
Cortaderia is a genus of plants in the Poaceae or grass family of plants.

Dactylis is a genus of Eurasian and North African plants in the bluegrass subfamily within the grass family. Dactylis is native to North Africa, they are found throughout the world, and are an invasive species. They are known in English as cock's-foot or cocksfoot grasses, also sometimes as orchard grasses.

Ammophila arenaria is a species of grass in the family Poaceae. It is known by the common names marram grass and European beachgrass. It is one of two species of the genus Ammophila. It is native to the coastlines of Europe and North Africa where it grows in the sands of beach dunes. It is a perennial grass forming stiff, hardy clumps of erect stems up to 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) in height. It grows from a network of thick rhizomes which give it a sturdy anchor in its sand substrate and allow it to spread upward as sand accumulates. These rhizomes can grow laterally by 2 metres in six months. One clump can produce 100 new shoots annually.
Agrostis trachychlaena is a species of grass in the family Poaceae. It is endemic to Inaccessible and Nightingale Islands, Tristan da Cunha. Its natural habitat is subantarctic grassland.

Cenchrus agrimonioides is a rare species of grass in the family Poaceae that is endemic to the Hawaiian Islands. Its common names include Kāmanomano and agrimony sandbur. It was formerly distributed throughout the major islands but today it is nearly limited to Oʻahu. Kāmanomano inhabits dry to moist forests and lava plains. It is threatened by competition with non-native plants, predation by ungulates, and wildfire. When this plant became a federally listed endangered species of the United States in 1996 there were fewer than 100 individuals remaining. More recent counts revealed 181 wild individuals on Oʻahu and over 300 more which have been planted to augment the populations. This plant is nearly restricted to the island of Oʻahu, but there are a few individuals known on Maui. A few patches of the grass have been planted on Kahoʻolawe, as well.
Setaria cernua is a species of grass in the family Poaceae. It is endemic to Ecuador, where it occurs in Imbabura, Carchi and Chimborazo Provinces. Some populations are protected in the Parque Nacional Llanganates, the Parque Nacional Sangay, and the Reserva Ecológica Cayambe-Coca. While its range is limited, it is common there.
The lilac-crowned fruit dove also known as the Rarotonga fruit-dove or Cook Islands fruit-dove is a species of bird in the family doves.

The Rarotonga monarch, also known as the Rarotonga flycatcher or Kākerōri, is a species of bird in the monarch flycatcher family Monarchidae. It is endemic to Rarotonga, Cook Islands, and has been introduced to Atiu, Cook Islands.

Chionochloa is a genus of tussock grass in the family Poaceae, found primarily in New Zealand with one known species in New Guinea and another on Lord Howe Island. Some of the species are referred to as snowgrass.
Lophopogon is a ditypic genus endemic to India, consisting of two well-known species Lophopogon tridentatus (Roxb.) Hackel and Lophopogon kingii Hook f. belonging to the tribe Andropogoneae in the grass family.

Streptochaeta is a genus of plants in the grass family. It is the only genus in the tribe Streptochaeteae of the family Poaceae.
Parahyparrhenia is a genus of Afro-Asian plants in the grass family. Globally, the genus comprises seven species. Two species are known to occur in India, where they are narrow endemic. The species show disjunct distribution in Africa and Asia. Parahyparrhenia bellariensis (Hack.) Clayton an extremely rare grass which was presumed extinct was rediscovered after the span of 184 years from its type locality in the state of Andhra Pradesh, South India by Mr. Shahid Nawaz, an agrostologist at the Blatter Herbarium. Following its rediscovery, it has been classified as Critically Endangered (CR) by following the guidelines of IUCN Criteria and Category.
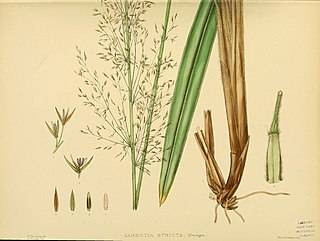
Garnotia is a genus of Asian, Australian, and tropical island plants in the grass family. Several of the species are native to Sri Lanka and southern India.

Homalium acuminatum, the Cook Islands homalium, is a species of tree in the willow family, Salicaceae. It is endemic to the Cook Islands, growing on the islands of Rarotonga, where it is known as mato, and Mangaia, where it is known as moto. It grows to a height of up to 20 m (66 ft). On Rarotonga it dominates steep mountain slopes. The IUCN Red List calls it the Rarotonga homalium and considers it endemic to Rarotonga, though the Cook Islands Biodiversity Database lists it as also present, but "uncommon" on Mangaia.

Myrsine cheesemanii, known as the Cook Islands myrsine or ka‘ika makatea, is a species of shrub within the family Myrsinaceae. It is endemic to the Cook Islands, growing on the islands of Rarotonga, Mangaia, Mauke and Mitiaro.

Pittosporum rarotongense is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Pittosporaceae. It is endemic to the Cook Islands, growing on the islands of Rarotonga, Mangaia, Mauke and Mitiaro. On Rarotonga, it grows inland in the island's temperate cloud forest habitat.

Aakia is a monotypic genus of grass in the family Poaceae. It is found in Central America and contains only the species Aakia tuerckheimii. It was described by J.R. Grande in Phytoneuron in 2014.
Psychotria whistleri, the Rarotonga psychotria, is a herbaceous plant, a member of the Rubiaceae family.

Coprosma laevigata, the Rarotongan coprosma, is a herbaceous plant, a member of the Rubiaceae family.

Vaccinium cereum is a species of flowering plant in the heath family, Ericaceae. It is a shrub native to the Cook Islands, Marquesas Islands, and Society Islands in the South Pacific.














