
Pope Boniface I was the bishop of Rome from 28 December 418 to his death on 4 September 422. His election was disputed by the supporters of Eulalius until the dispute was settled by Emperor Honorius. Boniface was active in maintaining church discipline, and he restored certain privileges to the metropolitical sees of Narbonne and Vienne, exempting them from any subjection to the primacy of Arles. He was a contemporary of Augustine of Hippo, who dedicated to him some of his works.
Pope Sixtus III was the bishop of Rome from 31 July 432 to his death on 18 August 440. His ascension to the papacy is associated with a period of increased construction in the city of Rome. His feast day is celebrated by the Roman Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodox Church on 28 March.

The Basilica of Saint Mary Major, or church of Santa Maria Maggiore, is one of the four major papal basilicas as well as one of the Seven Pilgrim Churches of Rome and the largest Marian church in Rome, Italy.
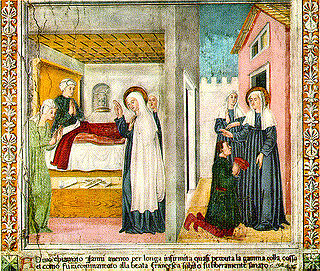
Francesca Bussa de' Leoni, known as Frances of Rome, was an Italian Catholic mystic, organizer of charitable services and a Benedictine oblate who founded a religious community of oblates, who share a common life without religious vows. She was canonized in 1608.

Pudens was an early Christian saint and martyr. He is mentioned as a layman of the Roman Church in 2 Timothy 4:21.

Andrea Corsini was an Italian Catholic prelate and professed member from the Carmelites who served as the Bishop of Fiesole from 1349 until his death.

The Clerics Regular of the Mother of God is a religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right. Its priests are dedicated to education and pastoral care. The Order was founded by St. John Leonardi, who worked with this congregation to spread devotion to the Blessed Virgin Mary, as well as the Forty Hours devotion, and frequent reception of the Blessed Sacrament.

Our Lady of Good Counsel is a title given to the Blessed Virgin Mary, after a painting said to be miraculous, now found in the thirteenth century Augustinian church at Genazzano, near Rome, Italy. Measuring 40 to 45 centimetres the image is a fresco executed on a thin layer of plaster no thicker than an egg shell. Over the centuries, devotions to Our Lady of the Good Counsel grew among saints and Popes, to the extent that a reference to it was added to the Litany of Loreto and the devotion spread throughout the world. Her feast day is 26 April.

Saint Praxedes, called "a Roman maiden", was a saint and virgin who lived in the Roman Empire during the 2nd century. Along with her sister, Saint Pudentiana, she provided for the poor and gave care and comfort to persecuted Christians and martyrs. Her veneration began in the 4th century and many churches have been dedicated to her.

Santa Maria in Campitelli or Santa Maria in Portico is a church dedicated to the Virgin Mary on the narrow Piazza di Campitelli in Rione Sant'Angelo, Rome, Italy. The church is served by the Clerics Regular of the Mother of God.

Mattia de Rossi was an Italian architect of the Baroque period, active mainly in Rome and surrounding towns.

The Pontifical French Seminary is a Roman College dedicated to training French-speaking Roman Catholic priests.

Papal appointment was a medieval method of selecting the Pope. Popes have always been selected by a council of Church fathers; however, Papal selection before 1059 was often characterized by confirmation or nomination by secular European rulers or by the preceding pope. The later procedures of the Papal conclave are in large part designed to prohibit interference of secular rulers, which to some extent characterized the first millennium of the Roman Catholic Church, e. g. in practices such as the creation of crown-cardinals and the claimed but invalid jus exclusivae. Appointment may have taken several forms, with a variety of roles for the laity and civic leaders, Byzantine and Germanic emperors, and noble Roman families. The role of the election vis-a-vis the general population and the clergy was prone to vary considerably, with a nomination carrying weight that ranged from nearly determinative to merely suggestive, or as ratification of a concluded election.

The Church of Our Lady of Mercy in the Teutonic Cemetery is a Roman Catholic church in the rione Borgo of Rome, Italy. It is located on the Via della Sagrestia.

The Church of Saint Lucy in Selci is an ancient Roman Catholic church, located in Rome, dedicated to Saint Lucy, a 4th-century virgin and martyr.

The Sisterhood of St. John the Baptist or Baptistines is a Roman Catholic religious institute dedicated to Saint John the Baptist. It was founded near Genoa in 1730 by Giovanna Solimani.

John Leonardi, OMD was an Italian Catholic priest and the founder of the Clerics Regular of the Mother of God of Lucca.

The Teutonic Cemetery is a burial site in Rome adjacent to St. Peter's Basilica. Burial is reserved for members of the Confraternity of Our Lady of the German Cemetery, which owns the cemetery. It is a place of pilgrimage for many German-speaking pilgrims.
Saint Gallicanus was a Roman martyr in Egypt in 363 AD, during the reign of Julian. A former general, he converted to Christianity and retired to Ostia where he was involved in a variety of charitable works. The Emperor exiled him to Egypt, where he was later martyred.

The church of Santa Galla was a church in Rome (Italy), in the Rione Ripa, on the road that connected Piazza Montanara with Piazza della Bocca della Verità. Both the church and the square in front of it were destroyed between 1928 and 1930 for the construction of the first stretch of Via del Mare ; the furnishings and the altar were relocated to the new church of Santa Galla at Garbatella, built in 1940.


















