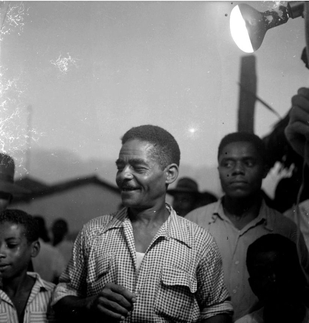Capoeira is an Afro-Brazilian martial art and game that includes elements of dance, acrobatics, music and spirituality.

Afro-Brazilians are Brazilians who have predominantly sub-Saharan African ancestry. Most members of another group of people, multiracial Brazilians or pardos, may also have a range of degree of African ancestry. Depending on the circumstances, the ones whose African features are more evident are always or frequently seen by others as "africans" - consequently identifying themselves as such, while the ones for whom this evidence is lesser may not be seen as such as regularly. It is important to note that the term pardo, such as preto, is rarely used outside the census spectrum. Brazilian society has a range of words, including negro itself, to describe multiracial people.

Maculelê is an Afro-Brazilian stick-dance from Bahia.

Manuel dos Reis Machado, commonly called Mestre Bimba, was a Brazilian capoeira mestre and the founder of the capoeira regional style. Bimba was one of the best capoeiristas of his time, undefeated in numerous public challenges against fighters from various martial arts.

João Pereira dos Santos, known as Mestre João Pequeno was capoeira Angola mestre and one of the principal students of mestre Pastinha.

Vicente Ferreira Pastinha, known as Mestre Pastinha, was a mestre of the Afro-Brazilian martial art capoeira and a codifier of the traditional capoeira Angola style.

Pedro Moraes Trindade, commonly known as Mestre Moraes, is a master of capoeira.

Capoeira de Angola or simply angola is the traditional style of capoeira, the Afro-Brazilian martial art. A newer style, based on the reform of capoeira Angola, is called regional.

João Oliveira dos Santos, better known as Mestre João Grande, is a Grão-Mestre of the Afro-Brazilian martial art of capoeira angola who has contributed to the spread of this art throughout the world. He was a student of the "father of Angola", Mestre Pastinha, and has an academy in New York City.
Grupo Capoeira Brasil is an organization that practices, teaches, and demonstrates the Afro-Brazilian martial art of Capoeira. Grupo Capoeira Brasil practices a style of Capoeira known as Capoeira Regional Contemporânea. This style is derived from movements and sequences developed and systematized by Mestre Bimba's Luta Regional Baiana, the adapted techniques of Grupo Senzala, as well as influences from the founding Mestres of Grupo Capoeira Brasil, each of whom brought personal contributions specific to their ideology, stylistic methodology and personality.
Joselito 'Amen' Santo (1965) is a mestre of the Afro-Brazilian martial art of capoeira. He has acted in roles practicing his art in two Hollywood movies, Only The Strong and Kickboxer 4, and created much of the former's fight choreography.
Pé de Chumbo is a master of Capoeira Angola, an Afro-Brazilian martial art, and a student of João Pequeno's. This mestre is one of the few capoeira angola mestres who carry on the Centro Esportivo de Capoeira Angola (CECA) school created by Mestre Pastinha. He has academies in Brazil and in Europe - including several academies in Sweden, Portugal, Mexico City, Germany and the United States. Mestre Pé de Chumbo was one of the first capoeira angola masters to take the Bahian art form to São Paulo and is known in capoeira circles for his low ground movements, dedication to his master and focus on the traditional aspects of the capoeira game.

The Brazilian martial art of capoeira, noted for its acrobatic movements and kicks, has often been featured in and influenced popular culture.
The Associação Brasileira de Apoio e Desenvolvimento da Arte-Capoeira (ABADÁ-Capoeira), in English translated as "The Brazilian Association for the Support and Development of the Art of Capoeira", is a nonprofit organization whose purpose is to spread and support Brazilian culture through the practice of capoeira. Founded in 1988 by Mestre Camisa, José Tadeu Carneiro Cardoso, ABADÁ is based in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is one of the largest capoeira organizations in the world with over 41,000 members representing schools throughout every state of Brazil as well as 30 different countries. ABADÁ is distinguished from other capoeira organizations by its worldwide growth as well as its style, standards, and philosophy.

The Assailant is a 2009 Brazilian action-drama film directed by João Daniel Tikhomiroff. The film is about Besouro Mangangá, a Brazilian Capoeirista from the early 1920s, to whom were attributed some heroic and legendary deeds.

Manoel Henrique Pereira, known as Besouro Mangangá was a legendary capoeira fighter from Bahia who ran capoeira school in Santo Amaro at the beginning of the 20th century.

The history of capoeira explores the origins and development of capoeira, the Brazilian martial art, that combines elements of dance, acrobatics, and music.
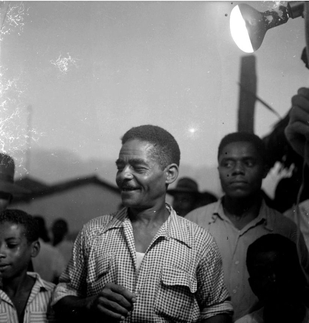
Waldemar Rodrigues da Paixão, known as Mestre Waldemar, was a Brazilian capoeira mestre and musician from the state of Bahia. He is considered one of the most artistic and skillful capoeira Angola players of his time.

Ápio Patrocínio da Conceição, known as Camafeu de Oxóssi, was a capoeira mestre, president of the Filhos de Gandhi, Obá de Xangô in candomblé, owner of the famous restaurant in the Mercado Modelo, musician, composer, and an iconic figure in the capital of Bahia, mentioned in books and songs.
In the Brazilian martial art capoeira, the title mestre designates the master practitioner. Manuel dos Reis Machado, also known as Mestre Bimba, is credited with transforming capoeira from a street activity to a sport.