
Agar, or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (Gracilaria) and "tengusa" (Gelidiaceae). As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, the linear polysaccharide agarose and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae and is released on boiling. These algae are known as agarophytes, belonging to the Rhodophyta phylum. The processing of food-grade agar removes the agaropectin, and the commercial product is essentially pure agarose.
A coenocyte is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without their accompanying cytokinesis, in contrast to a syncytium, which results from cellular aggregation followed by dissolution of the cell membranes inside the mass. The word syncytium in animal embryology is used to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm of invertebrates. A coenocytic cell is referred to as a coenobium, and most coenobia are composed of a distinct number of cells, often as a multiple of two.
Prochlorophyta is a group of photosynthetic bacteria, an important component of picoplankton. These oligotrophic organisms are abundant in nutrient poor tropical waters and use a unique photosynthetic pigment, divinyl-chlorophyll, to absorb light and acquire energy. Prochlorophyta lack red and blue phycobilin pigments and have stacked thylakoids, making them distinctly different from Cyanobacteria, but some authors consider them as part of the Cyanobacteria, as the group Prochlorales.

Acetabularia is a genus of green algae in the family Polyphysaceae, Typically found in subtropical waters, Acetabularia is a single-celled organism, but gigantic in size and complex in form, making it an excellent model organism for studying cell biology. In form, the mature Acetabularia resembles the round leaves of a nasturtium, is 4 to 10 cm tall and has three anatomical parts: a bottom rhizoid that resembles a set of short roots; a long stalk in the middle; and a top umbrella of branches that may fuse into a cap. Unlike other giant unicellular organisms, which are multinucleate, Acetabularia has a single nucleus, located in the rhizoid and allows the cell to regenerate completely if its cap is removed. The caps of two Acetabularia may also be exchanged, even from two different species. In addition, if a piece of the stem is removed, with no access to the nucleus in the rhizoid, this isolated stem piece will also grow a new cap.

Gelidium is a genus of thalloid red algae comprising 134 species. Its members are known by a number of common names.
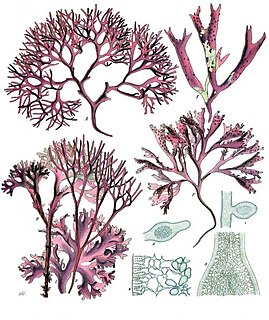
Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater, environments with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.
Syringodermataceae is a family of brown algae. It includes two genera, Microzonia and Syringoderma.

Scytothamnales is an order of brown algae.

Pediastrum duplex is a species of fresh water green algae in the genus Pediastrum.

Phlorotannins are a type of tannins found in brown algae such as kelps and rockweeds or sargassacean species, and in a lower amount also in some red algae. Contrary to hydrolysable or condensed tannins, these compounds are oligomers of phloroglucinol (polyphloroglucinols). As they are called tannins, they have the ability to precipitate proteins. It has been noticed that some phlorotannins have the ability to oxidize and form covalent bonds with some proteins. In contrast, under similar experimental conditions three types of terrestrial tannins apparently did not form covalent complexes with proteins.

Compsopogonales is an order of mostly freshwater red algae.

Cochlodinium polykrikoides is a species of red tide producing marine dinoflagellates known for causing fish kills around the world, and well known for fish kills in marine waters of Southeast Asia. C. polykrikoides has a wide geographic range, including North America, Central America, Western India, Southwestern Europe and Eastern Asia. Single cells of this species are ovoidal in shape, 30-50μm in length and 25-30μm in width.
Jean Feldmann (1905–1978) was a French biologist, specialising in marine algae.

Batrachospermaceae is a family of fresh water red algae (Rhodophyta). Genera within the Batrachospermaceae generally have a "Lemanea-type" life history with carpospores germinating to produce chantransia. Sporophyte phase with meiosis occurs in an apical cell to produce the gametophyte stage. Pit connections have two pit plug cap layers with the other layer enlarged. This family of freshwater red algae is uniaxial, meaning each filament with a single apical cell. The genera included within Batrachospermaceae are listed in the table below.

Michael Dominic Richard Guiry, is an Irish botanist, who specialises in phycology (algae). See for example the articles. He is the founder and director of the algal database, AlgaeBase.

Pyrenomonadaceae is a family of cryptomonads which includes three or four known genera. They are distinguished from other cryptomonads by their nucleomorphs being imbedded into the pyrenoid, and the presence of distinctive pigment phycoerythrin 545.
Cryptochrysis is a formerly recognized genus of cryptomonads first proposed by Adolf Pascher in 1911. He initially treated it as the sole genus in family Cryptochrysidaceae, but later treated it as a member of the Cryptochrysideae subfamily of Cryptomonadaceae, along with Rhodomonas, Chroomonas, and Cyanomonas. In 1967, R.W. Butcher relegated the group to a subgenus within Chroomonas.

Timothy John Entwisle, is an Australian botanist, much of whose research work is in phycology (algae). See for example the articles. He was awarded a Ph.D. from La Trobe University in 1986 for work on the taxonomy of Vaucheria.

The Pterocladiaceae is a small family of red algae containing 2 genera of agarophytes.

The Gracilariaceae is a small family of red algae containing several genera of agarophytes. It has a world-wide distribution. 24 species are found in China, and 6 species are found in Great Britain and Ireland. It is found in Australia and Chile.














