
Surigao del Norte, officially the Province of Surigao del Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Caraga region of Mindanao. The province was formerly under the jurisdiction of Region 10 until 1995. Its capital is Surigao City. The province comprises two major islands—Siargao and Bucas Grande—in the Philippine Sea, plus a small area at the northeastern tip of mainland Mindanao and other surrounding minor islands and islets. This mainland portion borders Agusan del Norte – between the Municipality of Alegria in Surigao del Norte and the Municipality of Kitcharao in Agusan del Norte; and the province of Surigao del Sur, to the south.

The Strait of Magellan, also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. The strait is approximately 570 km long and 2 km wide at its narrowest point. In 1520, the Spanish expedition of the Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan, after whom the strait is named, became the first Europeans to discover it.

Surigao Strait is a strait in the southern Philippines, between the Bohol Sea and Leyte Gulf of the Philippine Sea.

Samar is the third-largest and seventh-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 1,909,537 as of the 2020 census. It is located in the eastern Visayas, which are in the central Philippines. The island is divided into three provinces: Samar, Northern Samar, and Eastern Samar. These three provinces, along with the provinces on the nearby islands of Leyte and Biliran, are part of the Eastern Visayas region.

Loreto, officially the Municipality of Loreto, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Dinagat Islands, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 9,690 people.

Limasawa, officially the Municipality of Limasawa, is an island municipality in the province of Southern Leyte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 6,191 people, making it the least populated town in the province.

The Loaísa expedition was an early 16th-century Spanish voyage of discovery to the Pacific Ocean, commanded by García Jofre de Loaísa and ordered by King Charles I of Spain to colonize the Spice Islands in the East Indies. The seven-ship fleet sailed from La Coruña, Spain in July 1525 and became the second naval expedition in history to cross the Pacific Ocean, after the Magellan-Elcano circumnavigation. The expedition resulted in the discovery of the Sea of Hoces south of Cape Horn, and the Marshall Islands in the Pacific. One ship ultimately arrived in the Spice Islands in September 1526.

Dinagat Islands, officially the Province of Dinagat Islands, is an island province in the Caraga region of the Philippines, located on the south side of Leyte Gulf. The island of Leyte is to its west, across Surigao Strait, and mainland Mindanao is to its south. Its main island, Dinagat, is about 60 kilometres (37 mi) from north to south. San Jose serves as its provincial capital.

Suluan is an island barangay in the Philippines, in the municipality of Guiuan, Eastern Samar. It lies east of Leyte Gulf and west of Emden Deep. The inhabitants of the island were the first Filipinos to trade and interact with Ferdinand Magellan's expedition which anchored on the nearby island of Homonhon on March 16, 1521.
The Surigaonon people are an ethnolinguistic group who inhabited on the eastern coastal plain of Mindanao, particularly the provinces of Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur and Dinagat Islands. They are also present in the provinces of Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, and in Davao Oriental. They are part of the Bisaya people, who constitute the largest Filipino ethnolinguistic group in the country.

The Philippine Nautical Highway System, also the Road Roll-on/Roll-off Terminal System (RRTS) or simply the RoRo System, is an integrated network of highway and vehicular ferry routes which forms the backbone of a nationwide vehicle transport system in the Philippines. It is a system of roads and ports developed by the Philippine government to connect the major islands of Luzon, the Visayas and Mindanao. The 919-kilometer (571 mi) nautical highway was opened to the public on April 12, 2003 as the Strong Republic Nautical Highway (SRNH).

The Magellan expedition, sometimes termed the Magellan–Elcano expedition, was a 16th-century Spanish expedition planned and led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. One of the most important voyages in the Age of Discovery—and in the history of exploration—its purpose was to cross the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans to open a trade route with the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, in present-day Indonesia. The expedition departed Spain in 1519 and returned there in 1522 led by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, who crossed the Indian Ocean after Magellan's death in the Philippines. Totaling 60,440 km, or 37,560 mi, the nearly three-year voyage achieved the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. It also revealed the vast scale of the Pacific Ocean and proved that ships could sail around the world on a western sea route.

