| Geissois stipularis | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Oxalidales |
| Family: | Cunoniaceae |
| Genus: | Geissois |
| Species: | G. stipularis |
| Binomial name | |
| Geissois stipularis | |
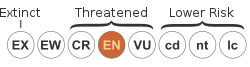
Geissois stipularis is a species of forest trees, constituting part of the plant family Cunoniaceae. They are endemic to Fiji. [1] [2]