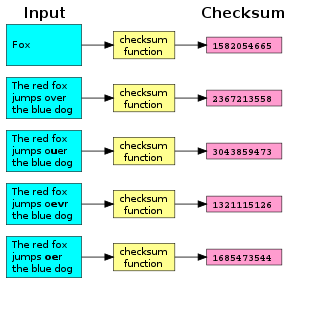
A checksum is a small-sized block of data derived from another block of digital data for the purpose of detecting errors that may have been introduced during its transmission or storage. By themselves, checksums are often used to verify data integrity but are not relied upon to verify data authenticity.
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is a standard that extends the format of email messages to support text in character sets other than ASCII, as well as attachments of audio, video, images, and application programs. Message bodies may consist of multiple parts, and header information may be specified in non-ASCII character sets. Email messages with MIME formatting are typically transmitted with standard protocols, such as the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), the Post Office Protocol (POP), and the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP).
A whitelist or allowlist is a list or register of entities that are being provided a particular privilege, service, mobility, access or recognition. Entities on the list will be accepted, approved and/or recognized. Whitelisting is the reverse of blacklisting, the practice of identifying entities that are denied, unrecognised, or ostracised.

Apache SpamAssassin is a computer program used for e-mail spam filtering. It uses a variety of spam-detection techniques, including DNS and fuzzy checksum techniques, Bayesian filtering, external programs, blacklists and online databases. It is released under the Apache License 2.0 and is a part of the Apache Foundation since 2004.
An email address identifies an email box to which messages are delivered. While early messaging systems used a variety of formats for addressing, today, email addresses follow a set of specific rules originally standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in the 1980s, and updated by RFC 5322 and 6854. The term email address in this article refers to just the addr-spec in Section 3.4 of RFC 5322. The RFC defines address more broadly as either a mailbox or group. A mailbox value can be either a name-addr, which contains a display-name and addr-spec, or the more common addr-spec alone.
Various anti-spam techniques are used to prevent email spam.

The Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography And Marketing (CAN-SPAM) Act of 2003 is a law passed in 2003 establishing the United States' first national standards for the sending of commercial e-mail. The law requires the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to enforce its provisions. Introduced by Republican Conrad Burns, the act passed both the House and Senate during the 108th United States Congress and was signed into law by President George W. Bush in December 2003 and was enacted on January 1, 2004.

Email spam, also referred to as junk email, spam mail, or simply spam, is unsolicited messages sent in bulk by email (spamming). The name comes from a Monty Python sketch in which the name of the canned pork product Spam is ubiquitous, unavoidable, and repetitive. Email spam has steadily grown since the early 1990s, and by 2014 was estimated to account for around 90% of total email traffic.
Naive Bayes classifiers are a popular statistical technique of e-mail filtering. They typically use bag-of-words features to identify email spam, an approach commonly used in text classification.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication method which ensures the sending mail server is authorized to originate mail from the email sender's domain. This authentication only applies to the email sender listed in the "envelope from" field during the initial SMTP connection. If the email is bounced, a message is sent to this address, and for downstream transmission it typically appears in the "Return-Path" header. To authenticate the email address which is actually visible to recipients on the "From:" line, other technologies such as DMARC must be used. Forgery of this address is known as email spoofing, and is often used in phishing and email spam.
Hashcash is a proof-of-work system used to limit email spam and denial-of-service attacks. Hashcash was proposed in 1997 by Adam Back and described more formally in Back's 2002 paper "Hashcash - A Denial of Service Counter-Measure". In Hashcash the client has to concatenate a random number with a string several times and hash this new string. It then has to do so over and over until a hash beginning with a certain number of zeros is found.
The EICAR Anti-Virus Test File or EICAR test file is a computer file that was developed by the European Institute for Computer Antivirus Research (EICAR) and Computer Antivirus Research Organization (CARO) to test the response of computer antivirus (AV) programs. Instead of using real malware, which could cause real damage, this test file allows people to test anti-virus software without having to use a real computer virus.
Email marketing is the act of sending a commercial message, typically to a group of people, using email. In its broadest sense, every email sent to a potential or current customer could be considered email marketing. It involves using email to send advertisements, request business, or solicit sales or donations. Email marketing strategies commonly seek to achieve one or more of three primary objectives: build loyalty, trust, or brand awareness. The term usually refers to sending email messages with the purpose of enhancing a merchant's relationship with current or previous customers, encouraging customer loyalty and repeat business, acquiring new customers or convincing current customers to purchase something immediately, and sharing third-party ads.
Email harvesting or scraping is the process of obtaining lists of email addresses using various methods. Typically these are then used for bulk email or spam.
A challenge–response system is a type of that automatically sends a reply with a challenge to the (alleged) sender of an incoming e-mail. It was originally designed in 1997 by Stan Weatherby, and was called Email Verification. In this reply, the purported sender is asked to perform some action to assure delivery of the original message, which would otherwise not be delivered. The action to perform typically takes relatively little effort to do once, but great effort to perform in large numbers. This effectively filters out spammers. Challenge–response systems only need to send challenges to unknown senders. Senders that have previously performed the challenging action, or who have previously been sent e-mail(s) to, would be automatically receive a challenge.
Nolisting is a technique to defend electronic mail domain names against e-mail spam.

Claws Mail is a free and open-source, C/GTK-based e-mail client, which is both lightweight and highly configurable. Claws Mail runs on both Windows and Unix-like systems such as Linux, BSD, and Solaris. It stores mail in the MH mailbox format. Plugins allow to read HTML mail, but there is none to compose HTML messages.

hMailServer was a free email server for Windows created by Martin Knafve. It ran as a Windows service and includes administration tools for management and backup. It had support for IMAP, POP3, and SMTP email protocols. It could use external database engines such as MySQL, MS SQL or PostgreSQL, or an internal MS SQL Compact Edition engine to store configuration and index data. The actual email messages were stored on disk in a raw MIME format. As of January 15th, 2022, active support and development were officially halted, although version 5.6 will continue to receive updates for critical bugs.
Srizbi BotNet is considered one of the world's largest botnets, and responsible for sending out more than half of all the spam being sent by all the major botnets combined. The botnets consist of computers infected by the Srizbi trojan, which sent spam on command. Srizbi suffered a massive setback in November 2008 when hosting provider Janka Cartel was taken down; global spam volumes reduced up to 93% as a result of this action.





