
The false stag beetles (Diphyllostoma) are a group of three species of rare beetles known only from California. Almost nothing is known of their life history beyond that the adults are diurnal and females are flightless; larvae have not been observed.

The Sisters is a group of three main islands located 16 kilometres (10 mi) north of Cape Pattison, Chatham Island. They are the northernmost members of the Chatham Archipelago, located 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island.

Lucanus cervus, known as the European stag beetle, or the greater stag beetle, is one of the best-known species of stag beetle in Western Europe, and is the eponymous example of the genus. L. cervus is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN Red List.

Xylotoles costatus, the Pitt Island longhorn beetle, is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It is endemic to the Chatham Islands. Once thought to be extinct, it is now known to survive on South East Island/Rangatira; being therefore an example of a so-called "Lazarus taxon".

Paralissotes reticulatus, also called the New Zealand reticulate stag beetle, is a native species of stag beetle from New Zealand. Although they do have wings they are flightless.

Geodorcus helmsi, known as New Zealand giant stag beetle or Helms's stag beetle, is a large, slow-moving, flightless stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It is endemic to New Zealand.

Hadramphus spinipennis, commonly called the coxella weevil, is a large, nocturnal, flightless weevil only found on Mangere and Rangatira Islands in the Chatham Islands, New Zealand.

Geodorcus alsobius, or Moehau stag beetle, is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It is found only on Mt Moehau, the highest mountain in the Moehau Range on the Coromandel Peninsula in New Zealand.

Geodorcus auriculatus is a large flightless stag beetle that is found in the southern part of the Coromandel Peninsula and on Mount Te Aroha in the Kaimai range of New Zealand.

Geodorcus ithaginis, the Mokohinau stag beetle, is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It was described by Thomas Broun in 1893 after being discovered in the Mokohinau Islands by Andreas Stewart Sandager, a lighthouse keeper on the islands. The species survives only on the small unnamed island "Stack H", in a patch of vegetation the size of a living room, and is in extreme danger of extinction.
Geodorcus montivagus is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It is known from only one female specimen found on the Victoria Range in New Zealand. It was found in tussock at 1,220 metres (4,000 ft) above sea level.
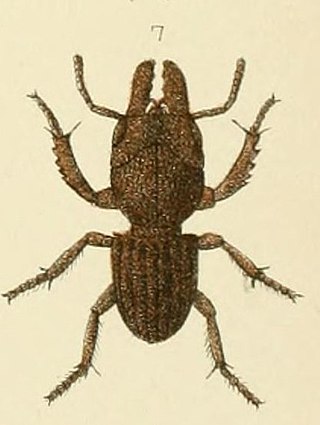
Geodorcus novaezealandiae is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It is the type species and smallest member of the genus Geodorcus. It is endemic to New Zealand.

Geodorcus philpotti is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It was named by Major Thomas Broun after Mr A. Philpott, who discovered it at Hump Ridge near Invercargill. It is endemic to New Zealand.

Geodorcus servandus is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It was discovered by P.R. Kettle in December 1960 and this holotype specimen is held in the New Zealand Arthropod Collection. It was first described by Beverley Holloway in 2007. Its type location is Mount Tuhua summit, near Lake Kaniere on the West Coast of New Zealand. The name servandus is a Latin word meaning "[something] to be preserved, conserved, looked after".

Geodorcus sororum is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It was discovered in 1973 by Mr. A. Wright on an expedition to Middle Sister Island/Te Awanui, one of The Sisters Islands/Rangitatahi which are part of the Chatham Islands in New Zealand. This holotype specimen is held in the New Zealand Arthropod Collection. It was first described by Beverley Holloway in 2007. The name sororum is translated from Latin to mean "belonging to the sisters".

Lyperobius huttoni is a New Zealand weevil found in alpine areas of the South Island and at sea level around the Wellington coast. It feeds only on speargrass (Aciphylla). Weevils from the endangered Wellington population have been translocated to predator-free Mana Island.

Paralissotes is a genus of stag beetle that is endemic to New Zealand.
Creophilus rekohuensis is a beetle of the Staphylinidae family, subfamily Staphylininae. This species occurs only on some small predator-free islands in the Chatham Islands, New Zealand, where it lives in seabird burrows. Its name derives from Rekohu, the Moriori name for Chatham Island.

Amychus manawatawhi, commonly known as the Three Kings click beetle, is a large flightless click beetle in the family Elateridae, found only on the Three Kings Islands of New Zealand.

Mecodema howitti, termed the Large Banks Peninsula ground beetle, is a carnivorous forest ground beetle in the genus Mecodema. It is endemic to Banks Peninsula, Canterbury, New Zealand, and is the largest of the 16 carabids found in the area.



