The Dinagat bushy-tailed cloud rat, Dinagat crateromys or Dinagat cloud rat is a species of cloud rat in the family Muridae. It is one of the eight cloud rats found only in the Philippines, and is specifically endemic to Dinagat Island. It is known locally as hawili. A single specimen was discovered in 1975 by Dioscoro S. Rabor and his team during a scientific survey in Dinagat. The natural habitat is tropical lowland forests, which are facing environmental threats. Habitat loss is caused by progressive deforestation from heavy logging and chromite mining in the area. Almost 40 years after the original discovery, five live specimens were discovered by Milada Řeháková, Václav Řehák and William L.R. Oliver, in 2012.
Rajah Humabon later baptized as Don Carlos Valderrama, was one of the recorded chiefs in Cebu who encountered Ferdinand Magellan in the 16th century. Humabon ruled at the time of the arrival of Portuguese-born Spanish explorer Ferdinand Magellan in the Philippines in 1521. Humabon, his wife, and his subjects were the first known Christian converts in the Philippines. However, since there were no Catholic priests in Cebu from 1521 to 1565, this Christianity was not practised until the return of the Spaniards to Cebu. There is no official record of Humabon's existence before the Spanish contact. The existing information was written by Magellan's Italian voyage chronicler, Antonio Pigafetta on Humabon and the indigenous Philippine peoples that existed prior to Spanish colonization. Rajah Humabon is cited as the reason for why Magellan fought in the Battle of Mactan, as the latter wanted to earn the trust of Humabon by helping him subdue his opponent Lapulapu, one of the chiefs of Mactan. Despite being referred to as "king" in the journal of Antonio Pigafetta, he was not one like in the manner of a monarch in centralized societies, it is plausible that the title was mistakenly applied because according to succeeding chroniclers, there were no kingdoms in the pre-colonial Philippines.

Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies, which achieved the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. During the expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fleet to pass from the Atlantic into the Pacific Ocean and perform the first European navigation to Asia via the Pacific. Magellan died in the Philippines during his voyage, and his crew completed the return trip to Spain in 1522.

The recorded history of the Philippines between 900 and 1565 begins with the creation of the Laguna Copperplate Inscription in 900 and ends with the beginning of Spanish colonization in 1565. The inscription records its date of creation in 822 Saka. The discovery of this document marks the end of the prehistory of the Philippines at 900 AD. During this historical time period, the Philippine archipelago was home to numerous kingdoms and sultanates and was a part of the Indosphere and Sinosphere.
The Dinagat Islands creation plebiscite was a plebiscite on the creation of the Province of Dinagat Islands from Surigao del Norte province in the Philippines. The plebiscite was held on December 2, 2006, and the results were announced on December 5, 2006.
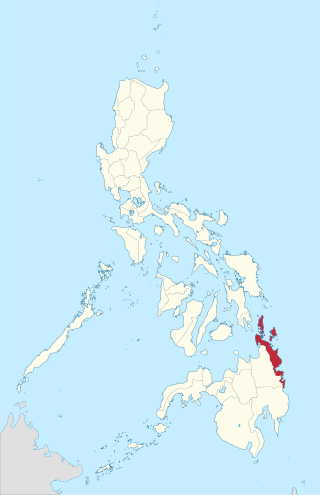
Surigao was a province of the Philippines. Originally a Spanish-era district, became a chartered province on May 15, 1901. The province was dissolved on 1960.

The Mindanao–Eastern Visayas rain forests ecoregion covers the lowland rain forests of the island of Mindanao and of the easternmost of the Visayas Islands in the Philippines. Although 63% of this ecoregion is covered with closed broadleaf evergreen forest or open forest, much of this has been disturbed in the past by human activity, and many of the rare species of the area have been relegated to the isolated areas or higher elevations.

















