS-PAGE in the presence of reducing agent 2-mercaptoethanol, while the molecular weight was determined to 76kD by gel chromotography in the presence of 6 M guanidine HCl. Protein L does not contain any interchain disulfide loops, nor does it consist of disulfide-linked subunits. It is an acidic molecule with a pI of 4.0. Unlike Protein A and Protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins (antibodies), Protein L binds antibodies through light chain interactions. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than Protein A or G. Protein L binds to representatives of all antibody classes, including IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. Single chain variable fragments (scFv) and Fab fragments also bind to Protein L.

The EGF-like domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain, which derives its name from the epidermal growth factor where it was first described. It comprises about 30 to 40 amino-acid residues and has been found in a large number of mostly animal proteins. Most occurrences of the EGF-like domain are found in the extracellular domain of membrane-bound proteins or in proteins known to be secreted. An exception to this is the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase. The EGF-like domain includes 6 cysteine residues which in the epidermal growth factor have been shown to form 3 disulfide bonds. The structures of 4-disulfide EGF-domains have been solved from the laminin and integrin proteins. The main structure of EGF-like domains is a two-stranded β-sheet followed by a loop to a short C-terminal, two-stranded β-sheet. These two β-sheets are usually denoted as the major (N-terminal) and minor (C-terminal) sheets. EGF-like domains frequently occur in numerous tandem copies in proteins: these repeats typically fold together to form a single, linear solenoid domain block as a functional unit.

DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ID3 gene.

Afamin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFM gene.
Affibody molecules are small, robust proteins engineered to bind to a large number of target proteins or peptides with high affinity, imitating monoclonal antibodies, and are therefore a member of the family of antibody mimetics. Affibody molecules are used in biochemical research and are being developed as potential new biopharmaceutical drugs. These molecules can be used for molecular recognition in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.

In molecular biology, the protein domain Sterile alpha motif is a putative protein interaction module present in a wide variety of proteins involved in many biological processes. The SAM domain that spreads over around 70 residues is found in diverse eukaryotic organisms. SAM domains have been shown to homo- and hetero-oligomerise, forming multiple self-association architectures and also binding to various non-SAM domain-containing proteins, nevertheless with a low affinity constant.
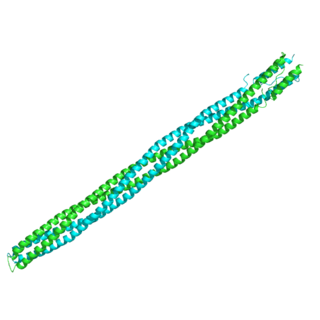
The Methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins are a family of transmembrane receptors that mediate chemotactic response in certain enteric bacteria, such as Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. These methyl-accepting chemotaxis receptors are one of the first components in the sensory excitation and adaptation responses in bacteria, which act to alter swimming behaviour upon detection of specific chemicals. Use of the MCP allows bacteria to detect concentrations of molecules in the extracellular matrix so that the bacteria may smooth swim or tumble accordingly. If the bacterium detects rising levels of attractants (nutrients) or declining levels of repellents (toxins), the bacterium will continue swimming forward, or smooth swimming. If the bacterium detects declining levels of attractants or rising levels of repellents, the bacterium will tumble and re-orient itself in a new direction. In this manner, a bacterium may swim towards nutrients and away from toxins

In molecular biology, a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) is a protein domain found in carbohydrate-active enzymes. The majority of these domains have carbohydrate-binding activity. Some of these domains are found on cellulosomal scaffoldin proteins. CBMs were previously known as cellulose-binding domains. CBMs are classified into numerous families, based on amino acid sequence similarity. There are currently 64 families of CBM in the CAZy database.

In molecular biology, the GntR-like bacterial transcription factors are a family of transcription factors.

In molecular biology, the H2TH domain is a DNA-binding domain found in DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes, which are involved in base excision repair of DNA damaged by oxidation or by mutagenic agents. Most damage to bases in DNA is repaired by the base excision repair pathway. These enzymes are primarily from bacteria, and have both DNA glycosylase activity EC 3.2.2.- and AP lyase activity EC 4.2.99.18. Examples include formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylases and endonuclease VIII (Nei).
















