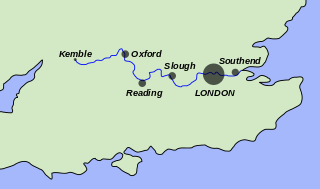
The River Thames, known alternatively in parts as the Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At 215 miles (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn.

The River Don is a river in South Yorkshire and the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It rises in the Pennines, west of Dunford Bridge, and flows for 70 miles (110 km) eastwards, through the Don Valley, via Penistone, Sheffield, Rotherham, Mexborough, Conisbrough, Doncaster and Stainforth. It originally joined the Trent, but was re-engineered by Cornelius Vermuyden as the Dutch River in the 1620s, and now joins the River Ouse at Goole. Don Valley is the local UK parliamentary constituency near the Doncaster stretch of the river.

Teddington Lock is a complex of three locks and a weir on the River Thames between Ham and Teddington in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, England. It was first built in 1810.

The Thames Path is a National Trail following the River Thames from its source near Kemble in Gloucestershire to the Thames Barrier at Charlton, south east London. It is about 184 miles (296 km) long. A path was first proposed in 1948 but it only opened in 1996.

The Tideway is the part of the River Thames in England that is subject to tides. This stretch of water is downstream from Teddington Lock and in its widest definition is just under 26 kilometres (16 mi) long. The Tideway includes the Thames Estuary, the Thames Gateway and the Pool of London.

Osney or Osney Island is a riverside community in the west of the city of Oxford, England. In modern times the name is applied to a community also known as Osney Town astride Botley Road, just west of the city's main railway station, on an island surrounded by the River Thames, Osney Ditch and another backwater connecting the Thames to Osney Ditch.

Iffley Lock is a lock on the River Thames in England near the village of Iffley, Oxfordshire. It is on the southern outskirts of Oxford. The original lock was built by the Oxford-Burcot Commission in 1631 and the Thames Navigation Commission replaced this in 1793. The lock has a set of rollers to allow punts and rowing boats to be moved between the water levels.

Clifton Lock is a lock on River Thames in Oxfordshire, England. It is located south of the village of Clifton Hampden and north of Long Wittenham. It is at the start of the Clifton Cut, which bypasses the river to the north of Long Wittenham. The lock was completed in 1822 by the Thames Navigation Commissioners.

Bell Weir Lock is a lock on the River Thames in England by the right bank, Runnymede which is a water meadow associated with Egham of importance for the constitutional Magna Carta. It is upstream of the terrace of a hotel and the a bridge designed by Edwin Lutyens who designed an ornamental park gate house along the reach. The bridge has been widened and carries the M25 and A30 road across the river in a single span. The lock was first built by the Thames Navigation Commission in 1817; it has one weir which is upstream. The lock is the eighth lowest of forty-five on the river and is named after the founder of the forerunner of the adjoining hotel who took charge of the lock and weir on its construction.

Old Windsor Lock is a lock on the River Thames in England on the right bank beside Old Windsor, Berkshire. The lock marks the downstream end of the New Cut, a meander cutoff built in 1822 by the Thames Navigation Commissioners which created Ham Island. The lock and a wider footbridge give access to the island. Two weirs are associated; the smaller adjoins and the larger is upstream. The lock is the ninth lowest of the forty-five on the river.

Cleeve Lock is a lock on the River Thames, in Oxfordshire, England. It is located just upstream of Streatley on the same side of the river. The village of Cleeve is on the opposite bank near Goring.

Culham Lock is a lock on the River Thames in England close to Culham, Oxfordshire. It is on a lock cut to the north of the main stream, which approaches the large village of Sutton Courtenay. The lock was built of stone by the Thames Navigation Commission in 1809.

Osney Lock is a lock on the River Thames in Oxford, England, where the village or island of Osney is next to the river.

Shifford Lock is a lock on the River Thames in England. It is in the centre of a triangle formed by the small villages of Shifford, Duxford and Chimney in Oxfordshire. It is at the start of a navigation cut built with the lock by the Thames Conservancy in 1898. This was the only new lock built on the non-tidal Thames in the era of falling revenue after the Thames Conservancy took over responsibilities of the Thames Navigation Commission. It replaced a flash lock in a weir about 3/4 mile downstream.
Radcot Lock is a lock on the River Thames in England just downstream of Radcot, Oxfordshire, on the southern bank.

Osney Rail Bridge is a railway bridge over the River Thames at Oxford in England. It carries the Cherwell Valley Line between Didcot and Oxford across the river on the reach between Iffley Lock and Osney Lock.

Castle Mill Stream is a backwater of the River Thames in the west of Oxford, England. It is 5.5 km long.

Grandpont Bridge is a footbridge across the River Thames near the centre of Oxford, England. It links Friars Wharf in St Ebbes on the north bank to the Geoffrey Arthur Building of Pembroke College, built in 1990, and the Grandpont area. It crosses the Thames on the reach between Iffley Lock and Osney Lock.

Mill Street is a street in Oxford, England. It is a cul-de-sac that runs south from the Botley Road close to Oxford railway station. It includes residential houses, mainly terraced, and some office space. Mill Street was built in the 1860s as part of the development of New Osney on what was then known as Osney Island.

Sheepwash Channel connects the River Thames to the west and the Castle Mill Stream next to the Oxford Canal to the east, in west Oxford, England. To the north are Cripley Meadow and Fiddler's Island. To the south are Osney Island and the Botley Road.




















